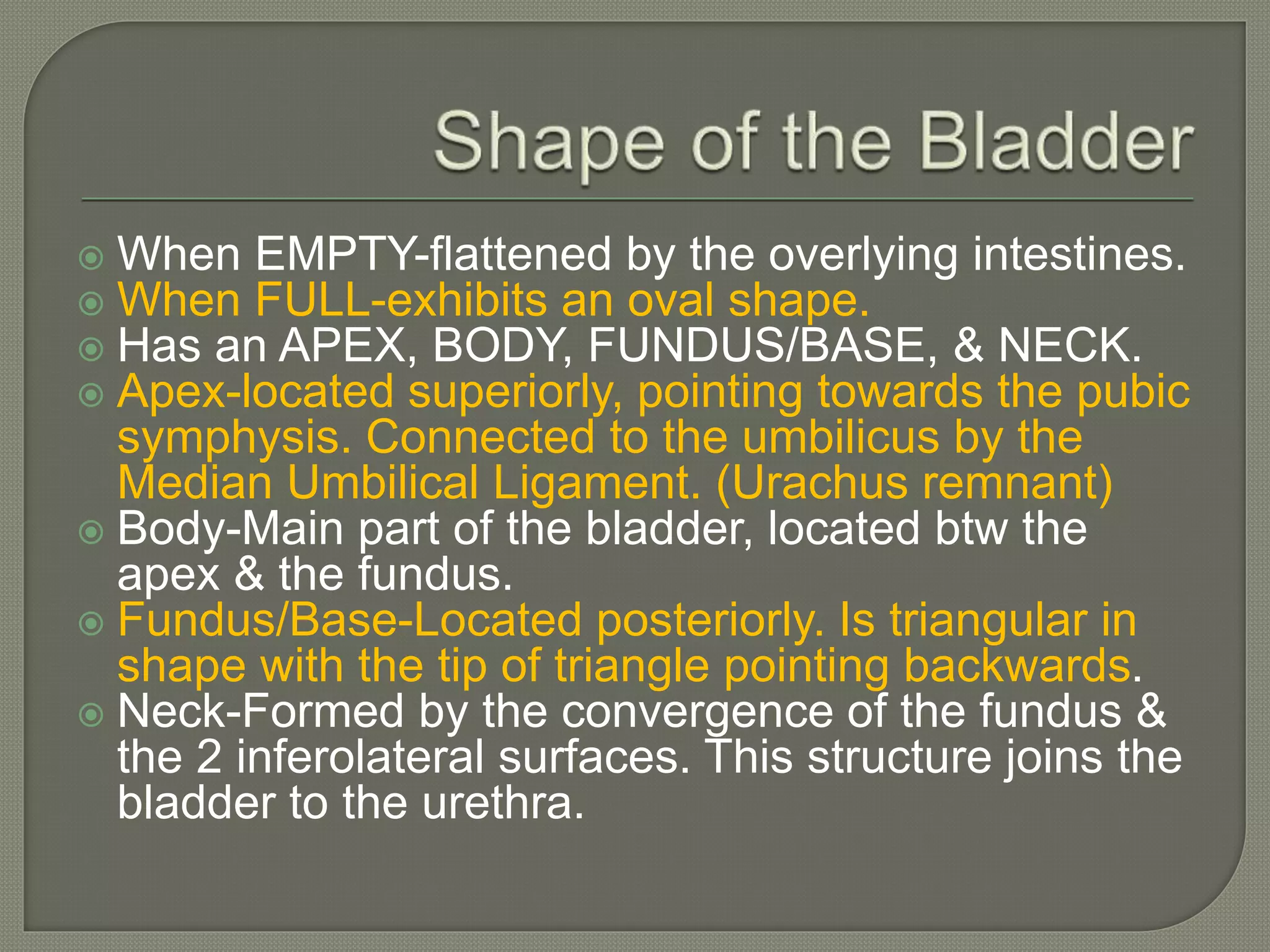
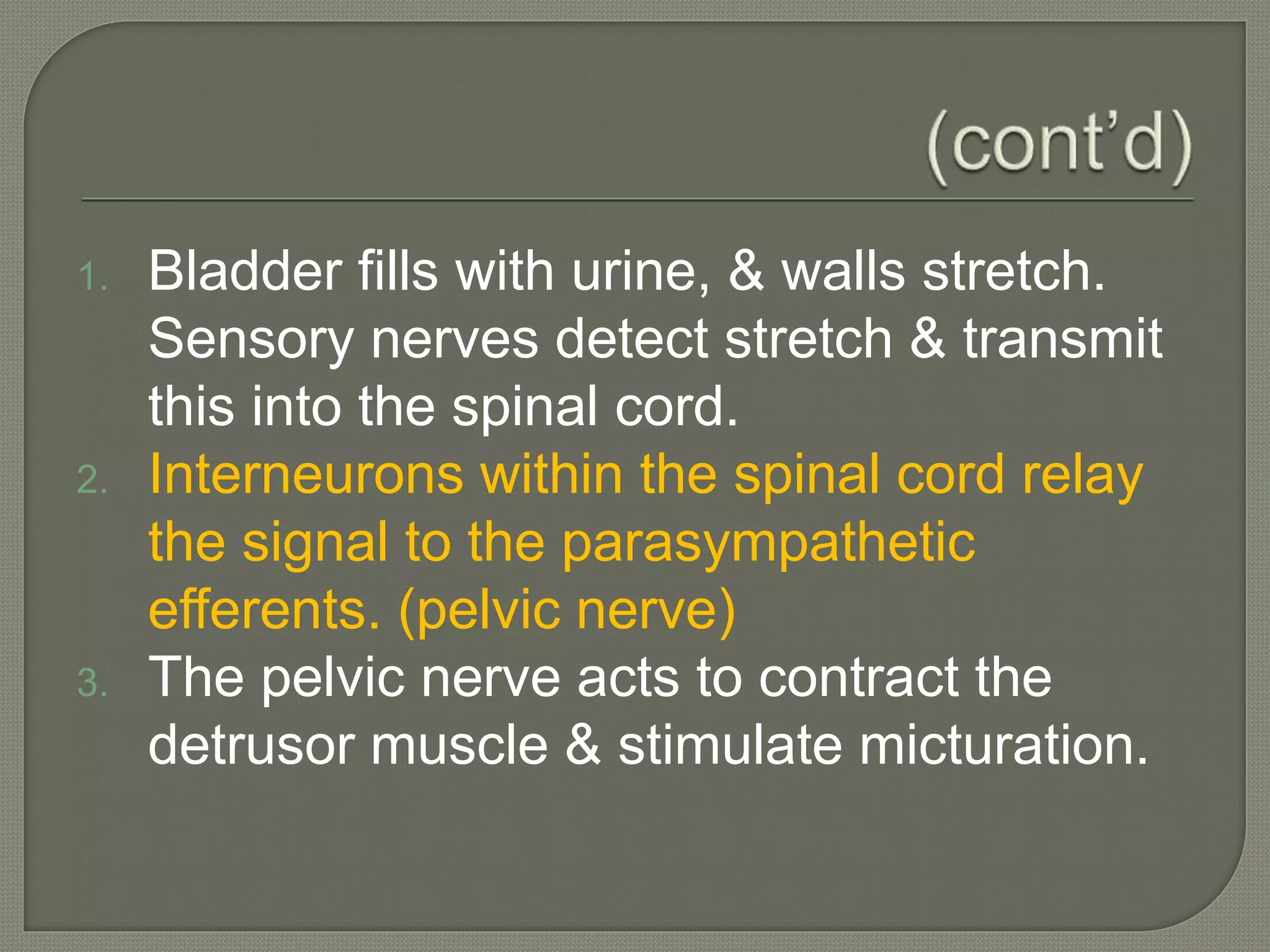
The bladder is a hollow organ located in the pelvis that collects and stores urine before expelling it. It has unique muscular and neurological properties to allow filling and emptying. The bladder receives urine from the ureters and expels it through the urethra, with internal and external sphincters controlling outflow.