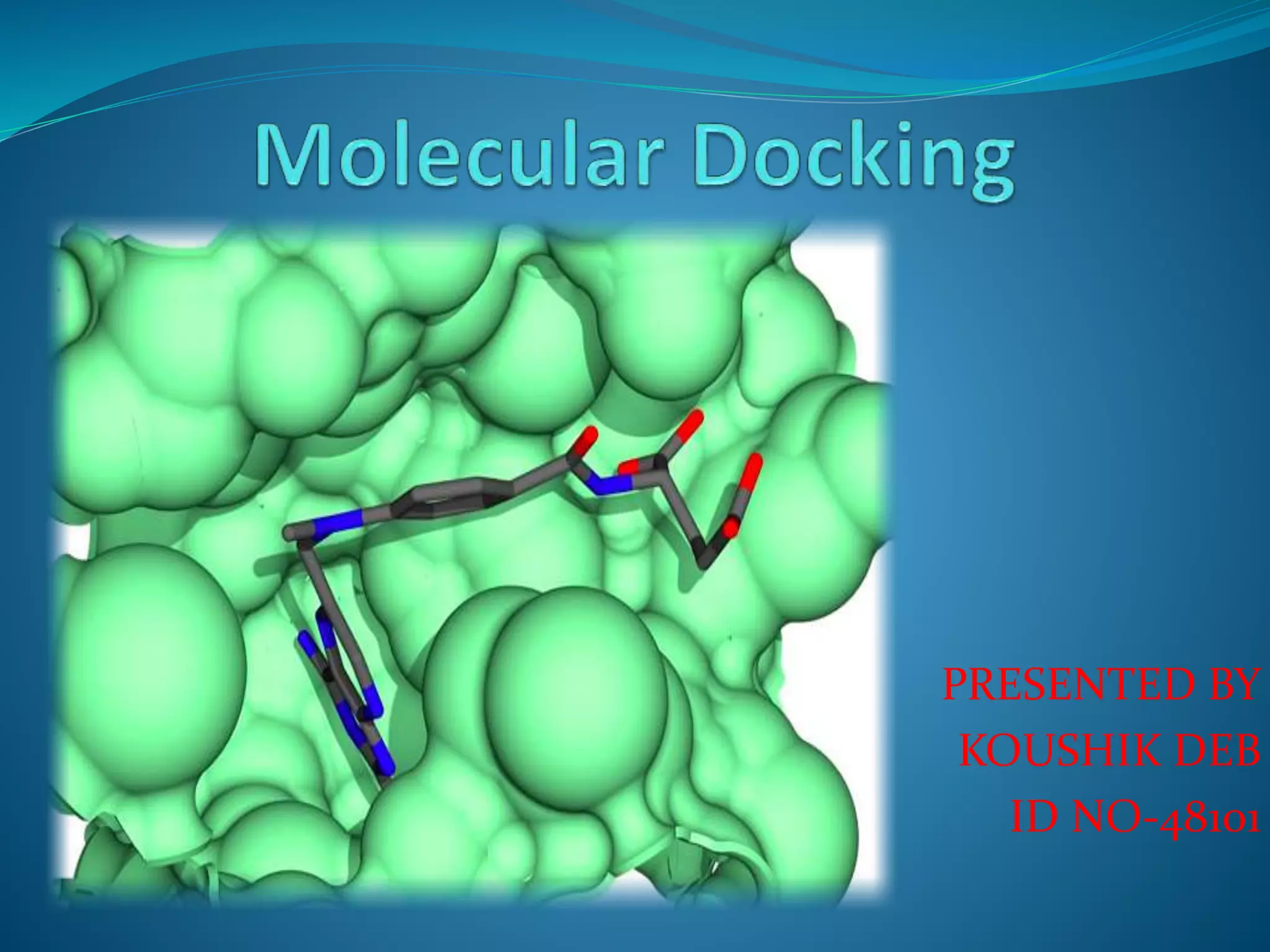
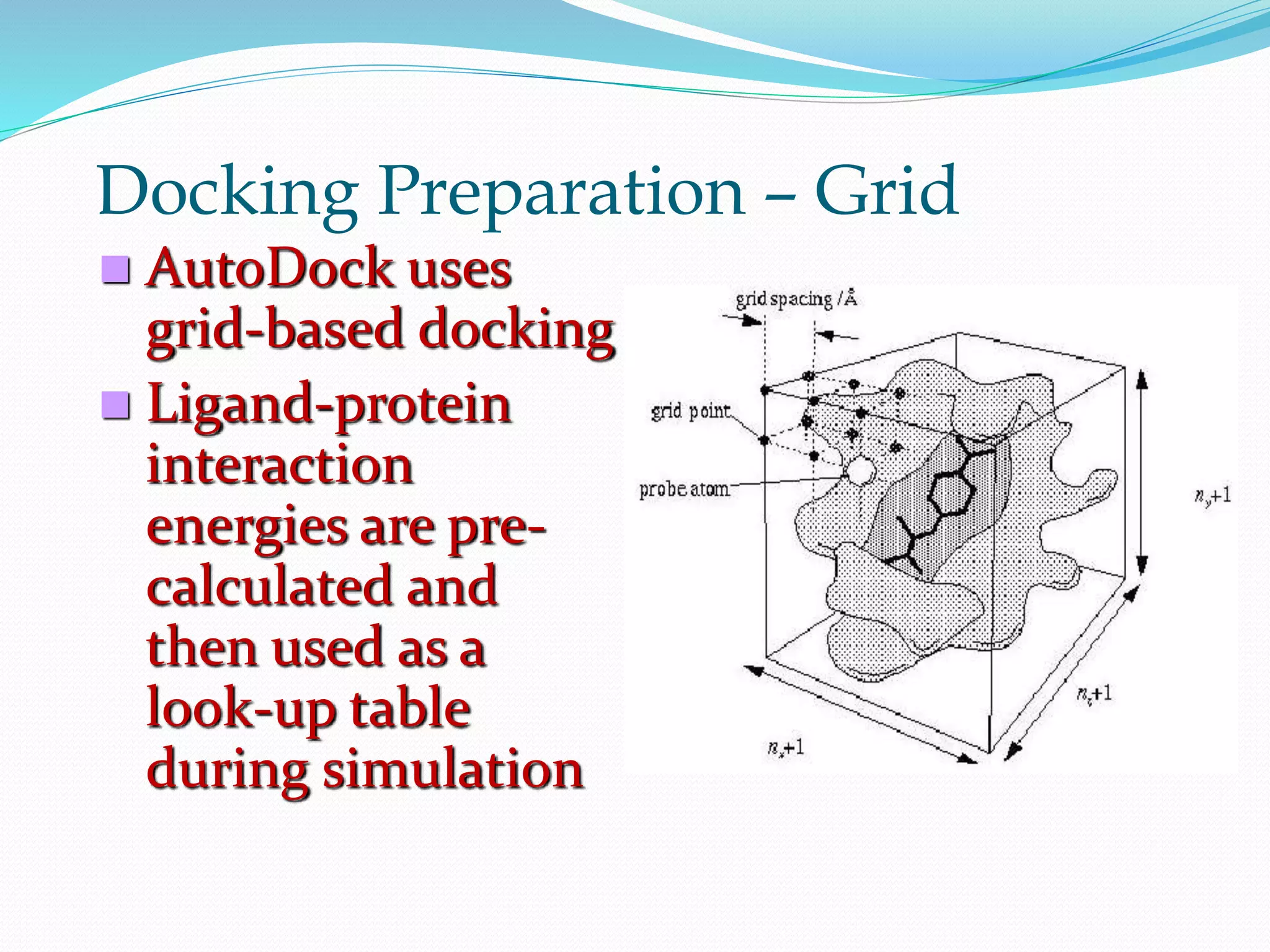
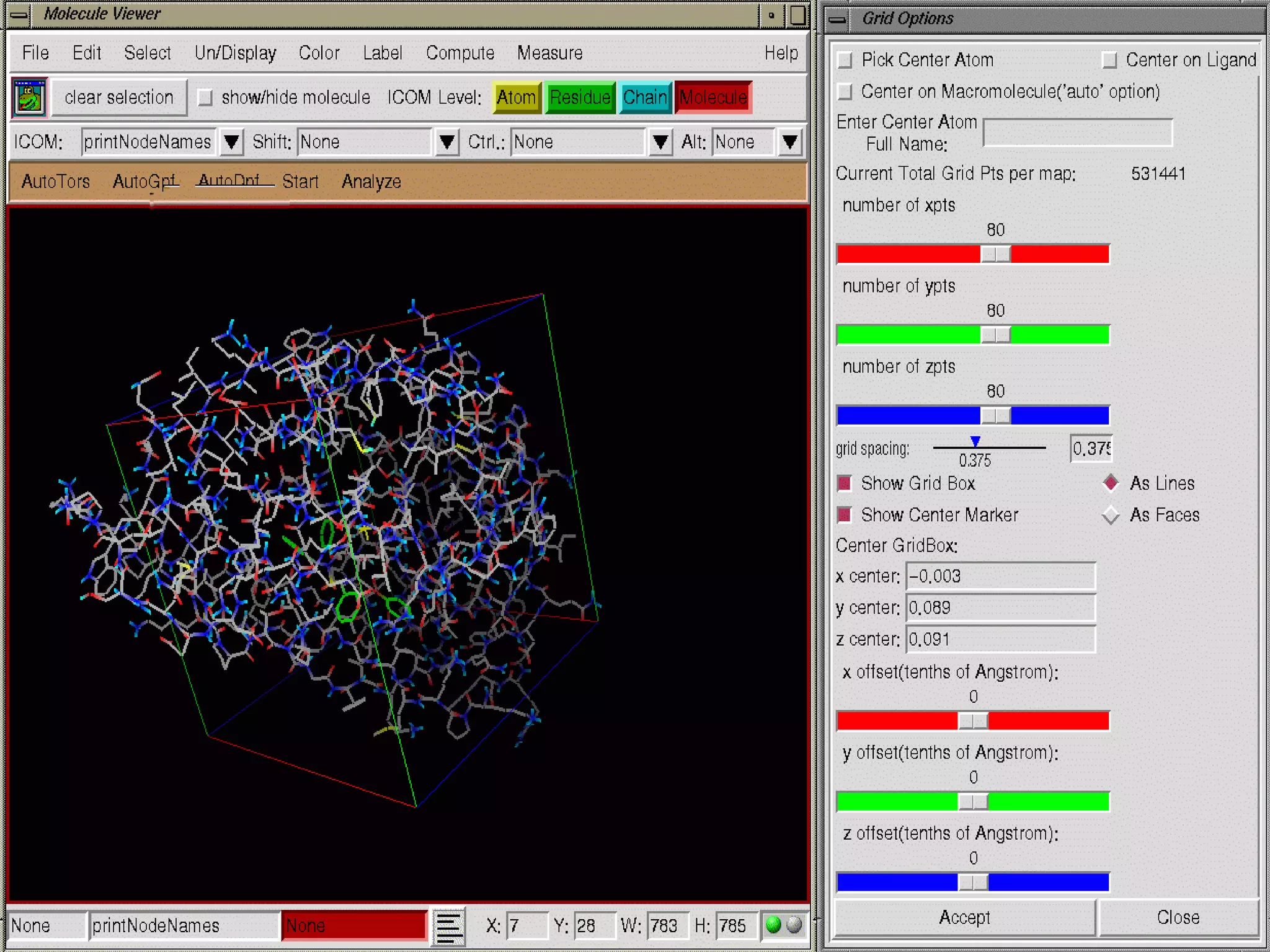
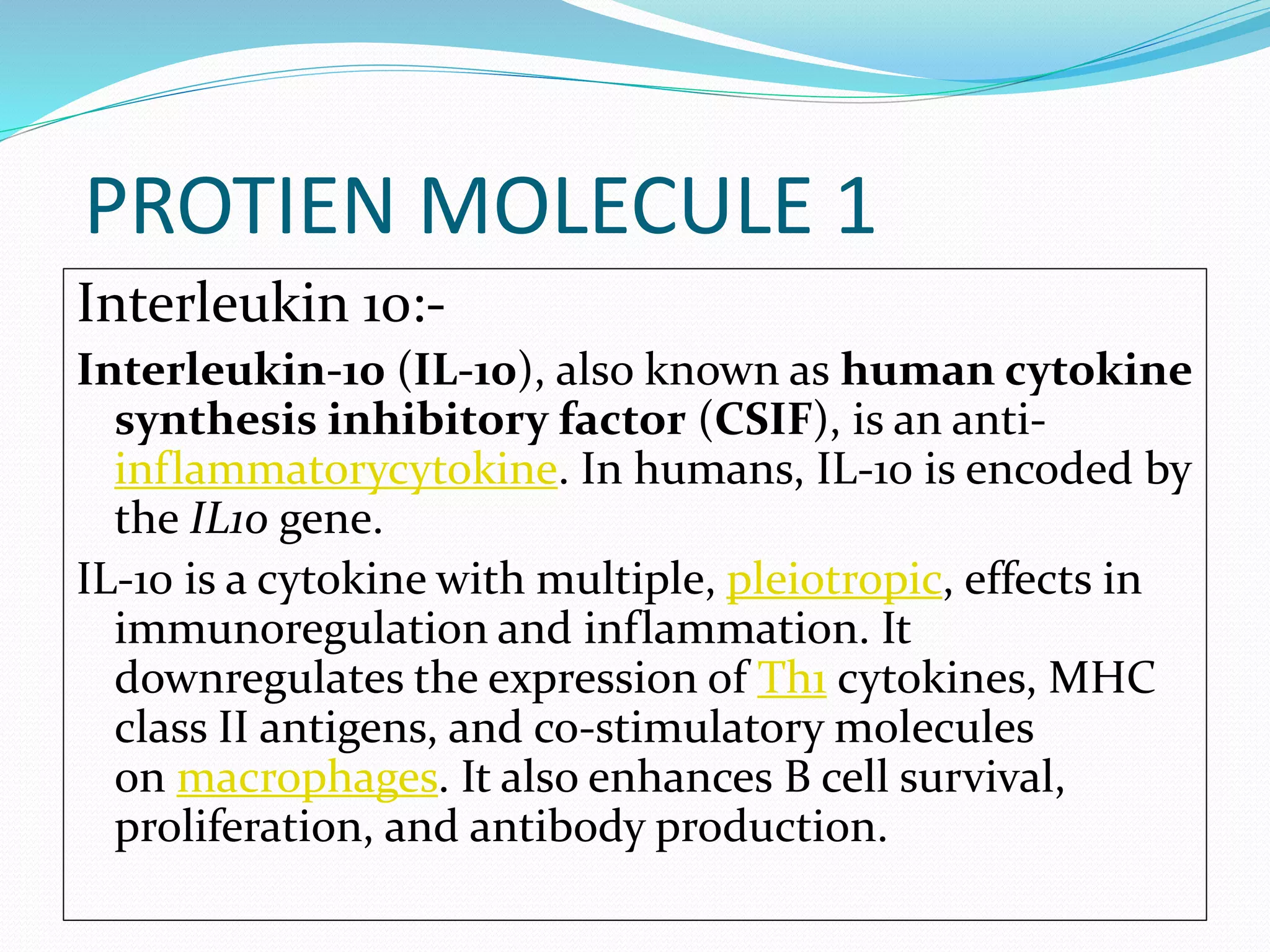
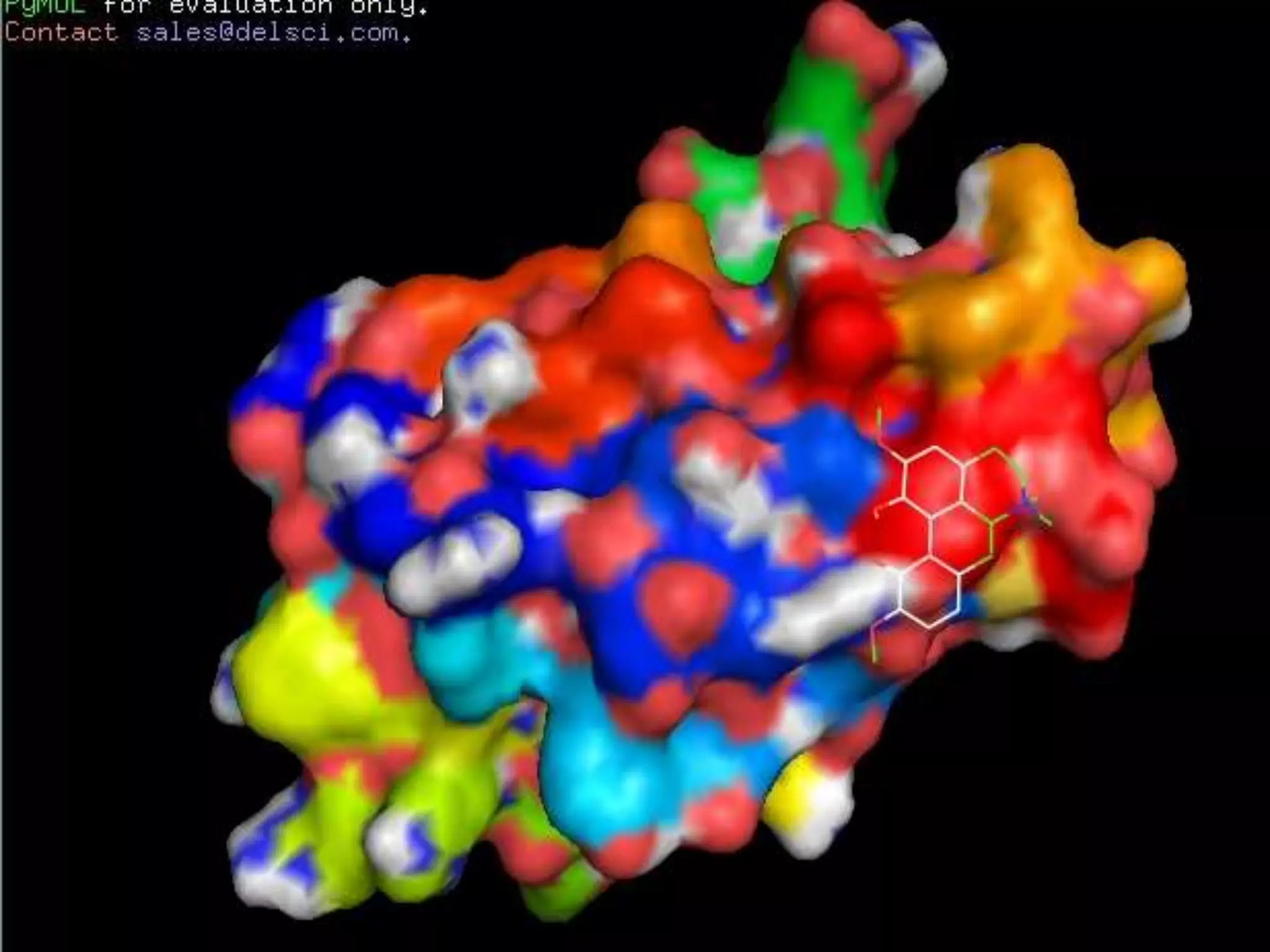
The document discusses docking, which predicts the optimal binding configuration between two molecules by optimizing their orientation and interaction energy. It describes protein-protein docking where both molecules are rigid, and protein-ligand docking where the ligand is flexible but the protein is rigid. It also discusses the AutoDock software, which uses grids and heuristic search algorithms like genetic algorithms to model docking. It provides examples of docking interleukin-10 to an alkaloid ligand, and nuclear factor kappa-B to a ligand. The document advises considering compounds with binding energies close to or better than a positive control as potential hits.