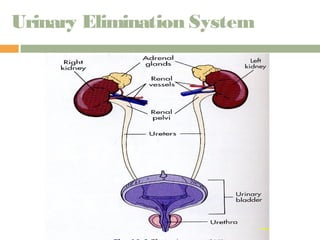
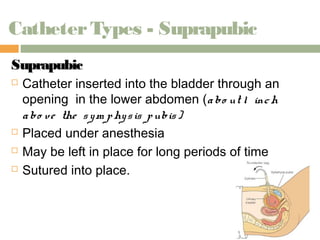
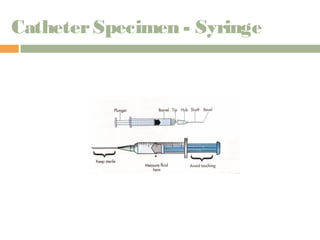
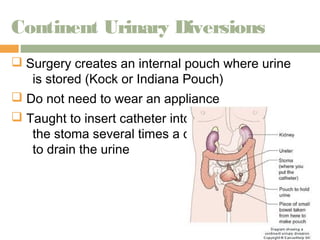
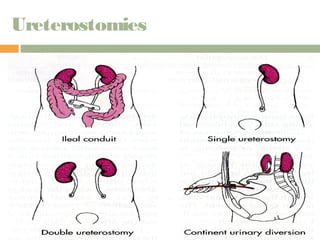
This document provides information on urinary elimination and catheters. It discusses catheter types including condom, straight, indwelling, and suprapubic catheters. Proper technique is outlined for inserting and removing catheters as well as caring for a patient with a catheter. Complications during insertion and their management are also reviewed.