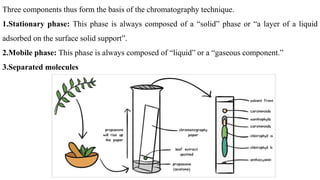
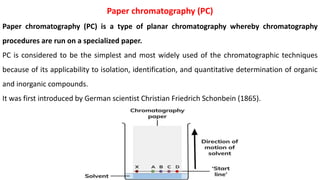
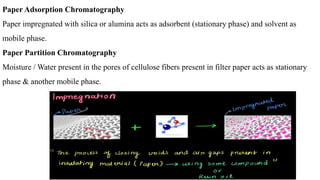
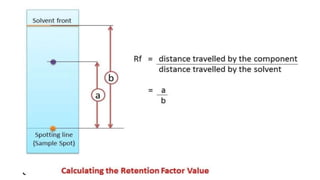
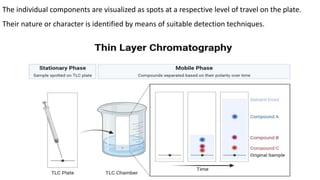
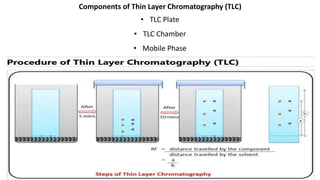
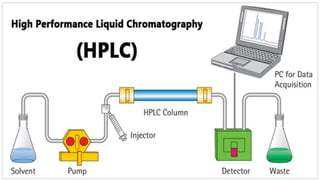
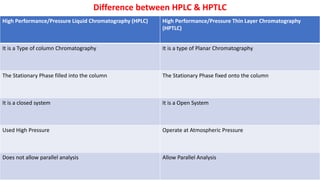
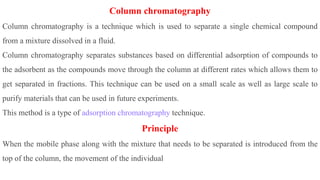
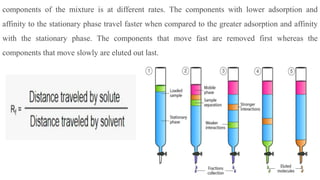
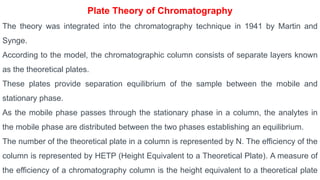
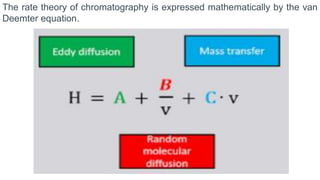
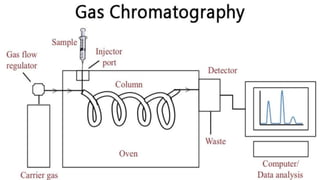
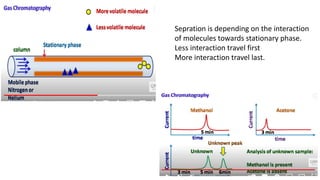
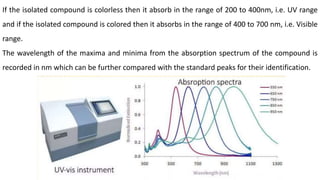
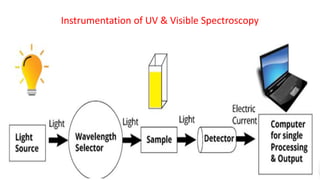
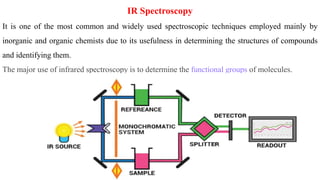
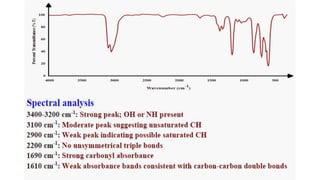
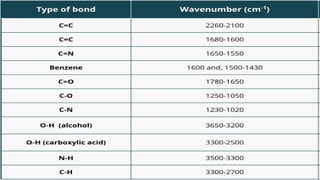
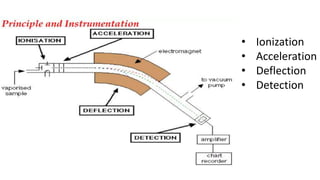
Chromatography is a technique used to separate mixtures by exploiting differences in how components interact with a stationary and mobile phase. There are several types including paper chromatography, thin layer chromatography, column chromatography, gas chromatography, and high performance liquid chromatography. Chromatography works by separating components of a mixture as they travel through a stationary phase at different rates based on properties like size, binding affinity, and charge. It is widely used across sciences for applications such as analyzing drugs, pollutants, and other chemical mixtures.