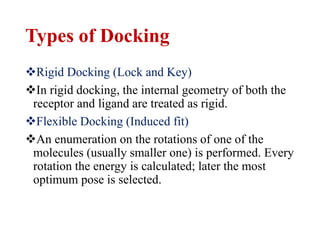
Docking is a computational method that predicts the preferred orientation of one molecule to another when bound to form a stable complex. It involves searching high-dimensional spaces to find the best matching between two molecules, such as a protein and ligand. Successful docking methods effectively search these spaces and use scoring functions to correctly rank candidate dockings in order to identify the correct ligand binding position and predict binding affinity.