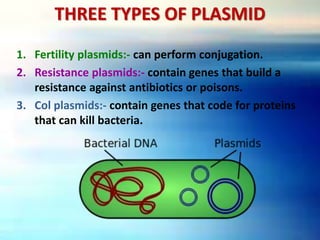
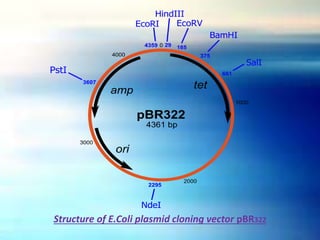
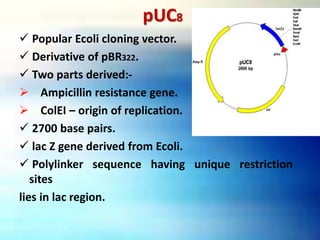
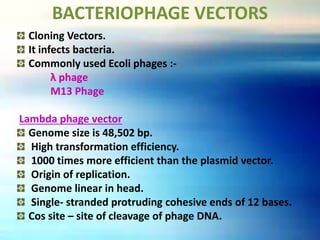
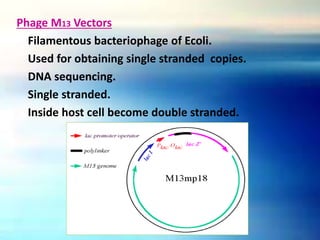
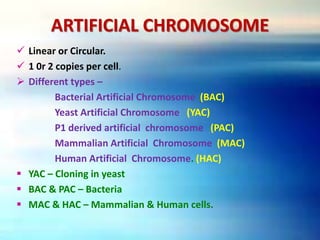
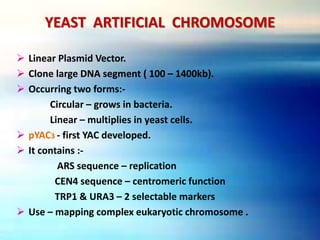
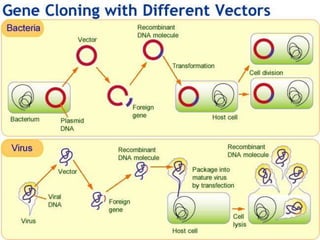
Vectors are DNA molecules that can carry foreign DNA fragments into host cells. The main types of vectors discussed are plasmids, bacteriophages, hybrid vectors, and artificial chromosomes. Vectors must be capable of self-replication and have characteristics like origins of replication, selectable markers, and cloning sites to incorporate foreign DNA. Common vector types include plasmids like pBR322, phages like lambda and M13, cosmids that combine plasmid and phage components, and artificial chromosomes like BACs, YACs and MACs that can replicate in bacteria, yeast or mammalian cells respectively.