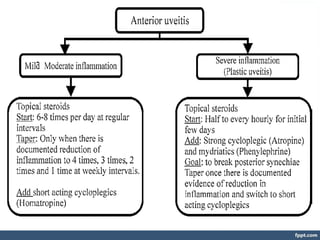
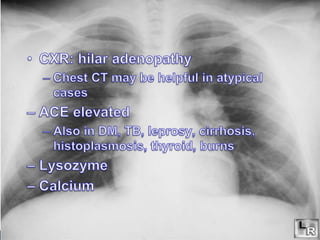
This document discusses investigations and treatments for uveitis. It begins by outlining general investigations like bloodwork and imaging that can be used to determine the cause of uveitis based on factors like age, ethnicity, type of uveitis, and symptoms. It then discusses specific infectious and non-infectious diseases that can cause uveitis, listing relevant tests and treatments for conditions like tuberculosis, syphilis, sarcoidosis, and more. The document emphasizes that determining the underlying cause of uveitis through appropriate investigations is important for guiding effective treatment.