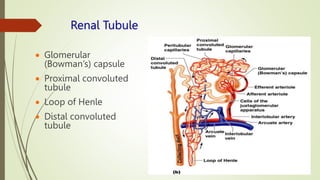
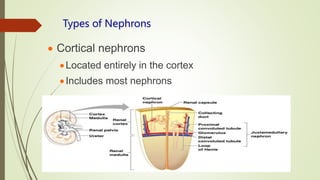
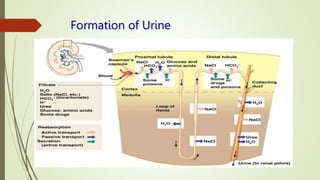
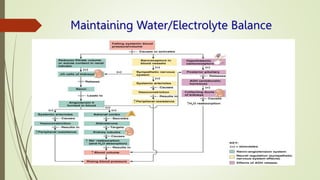
The urinary system functions to eliminate waste from the body, regulate homeostasis, and maintain fluid balance. It includes the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys contain nephrons, which are the functional filtering units that form urine by filtering blood and regulating water, electrolyte and acid-base balance. Urine is transported from the kidneys to the bladder via the ureters and is then emptied via the urethra in a process regulated by sphincter muscles. Proper fluid balance is maintained through hormonal control of water and electrolyte reabsorption in the kidneys.