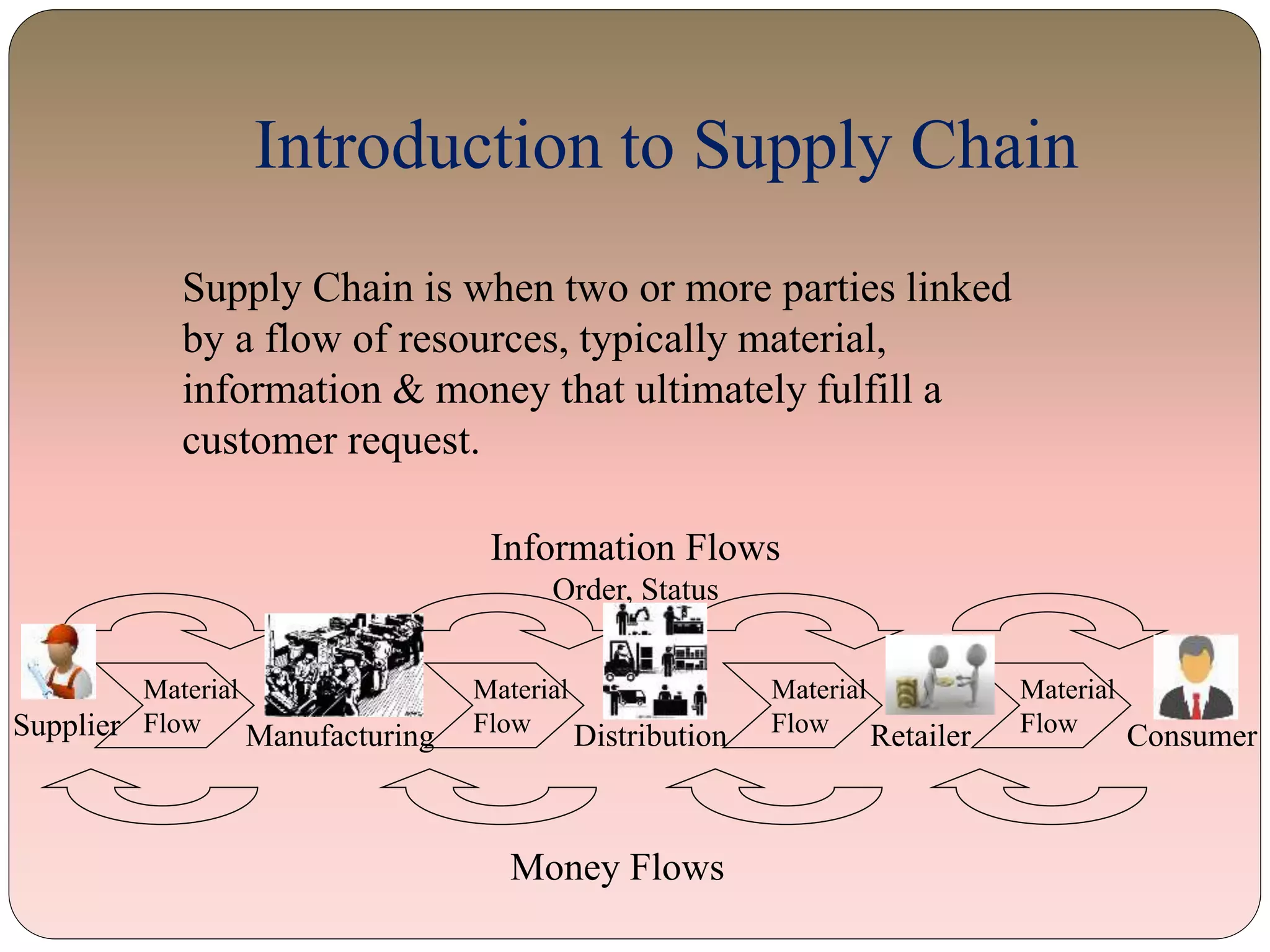
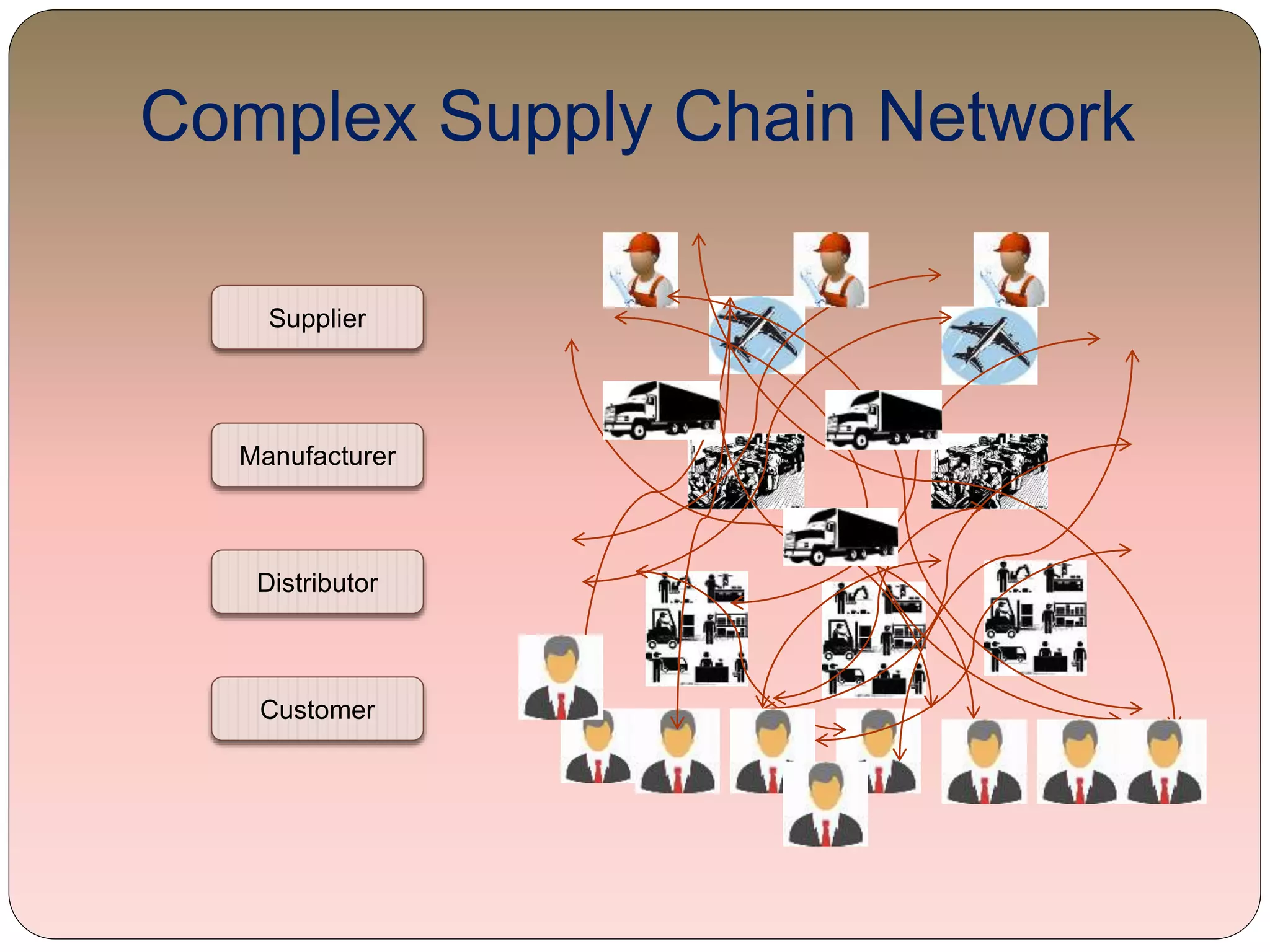
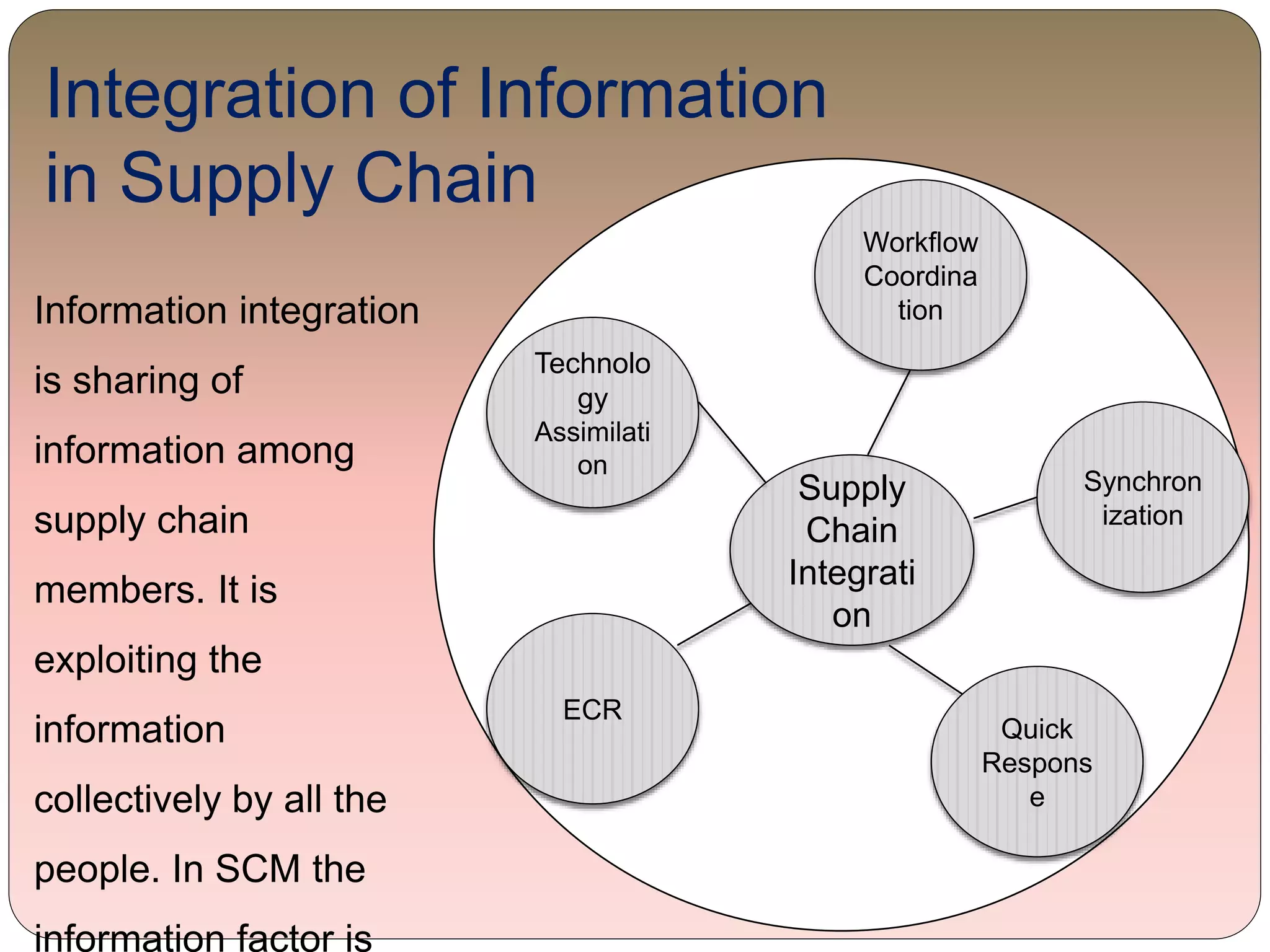
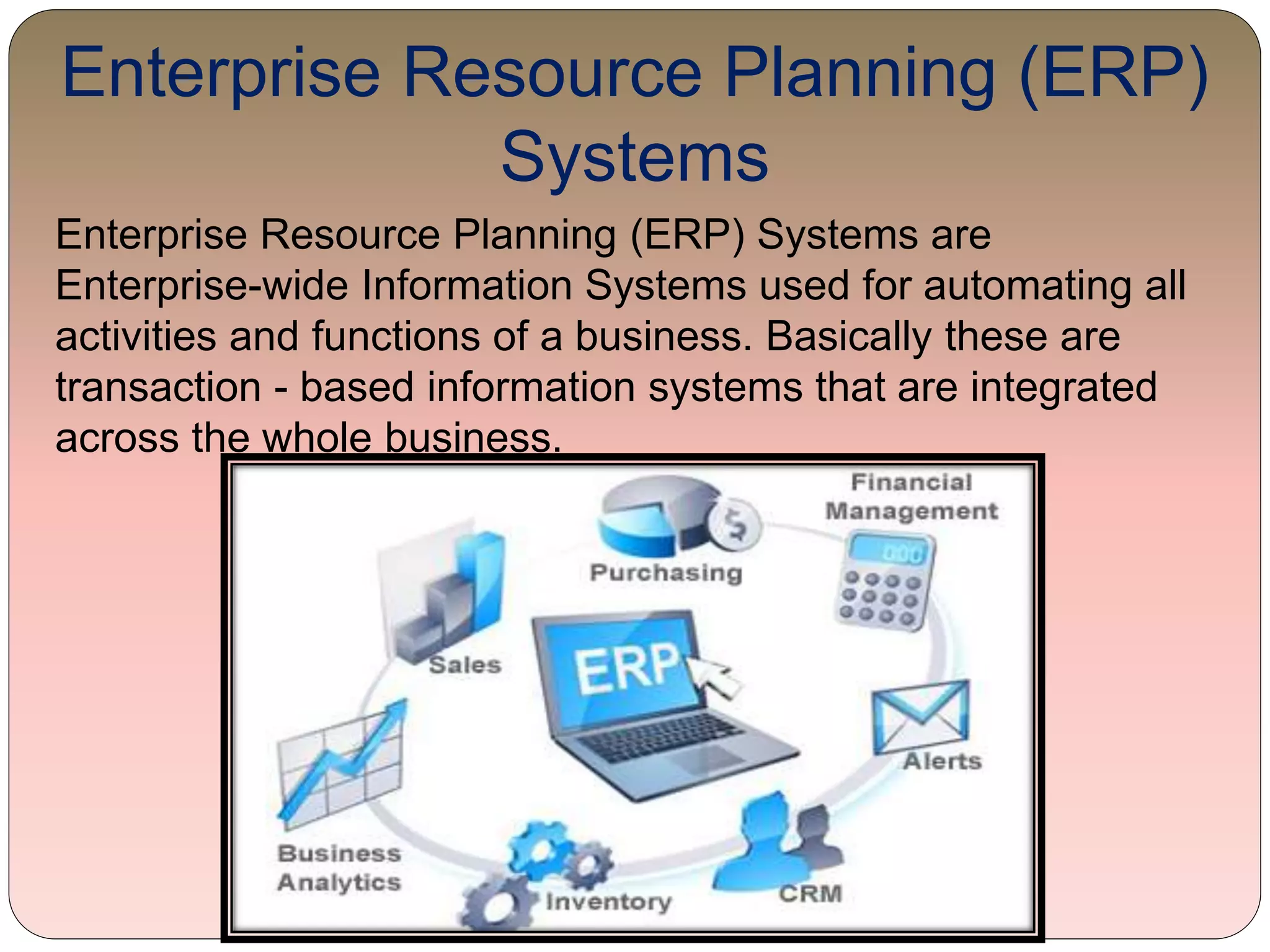
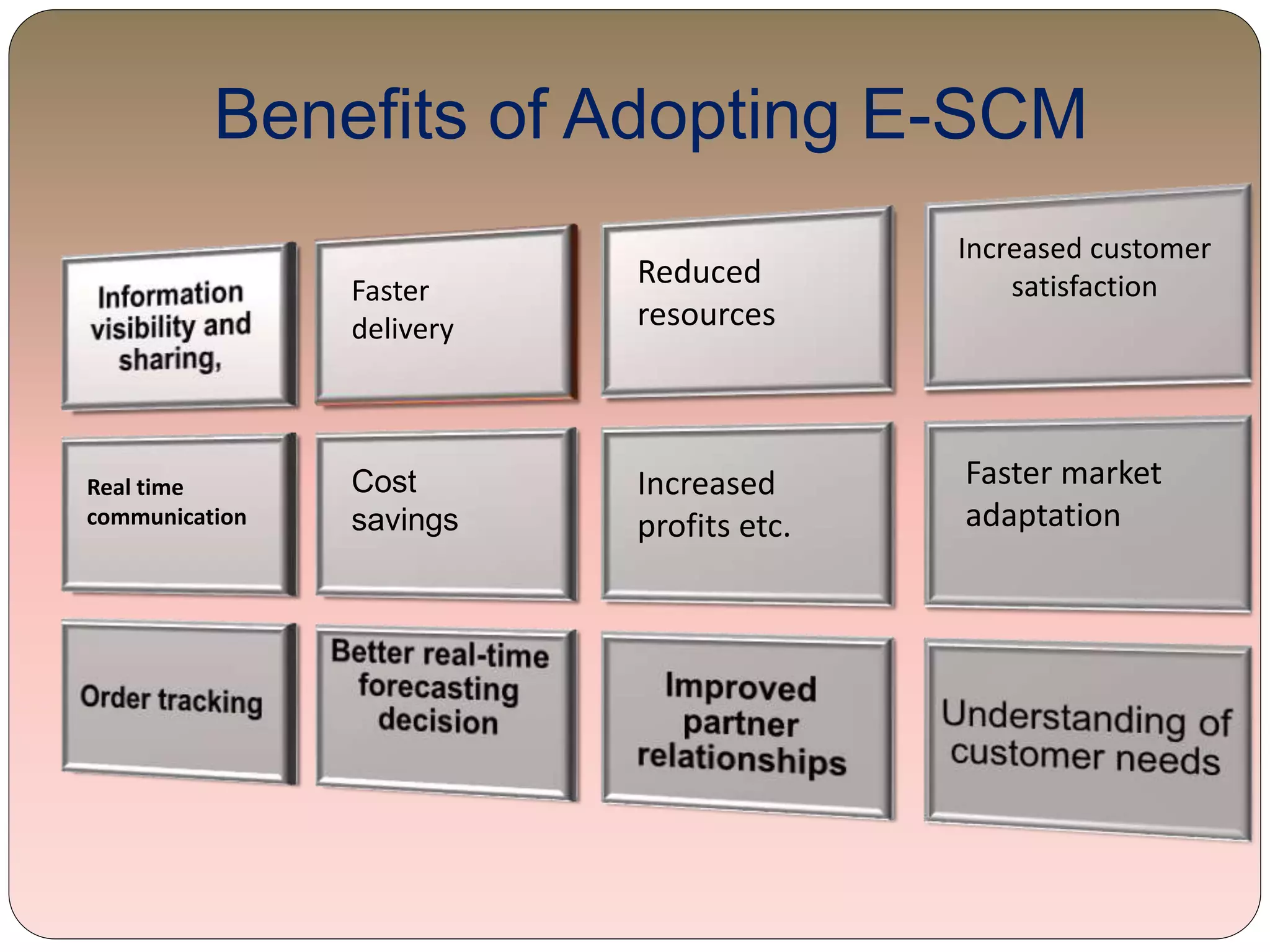
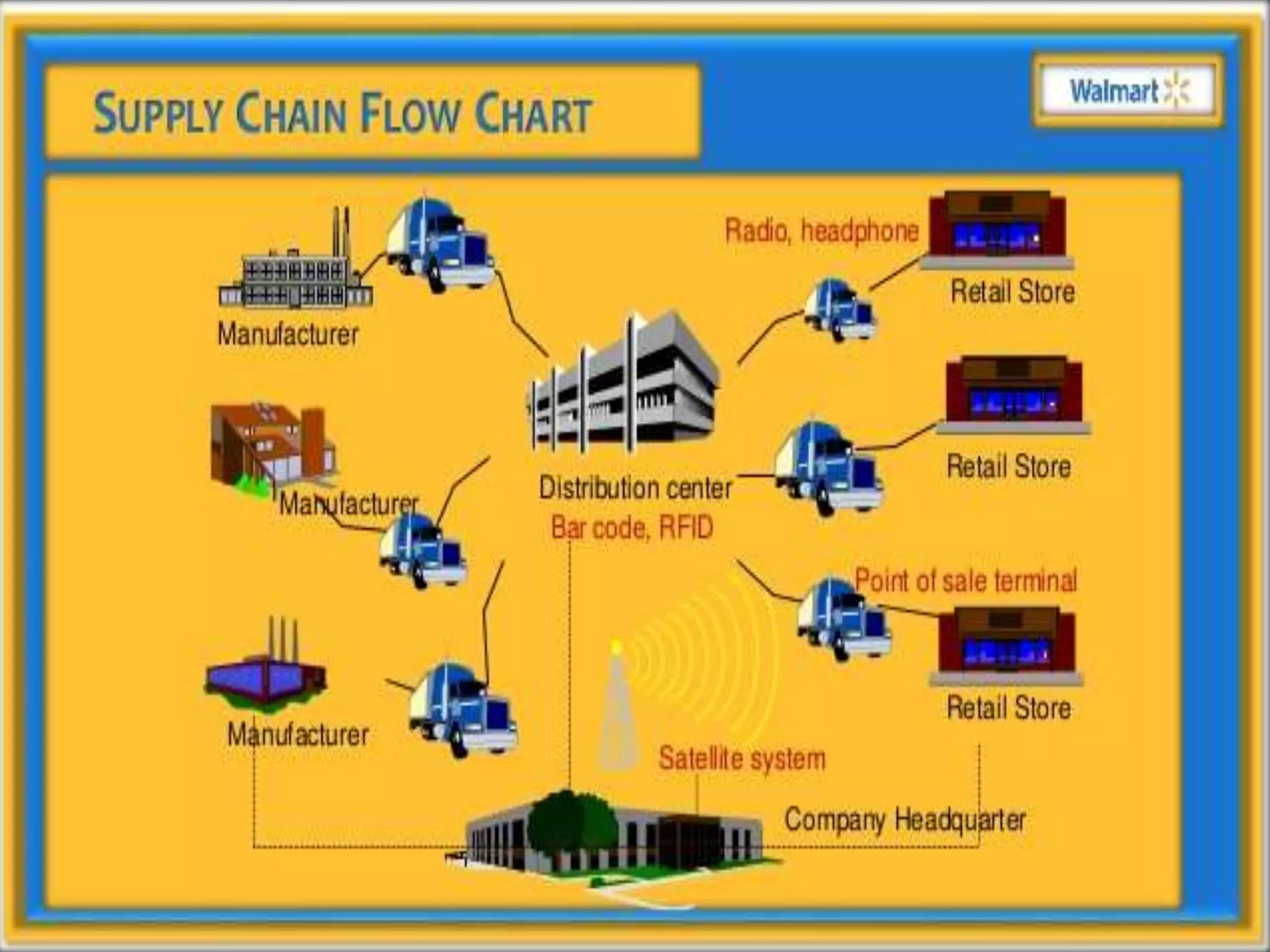
This document provides an overview of information technology management in supply chain operations, using Walmart as a case study. It discusses key concepts like traditional vs integrated supply chain views, the importance and benefits of IT in supply chain management. It also describes various types of IT systems used in supply chains, including ERP, transportation management, inventory management, EDI, barcoding, RFID and e-commerce systems. Finally, it discusses management of supply chain information systems and the development process.