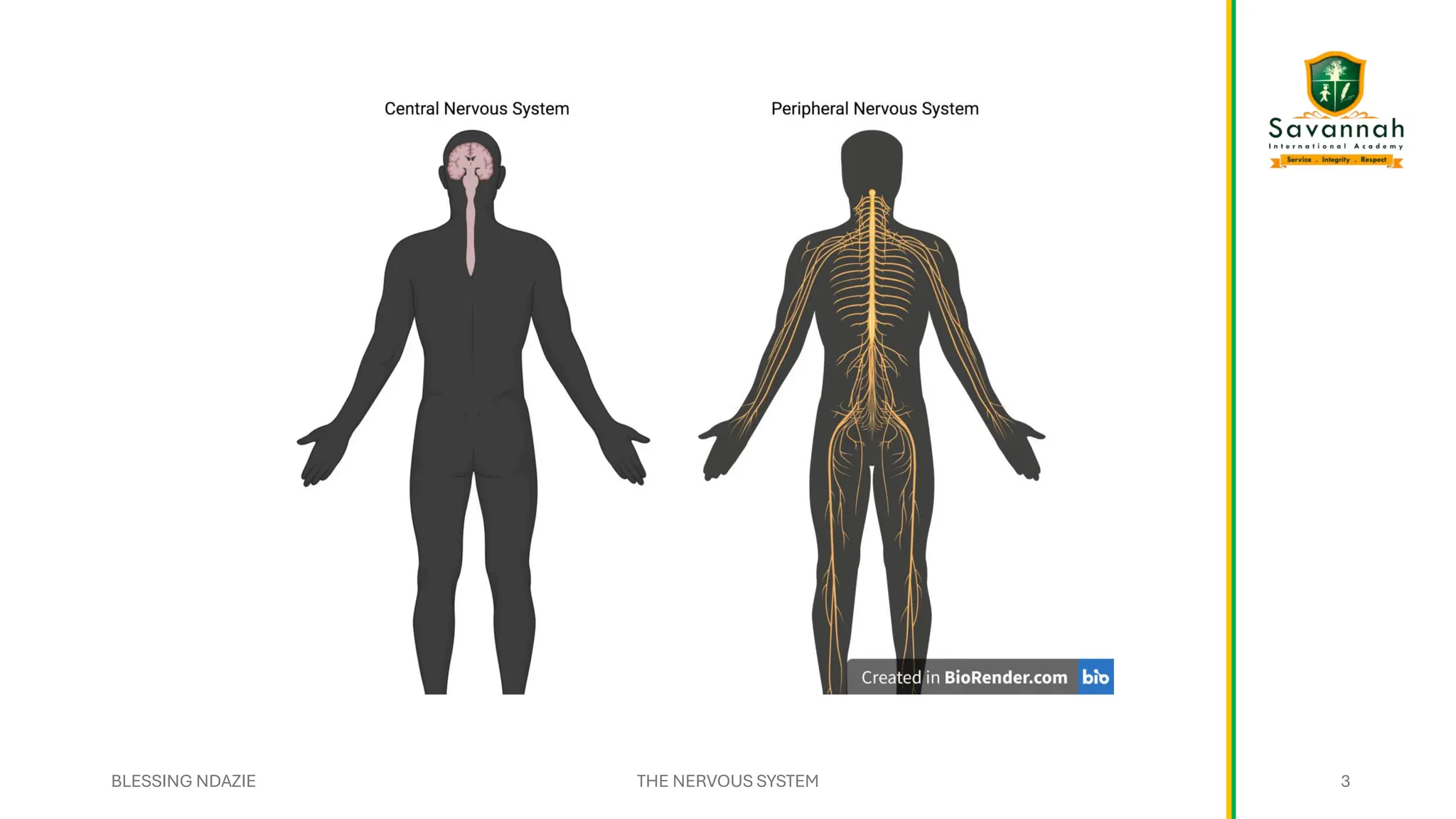
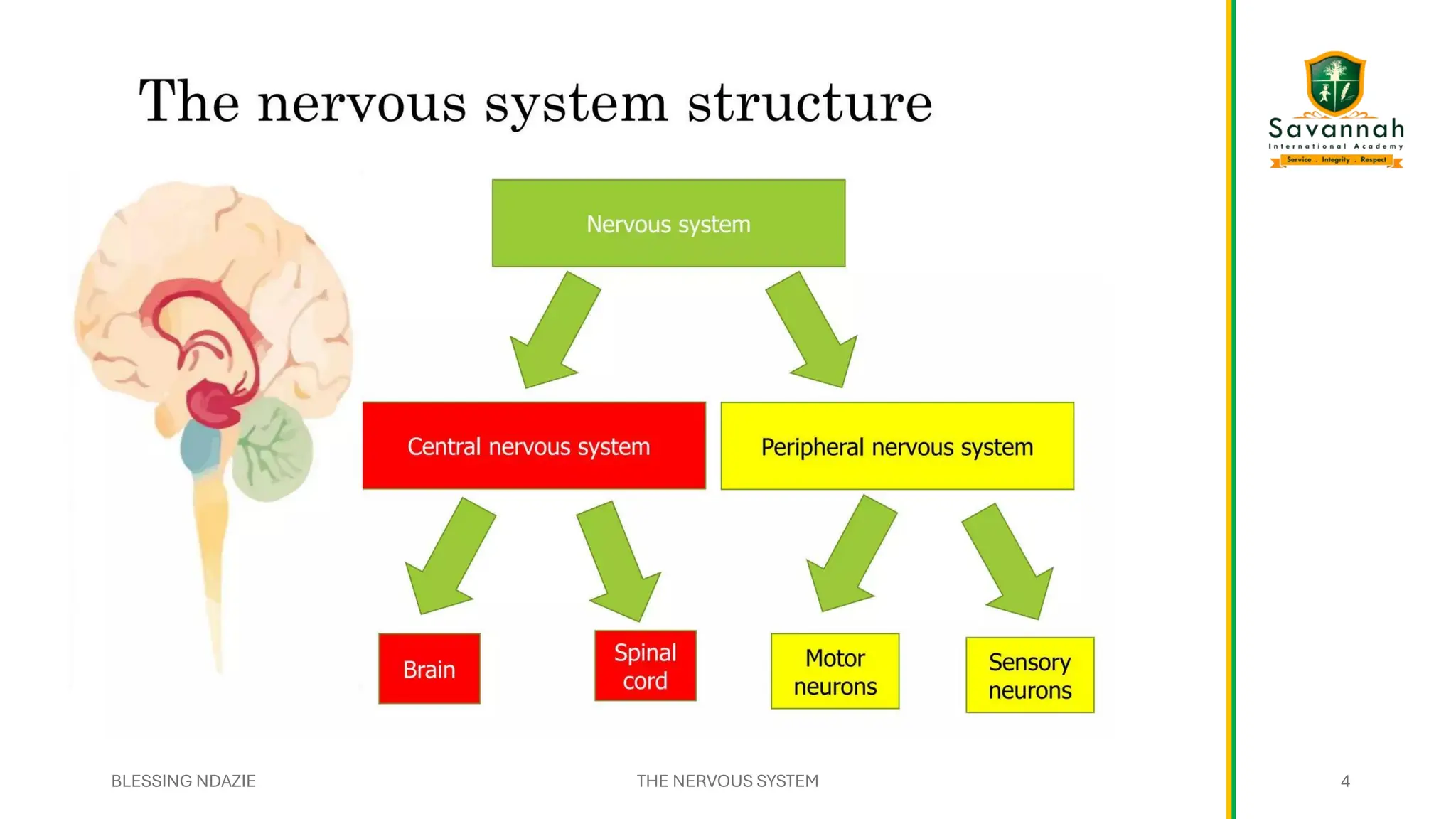
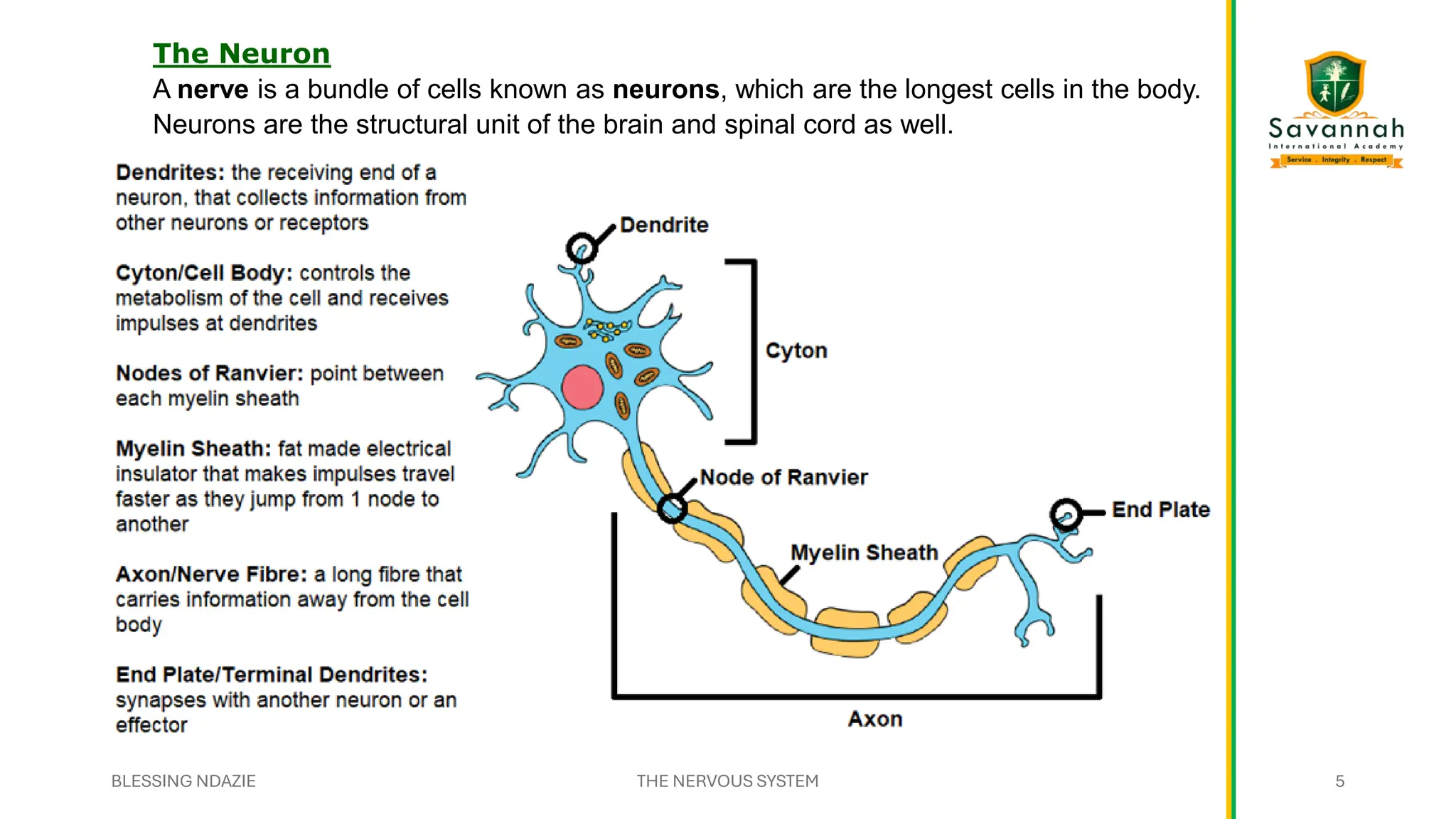
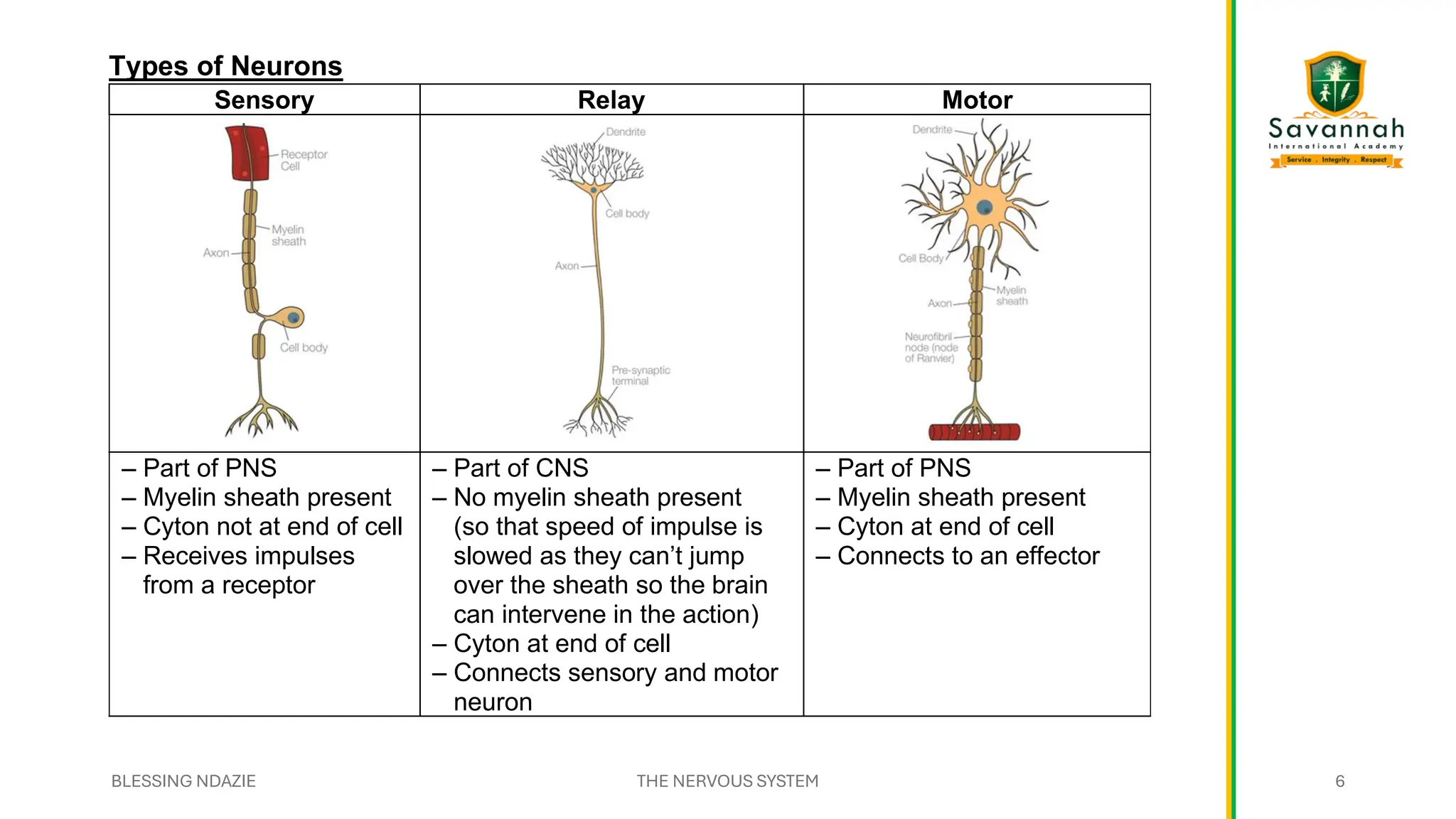
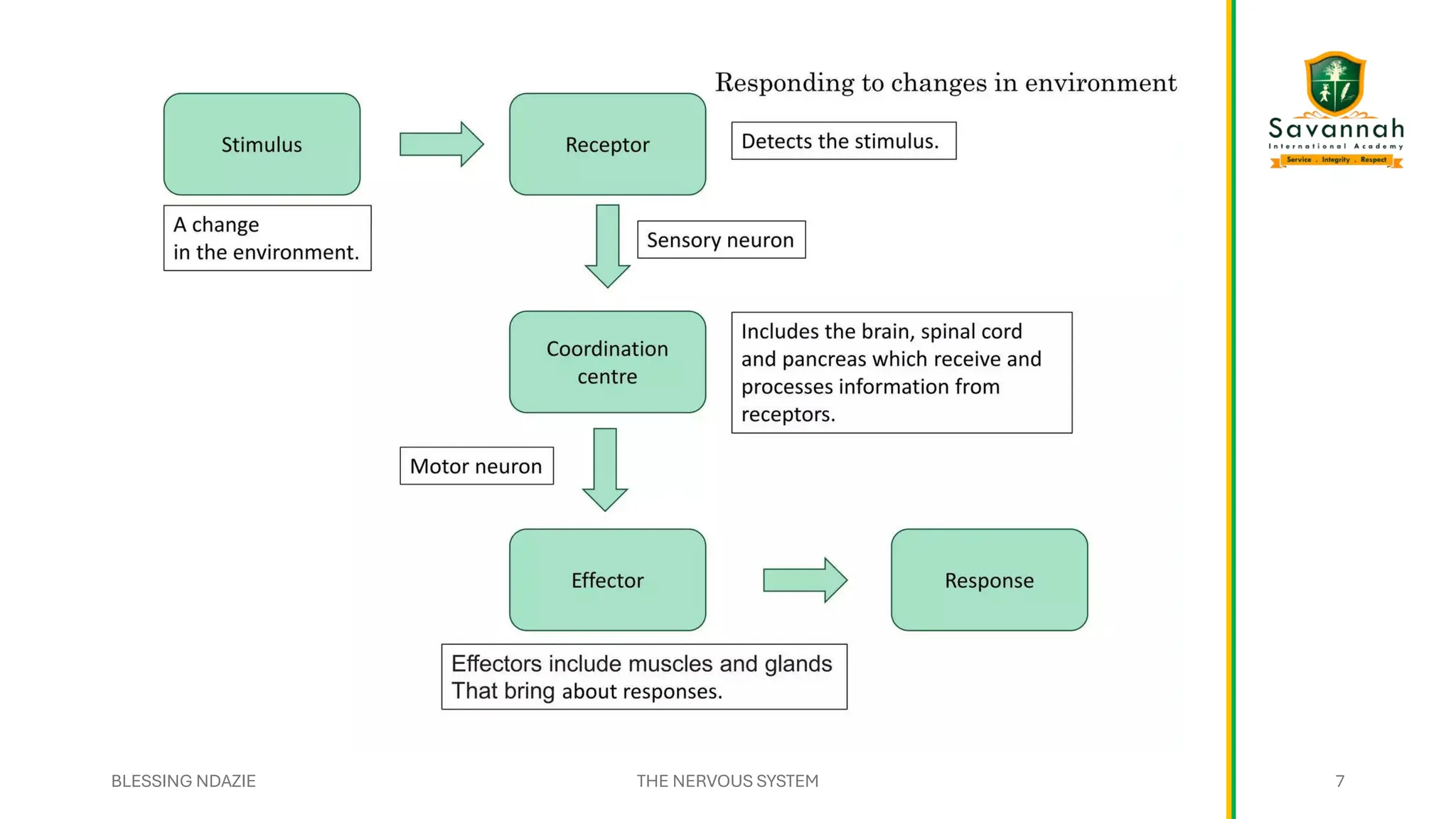
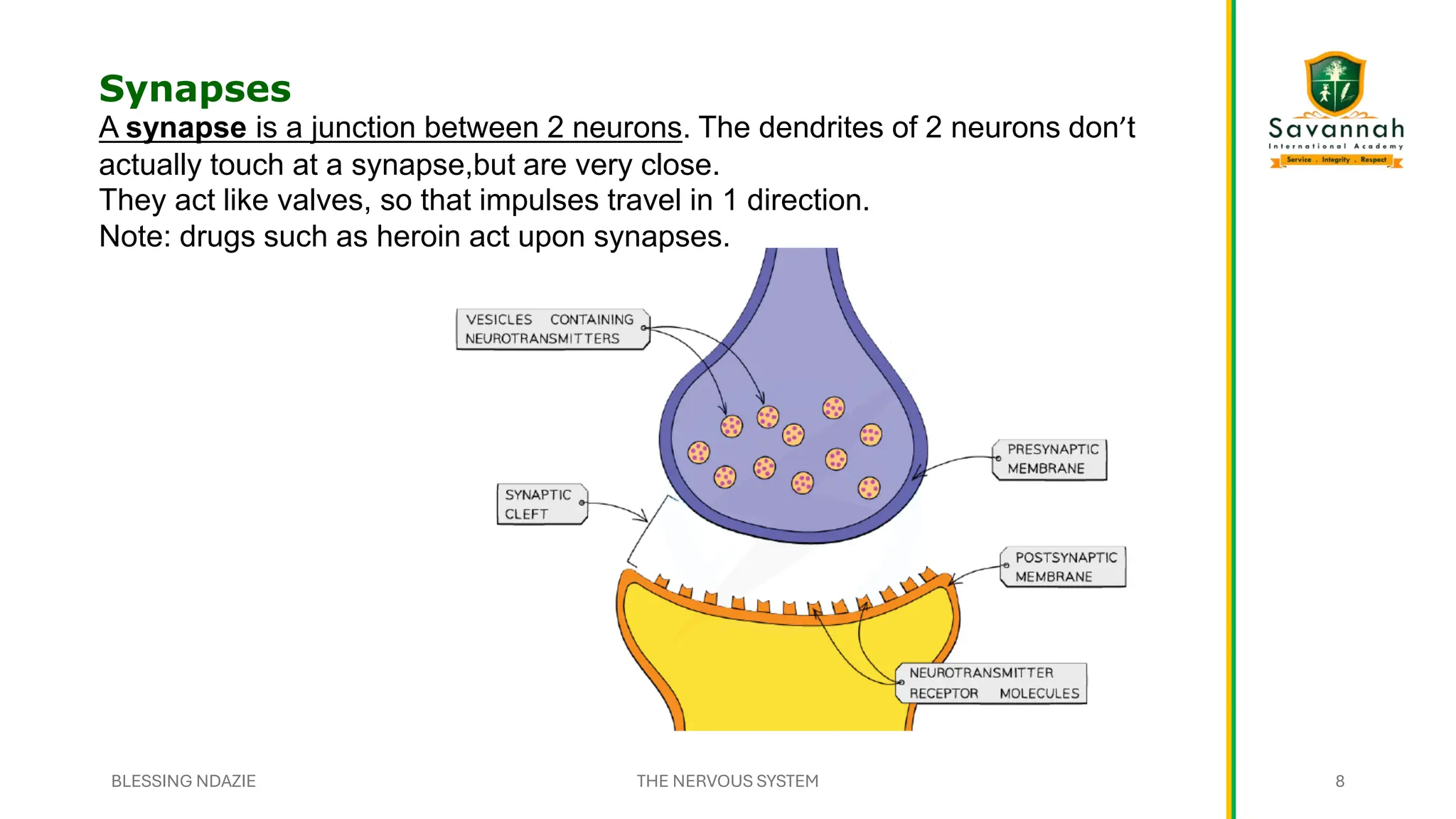
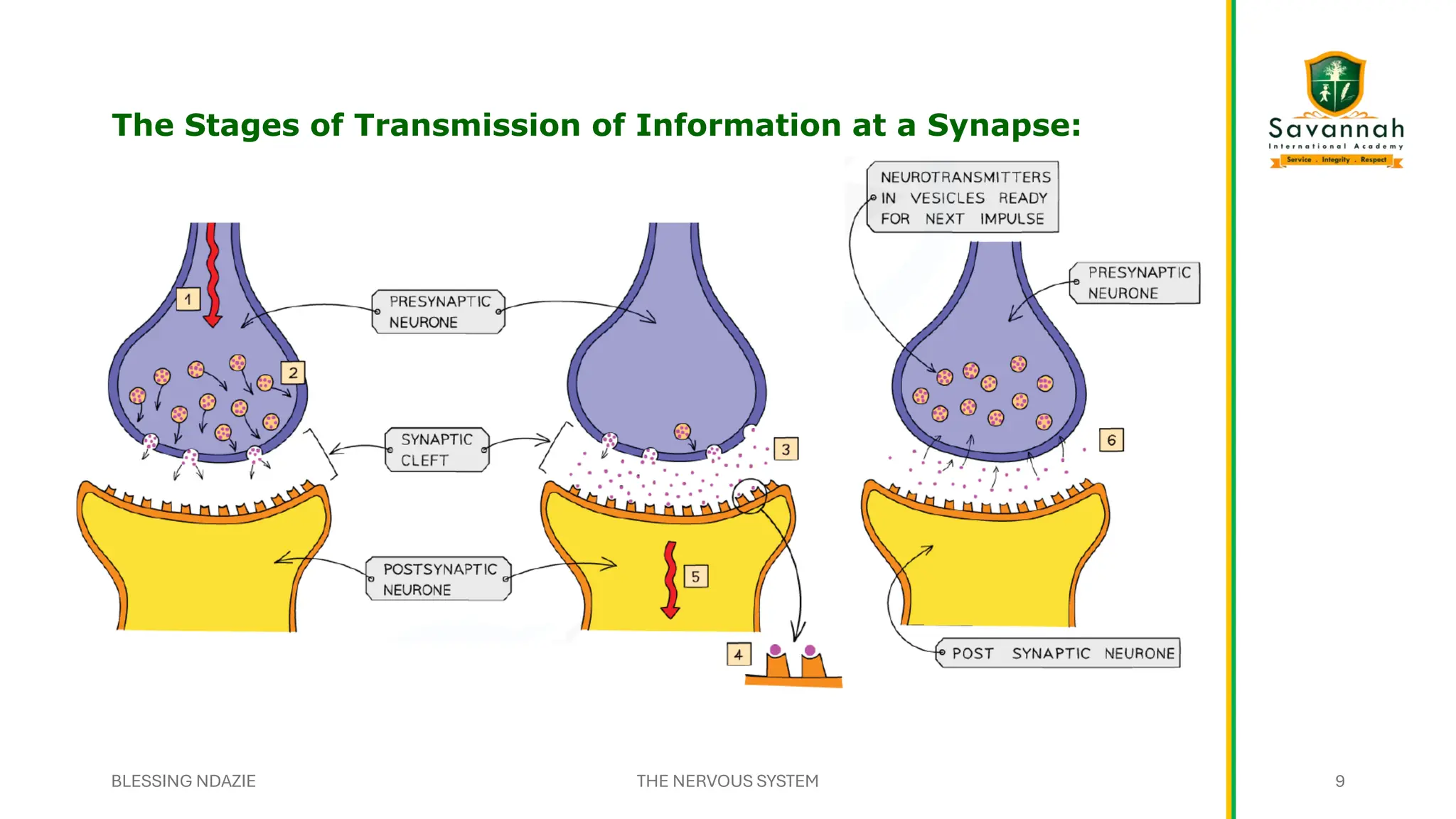
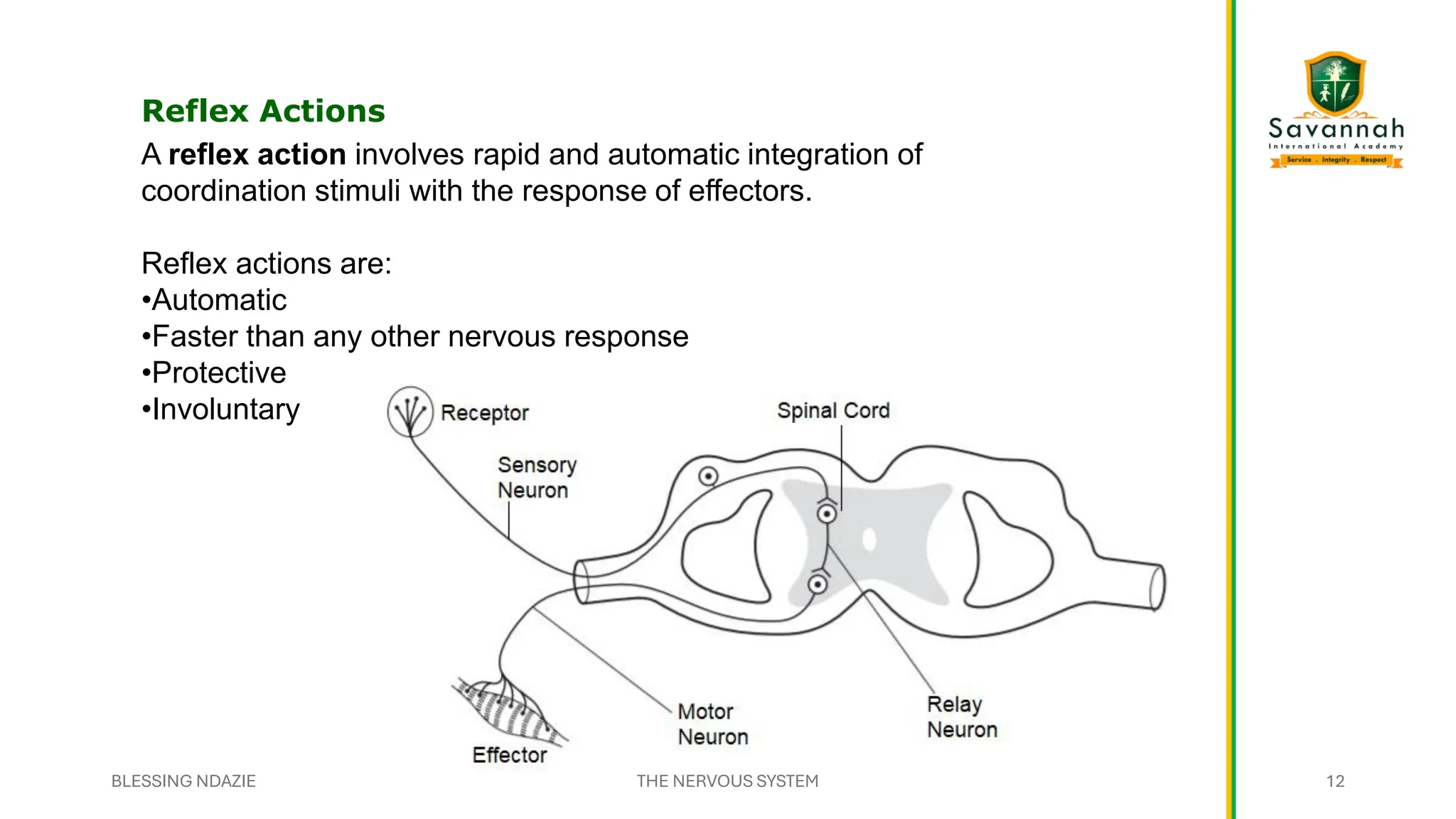
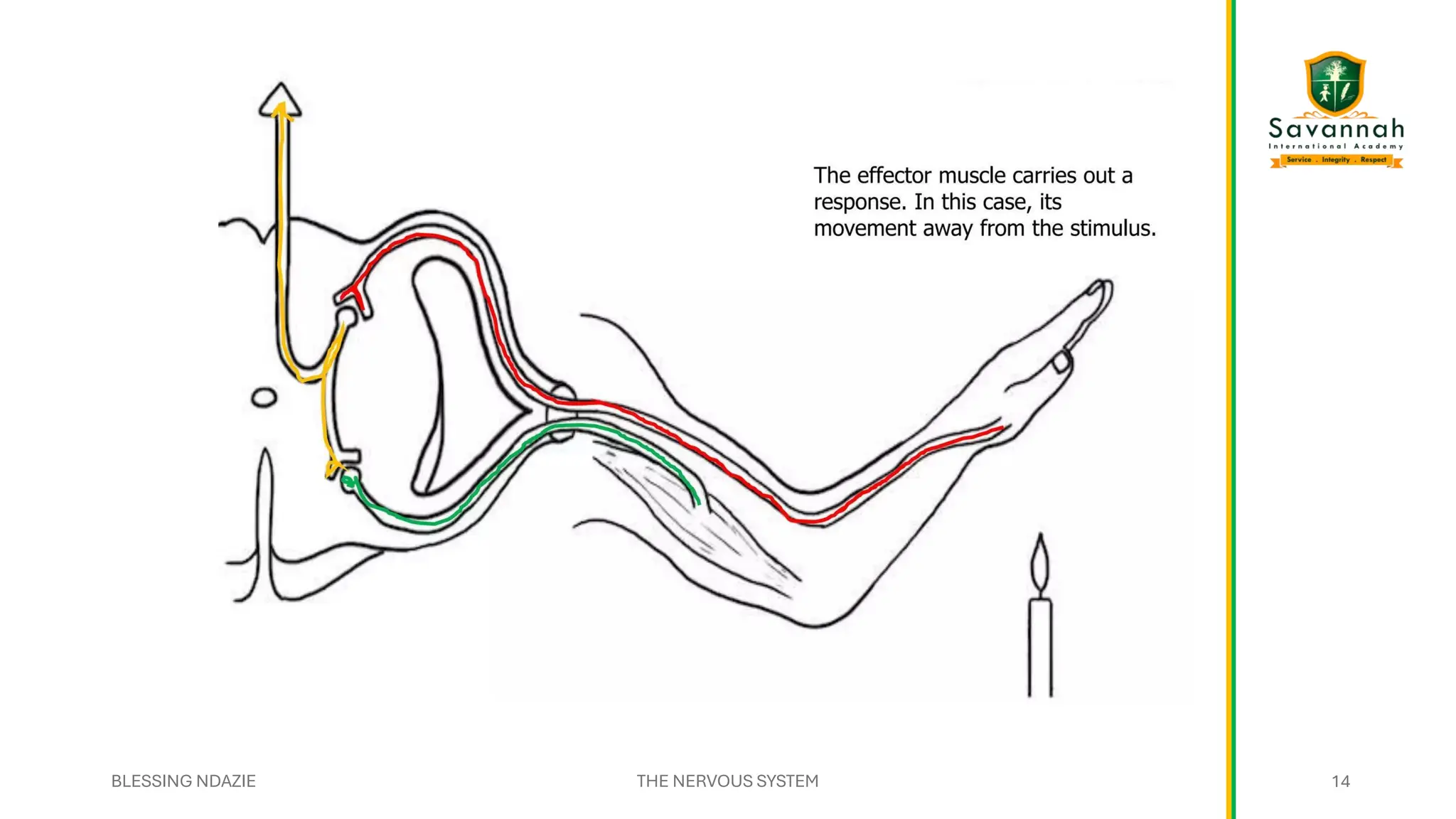
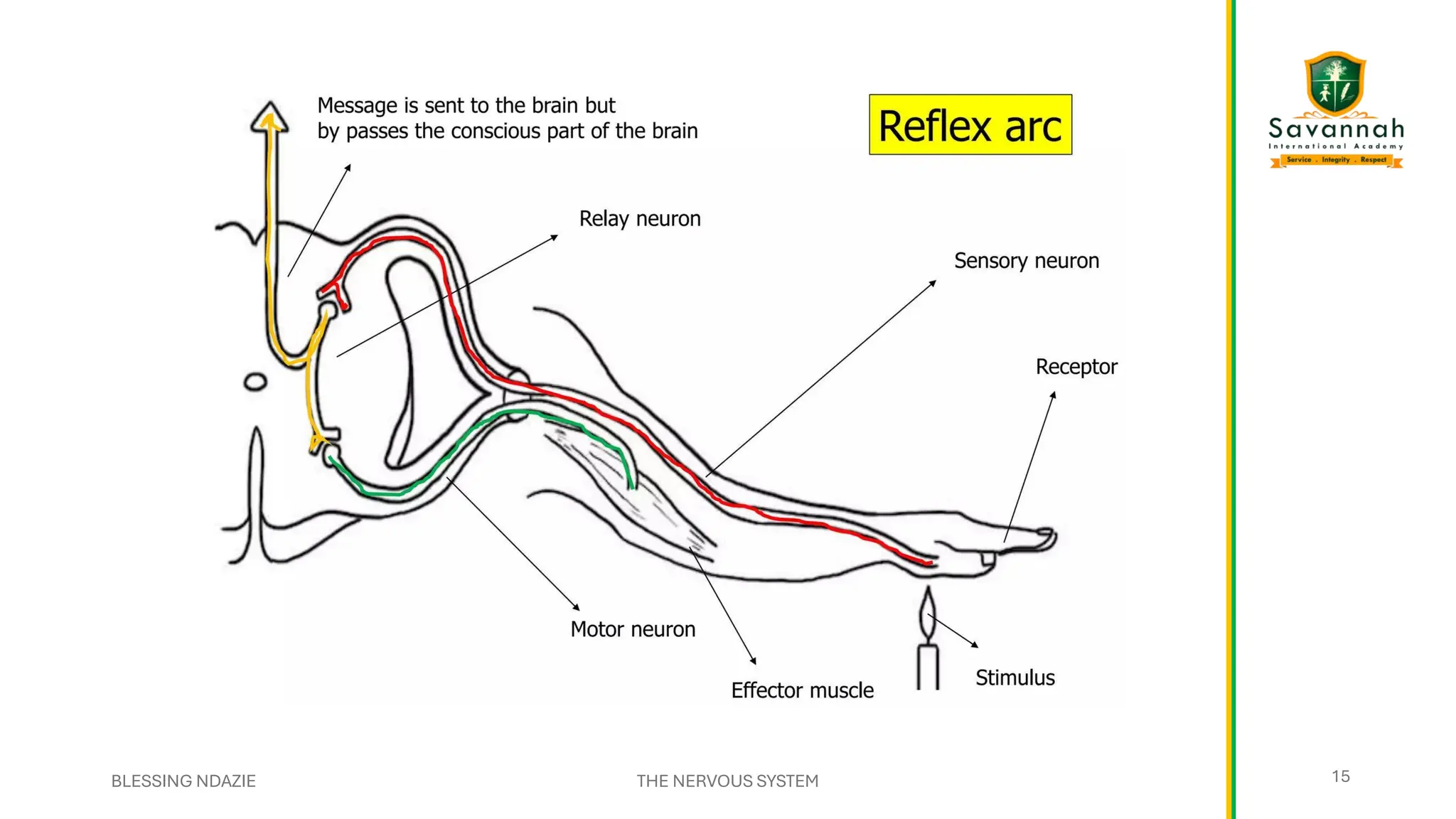
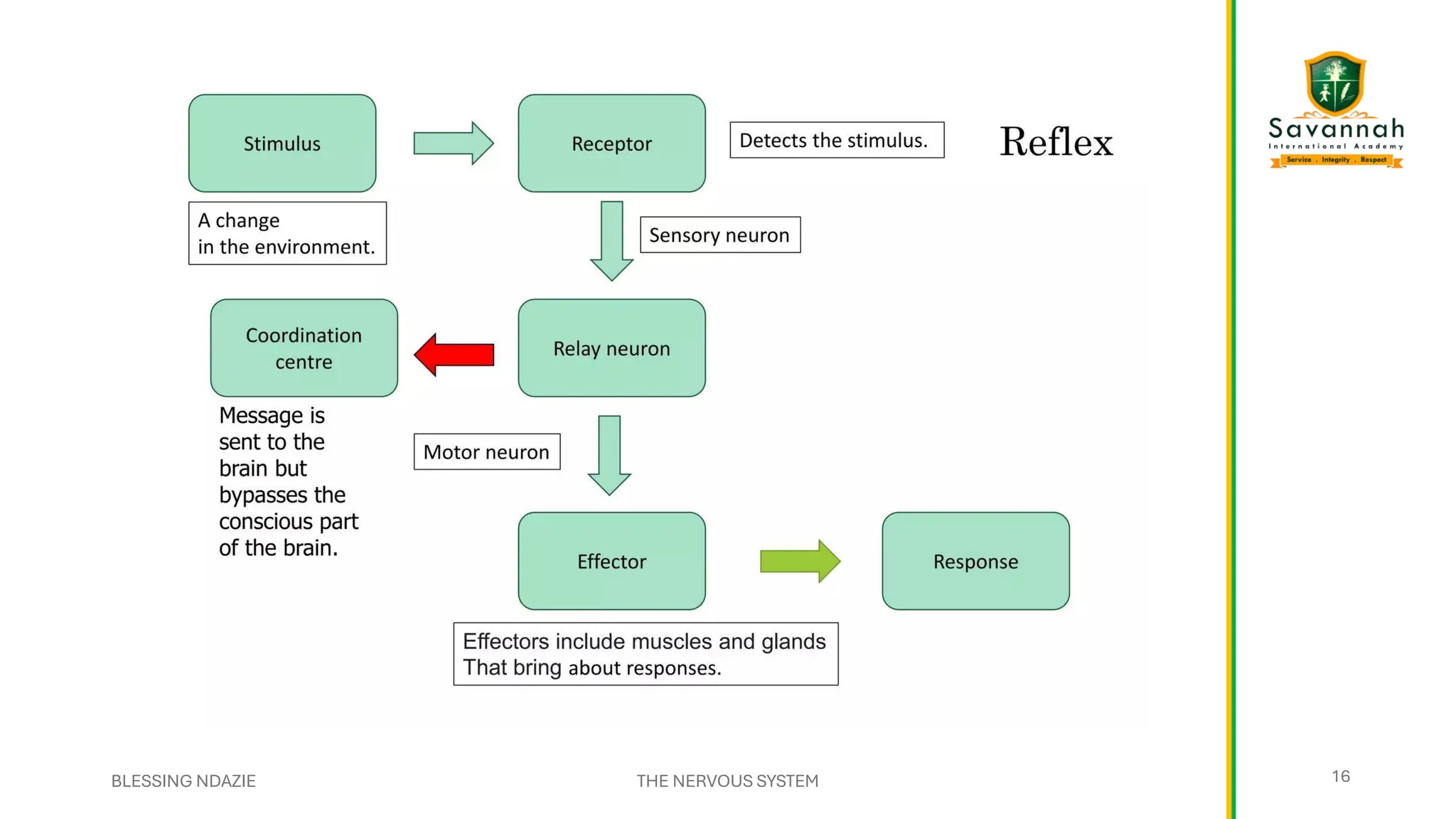
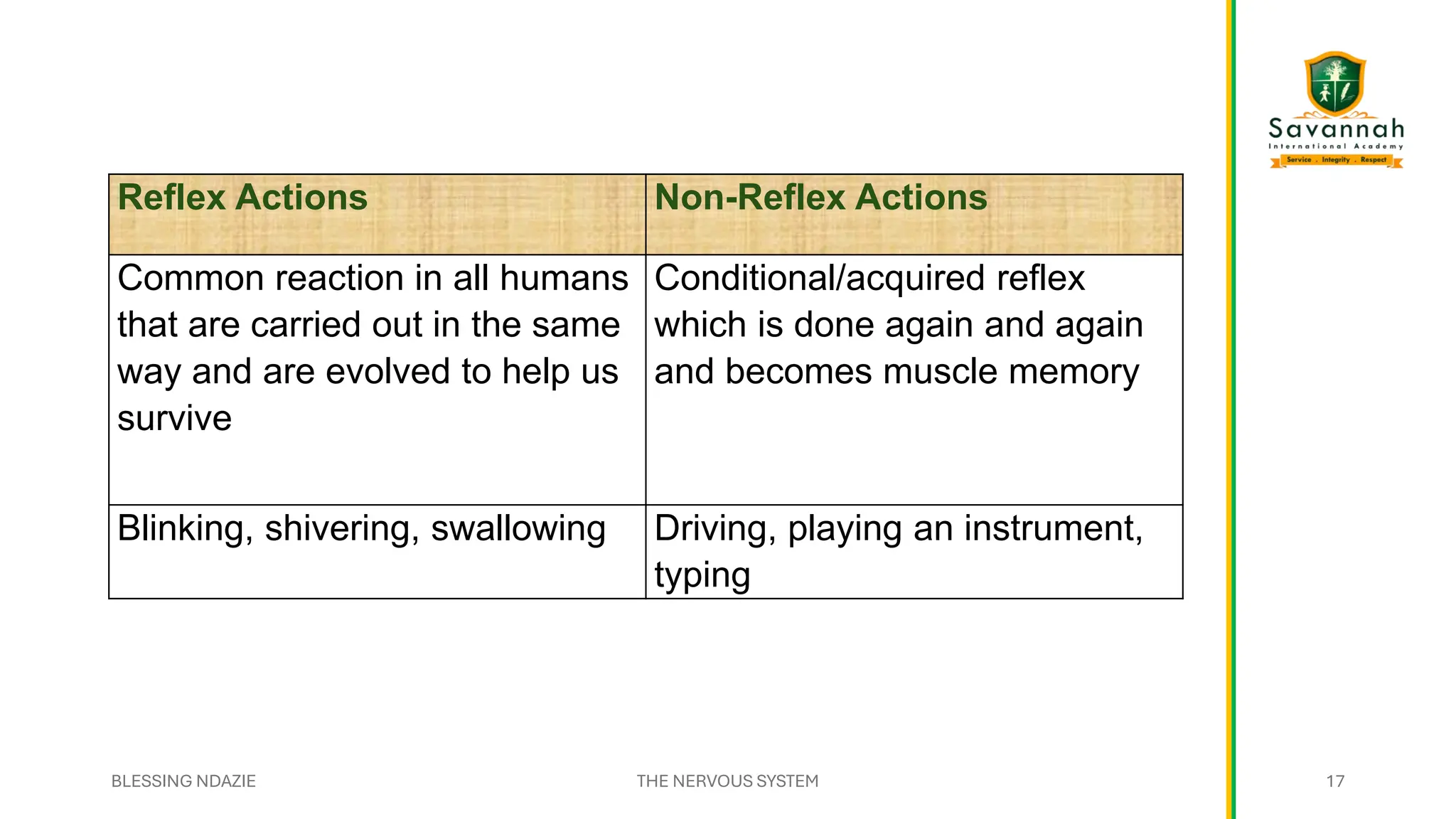
This comprehensive IGCSE Biology presentation explains the nervous system, focusing on how the body coordinates and responds to stimuli. Learn about the central and peripheral nervous systems, reflex actions, neurons, synapses, and the role of neurotransmitters. Understand the differences between voluntary and involuntary responses and how the nervous system interacts with other body systems. Ideal for Cambridge IGCSE students preparing for exams!