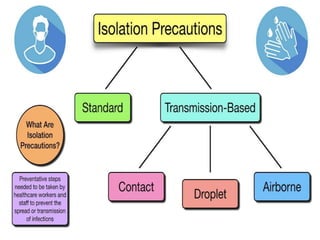
Standard precautions including hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment like gloves and gowns, and environmental cleaning are the basic level of infection control and should be followed for all patient care. Additional transmission-based precautions like airborne, droplet, or contact precautions are implemented based on the pathogen and route of transmission. Proper use of personal protective equipment, patient placement, and monitoring of isolation practices helps prevent the spread of infectious diseases in healthcare settings.