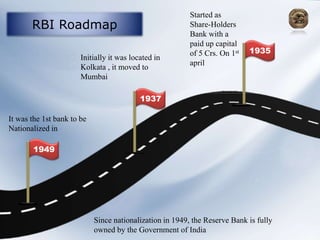
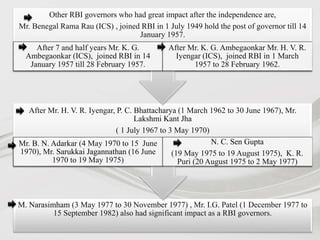
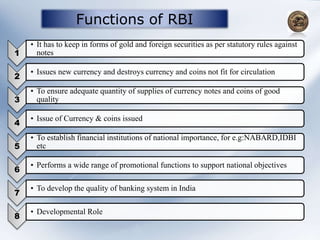
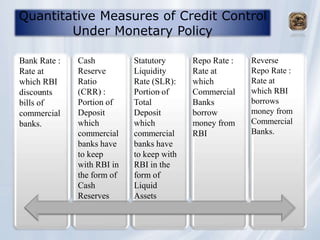
The document provides information about the roles and functions of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). It discusses RBI's role as a monetary authority, banker's bank, money regulator, issuer of currency and licenses. It outlines the powers of RBI in controlling money supply through various quantitative measures like cash reserve ratio (CRR), statutory liquidity ratio (SLR), repo rate, and reverse repo rate. Examples are given of how CRR, SLR and repo rate work. Past and recent governors of RBI are also mentioned.