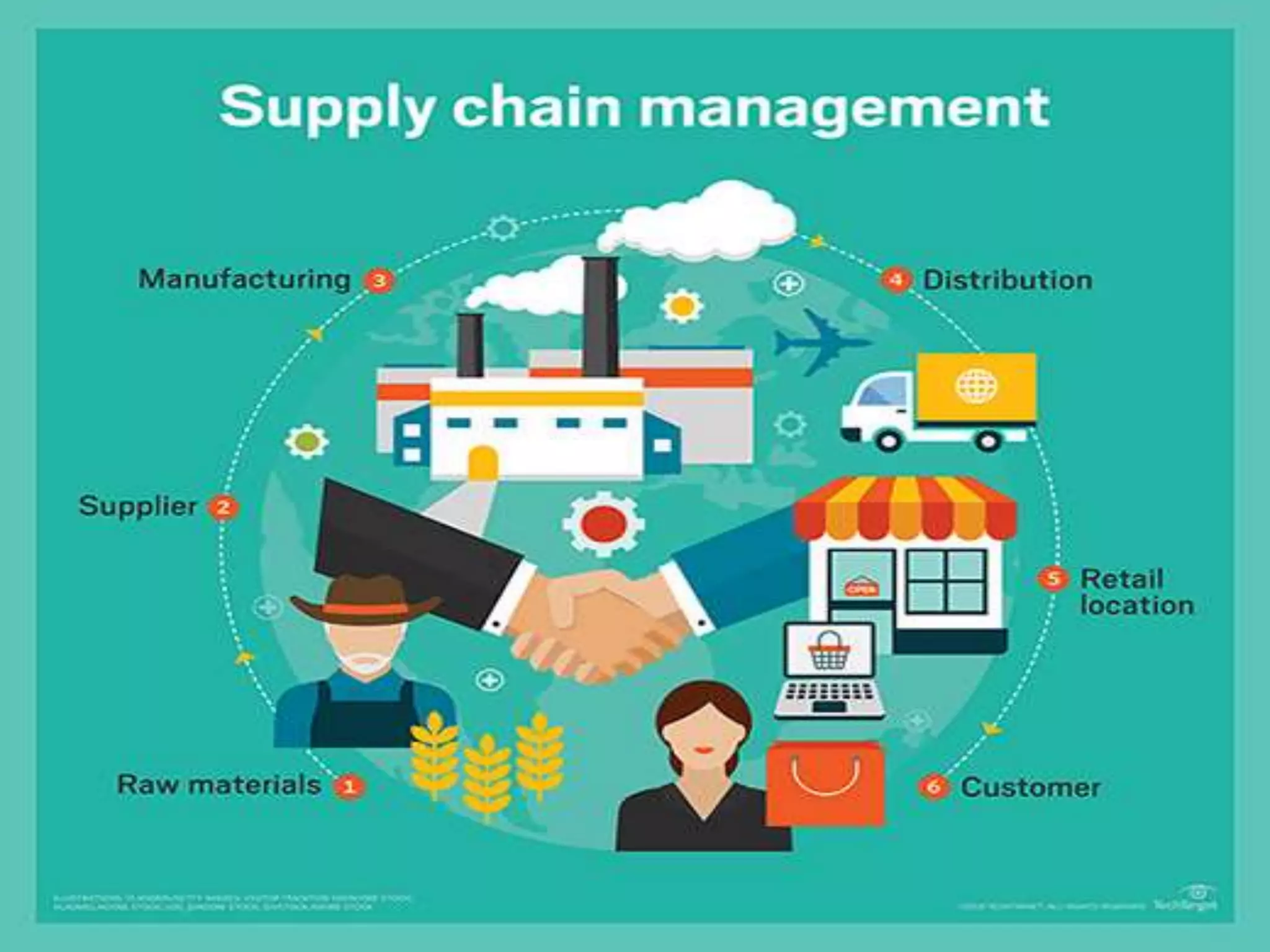
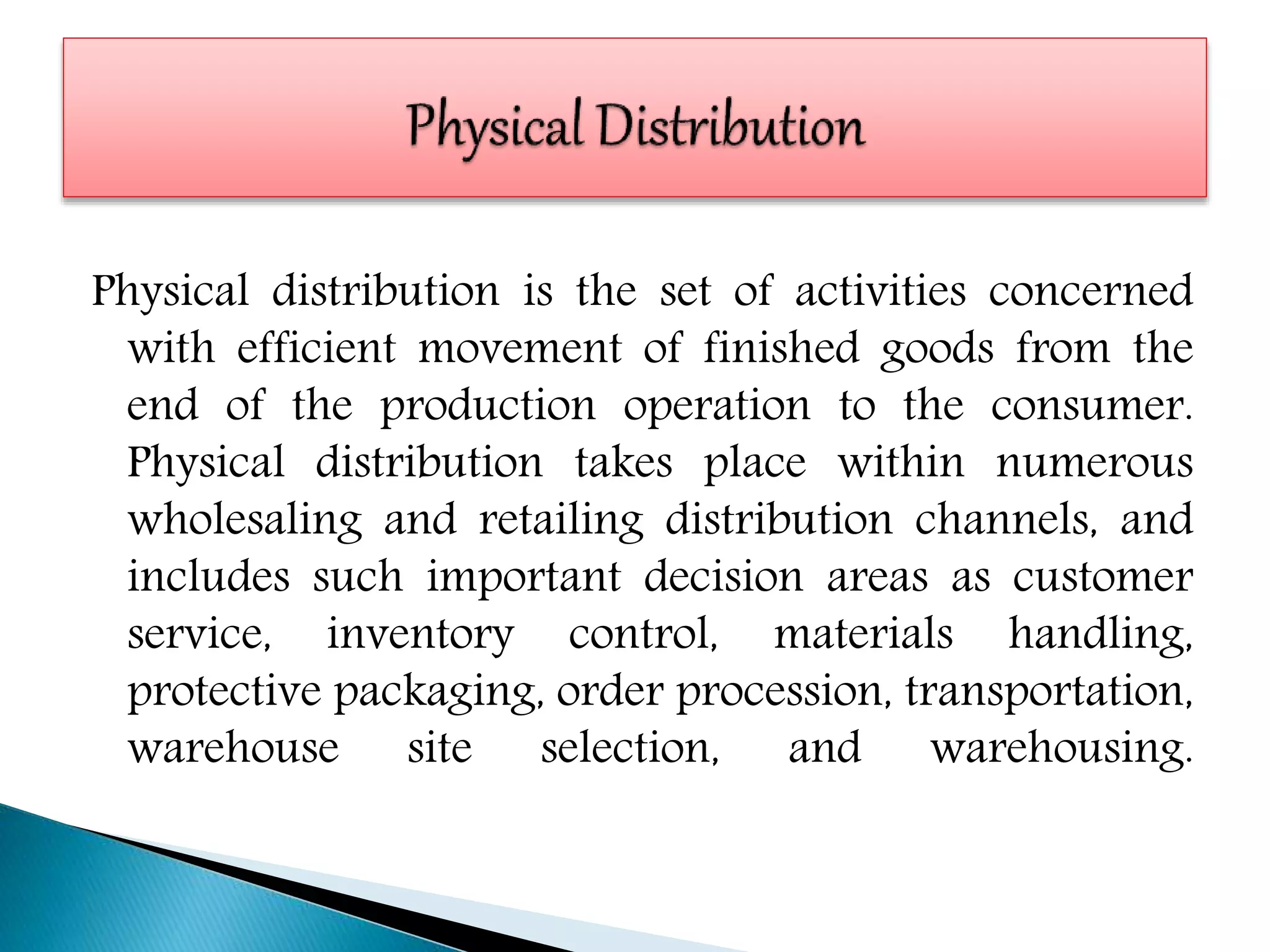
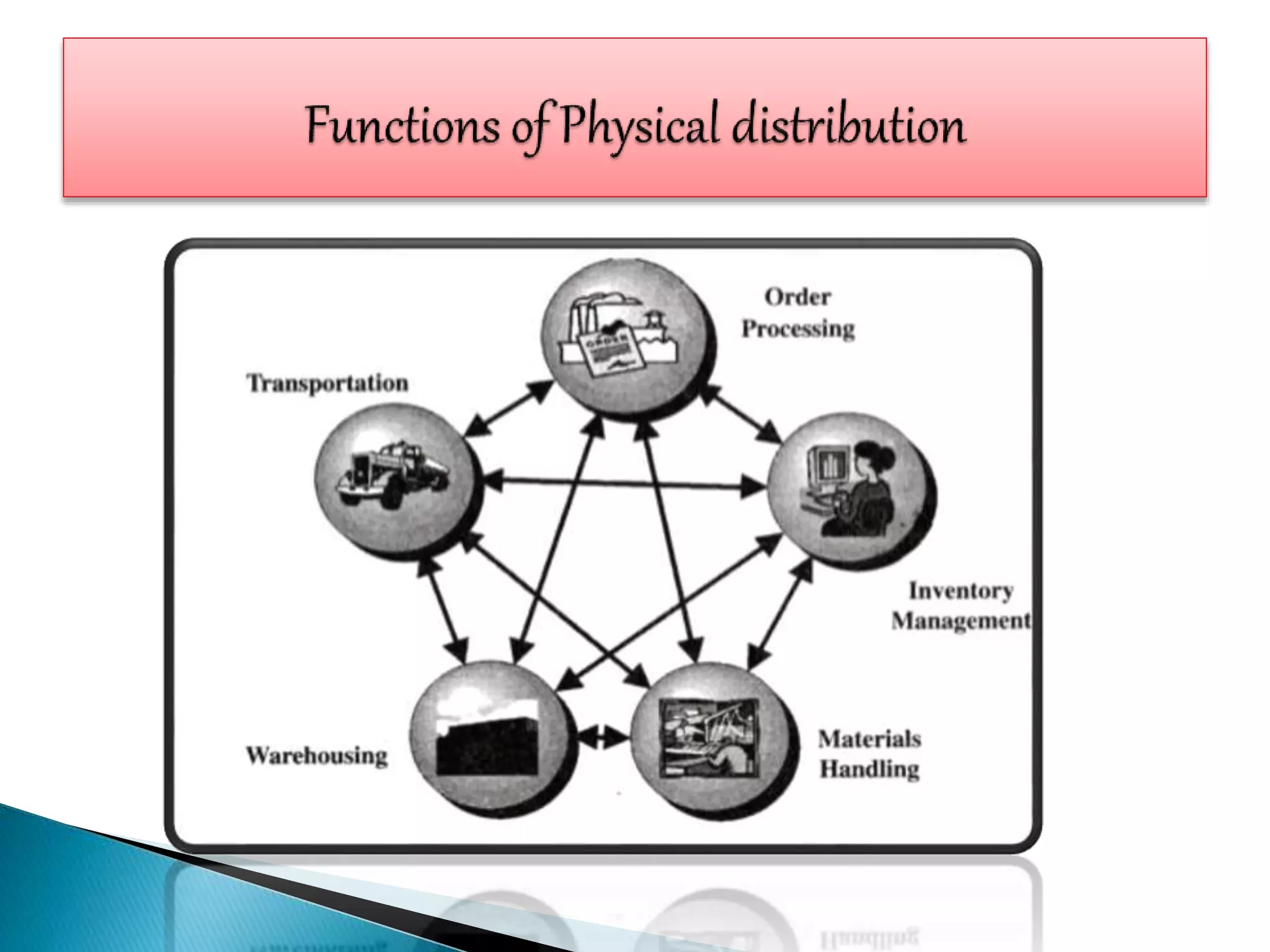
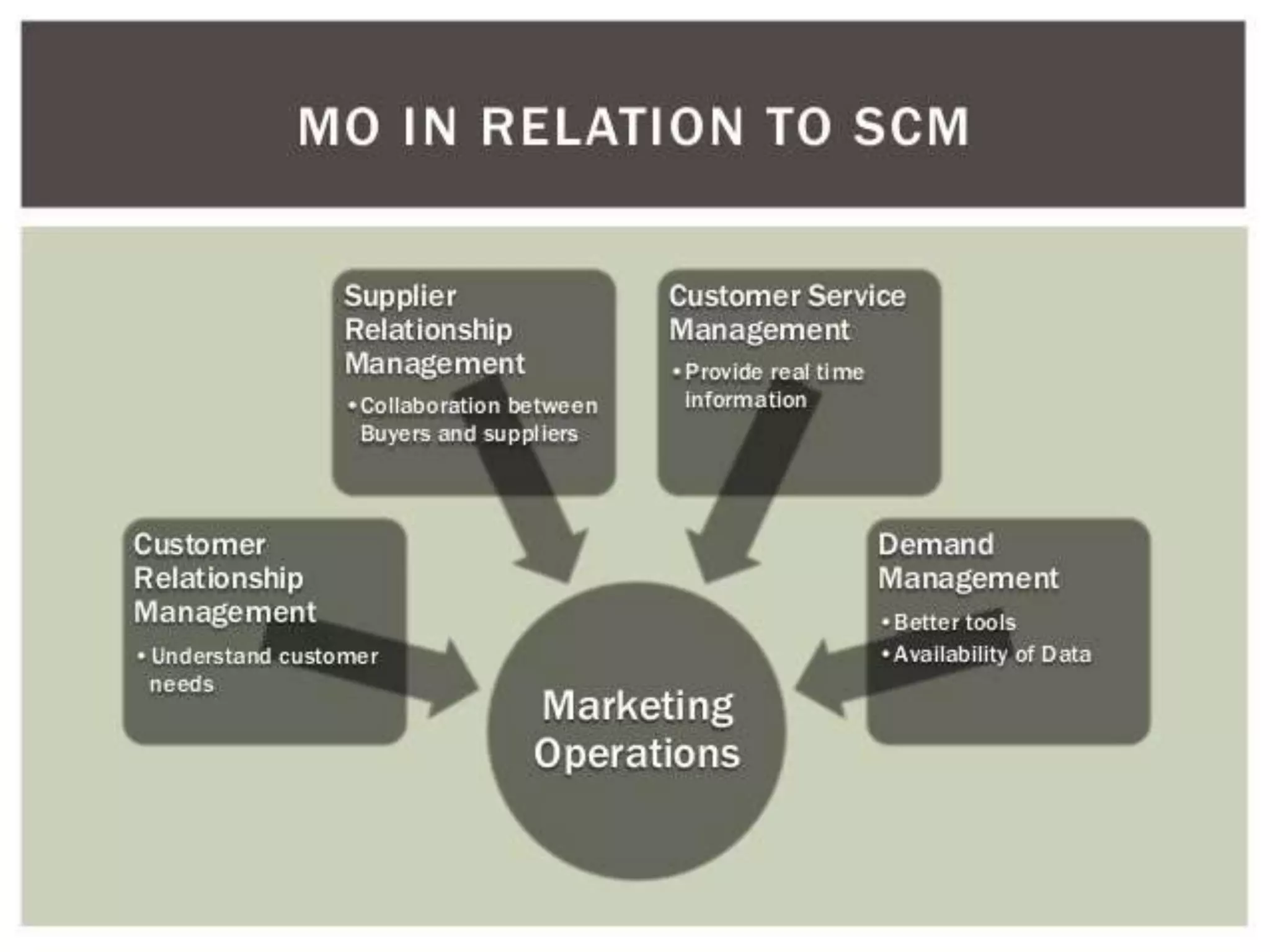
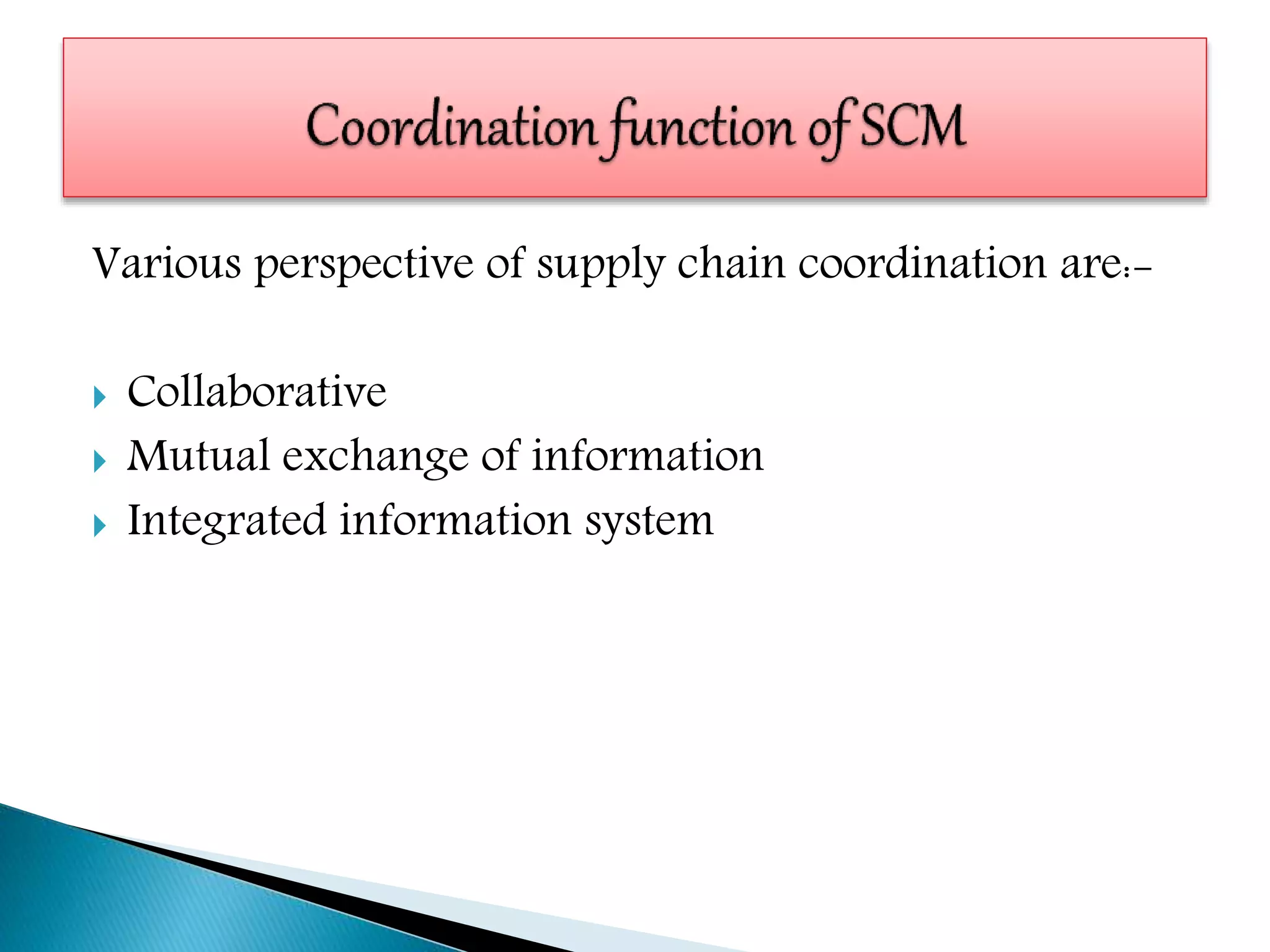
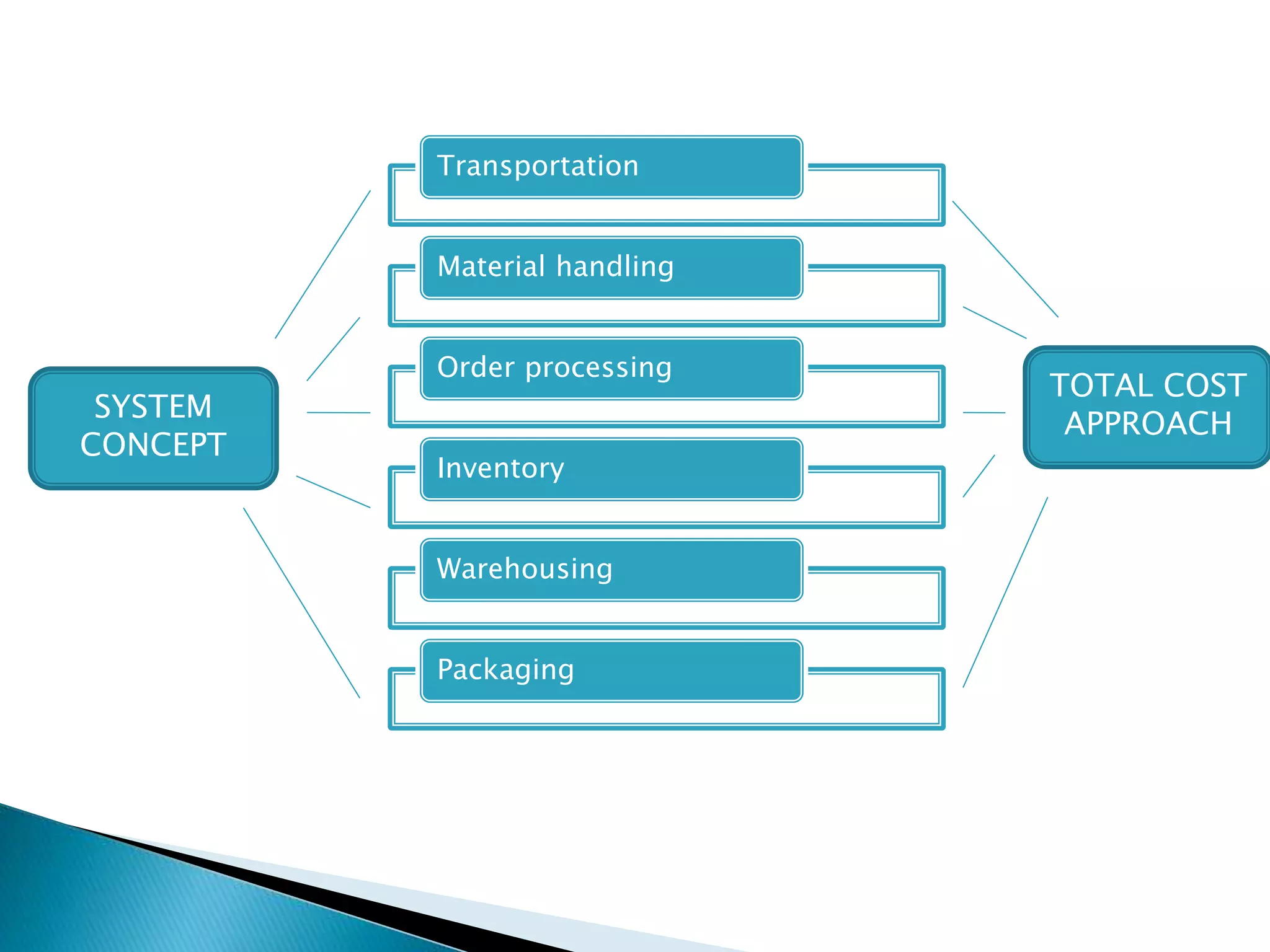
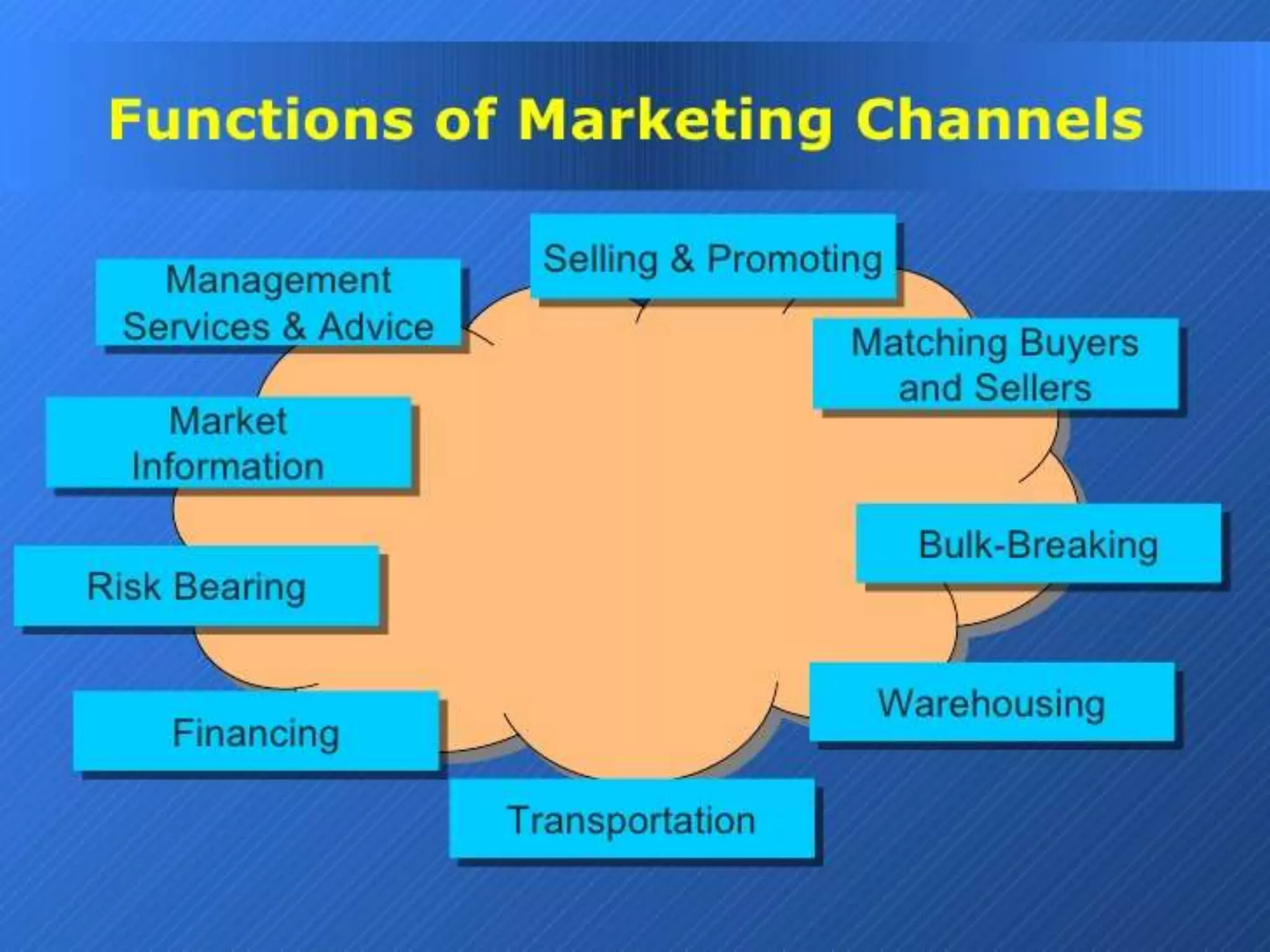
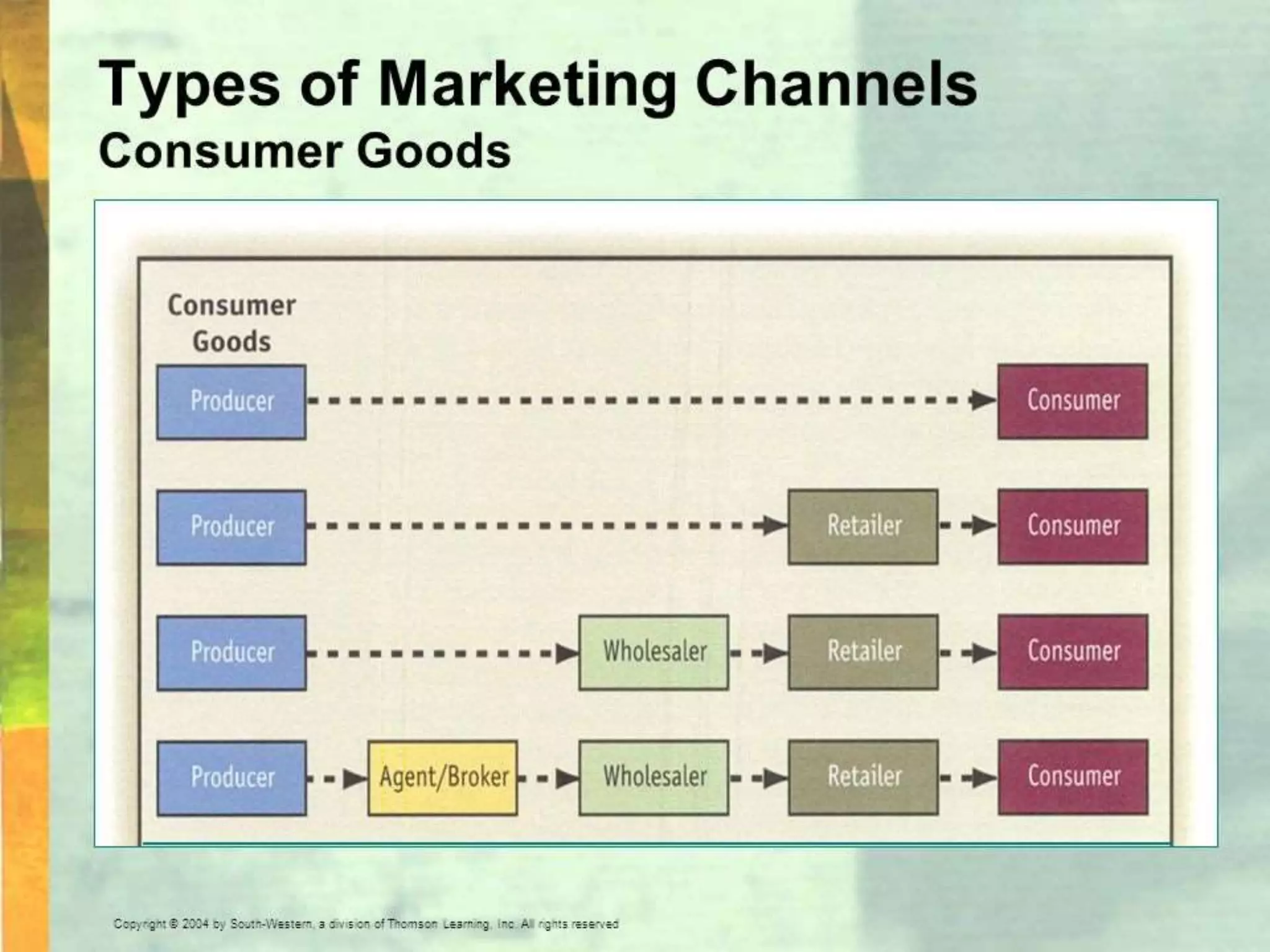
Supply chain management involves coordinating all supply chain activities including product development, production, logistics, and information sharing to maximize customer value. Effective supply chain management can increase revenue and decrease costs by creating efficiencies. Key activities include physical distribution, transportation, inventory management, and ensuring the right products reach customers through the appropriate channels at the right time and in the right condition. Coordinating the supply chain is important for meeting customer demands profitably.