Embed presentation
Download to read offline


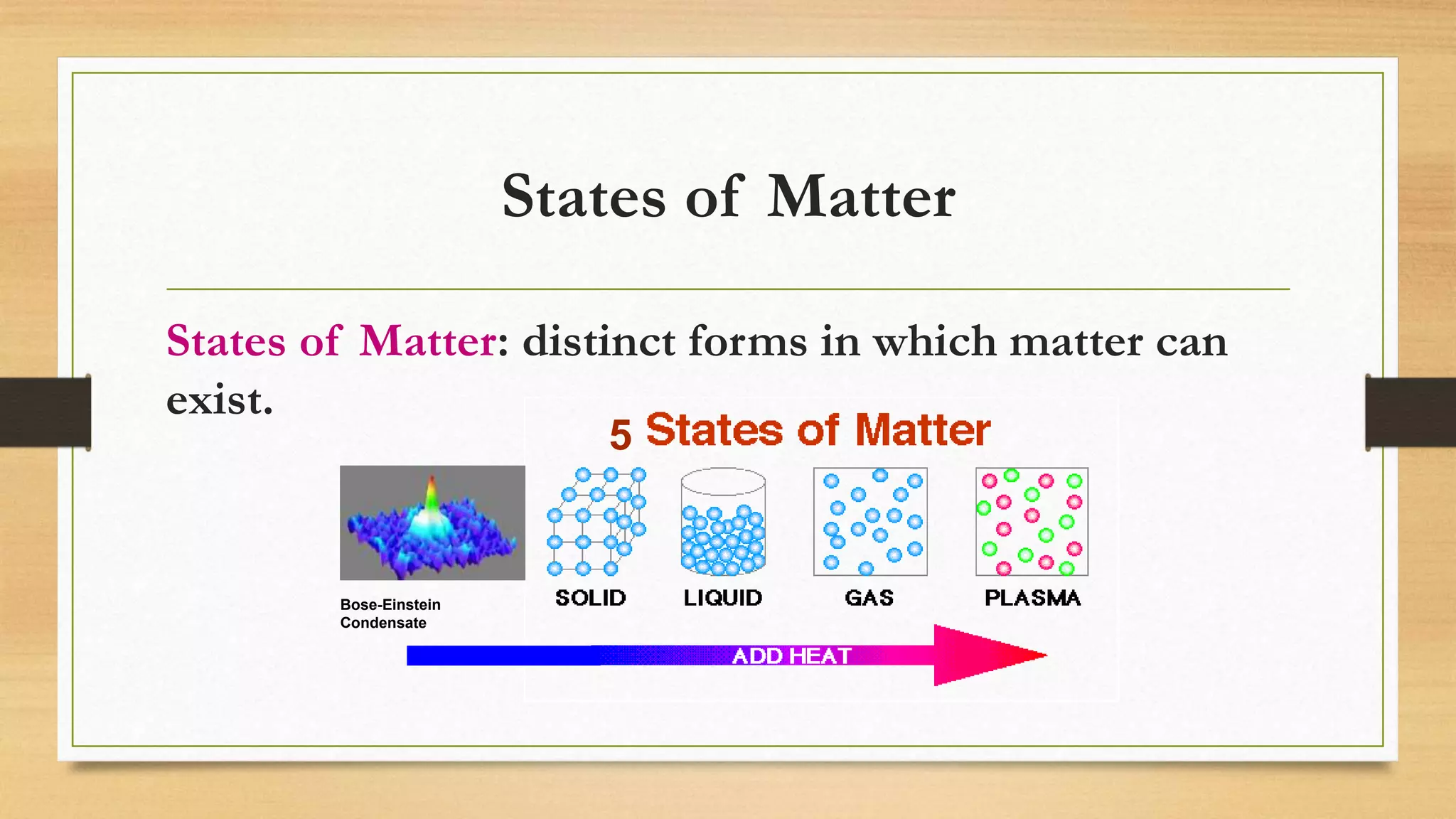
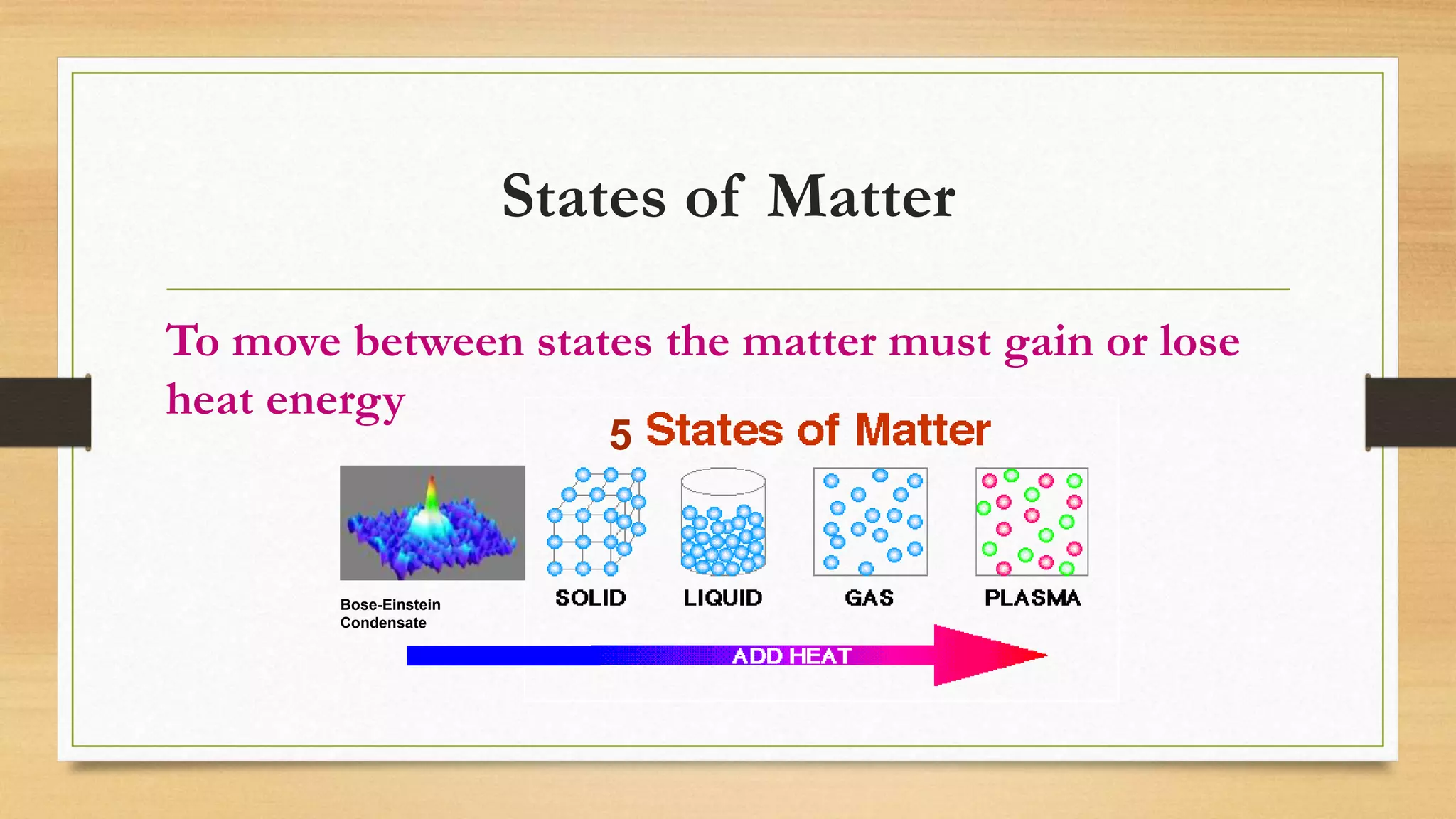
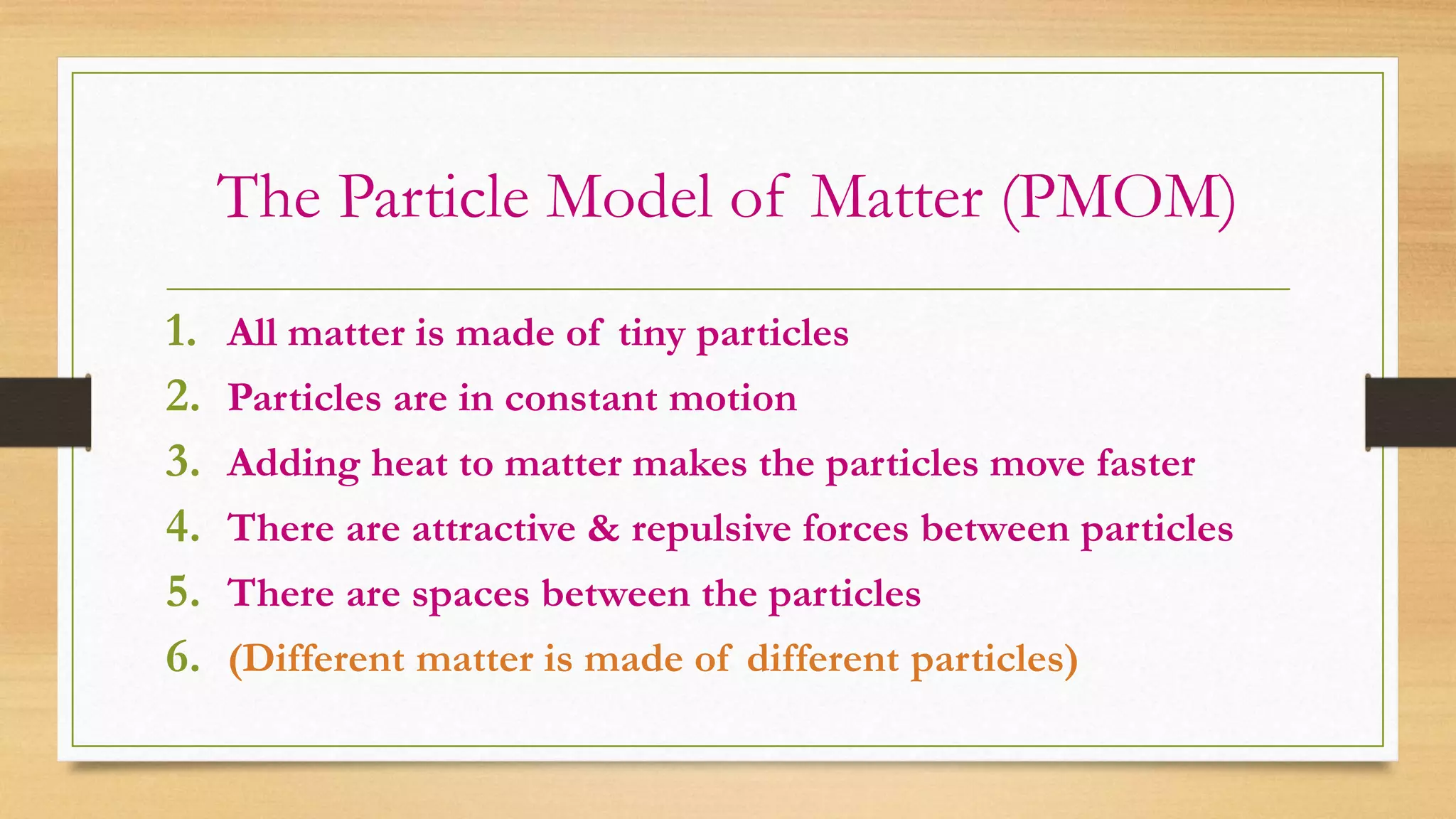
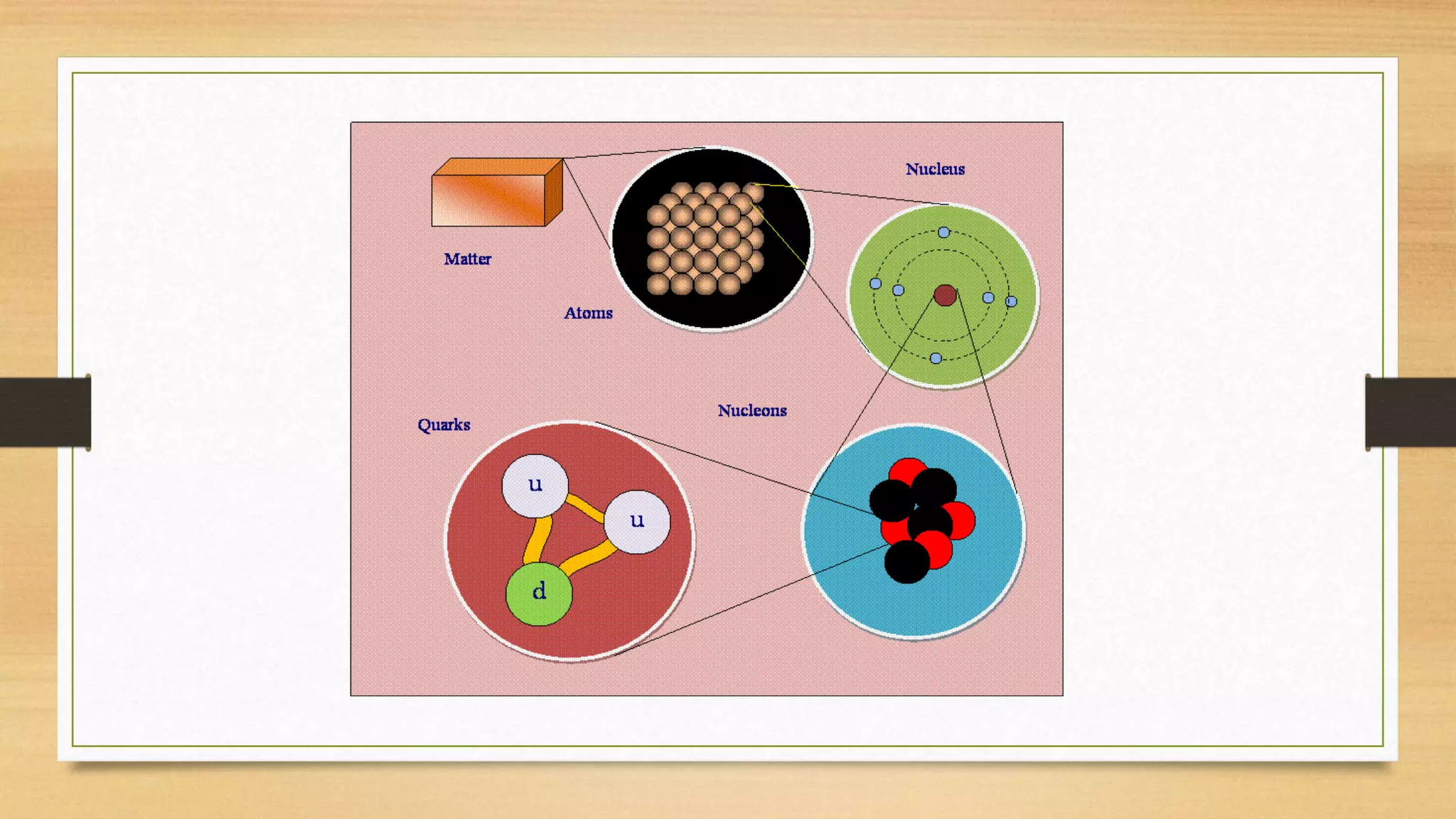
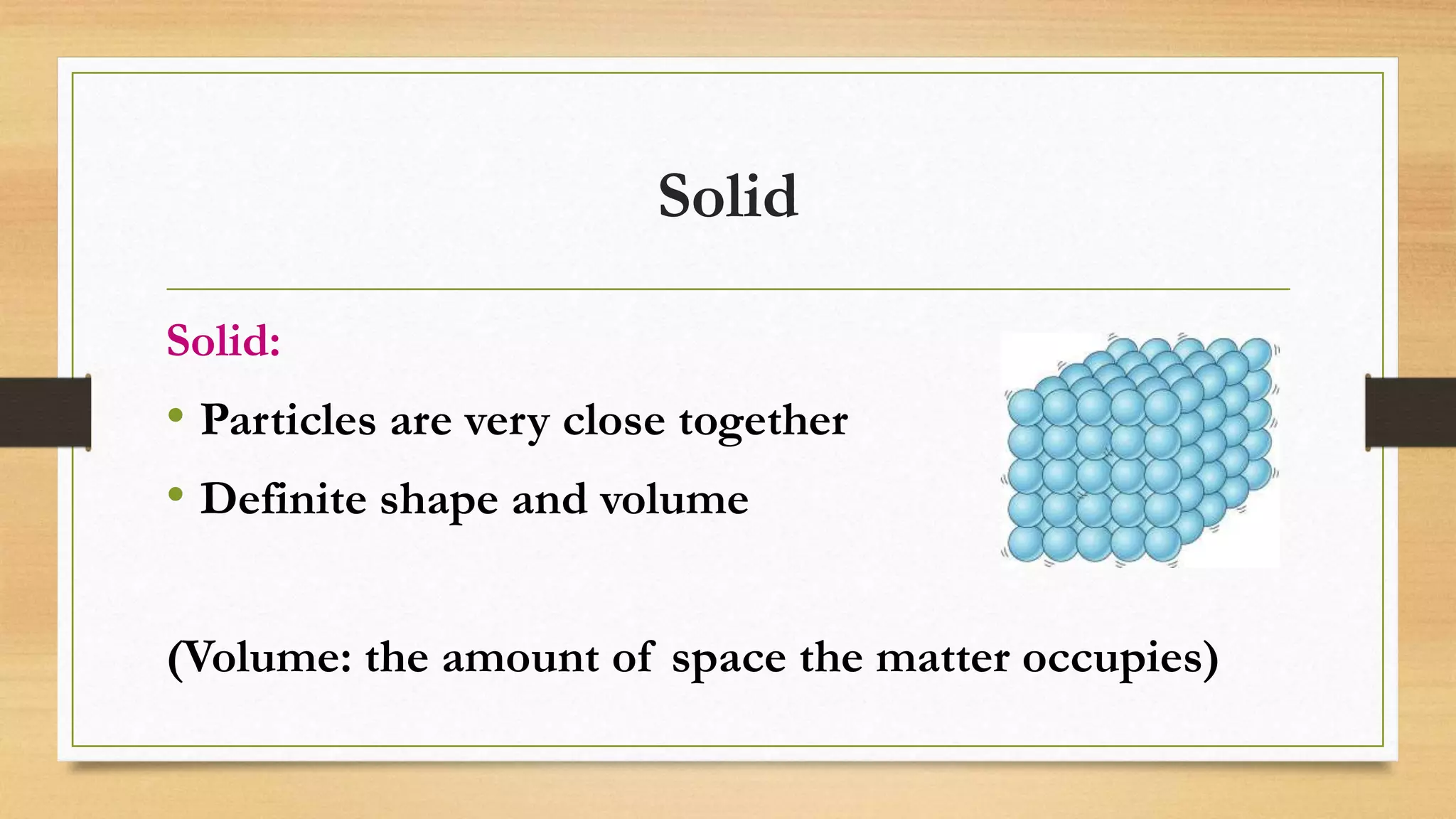

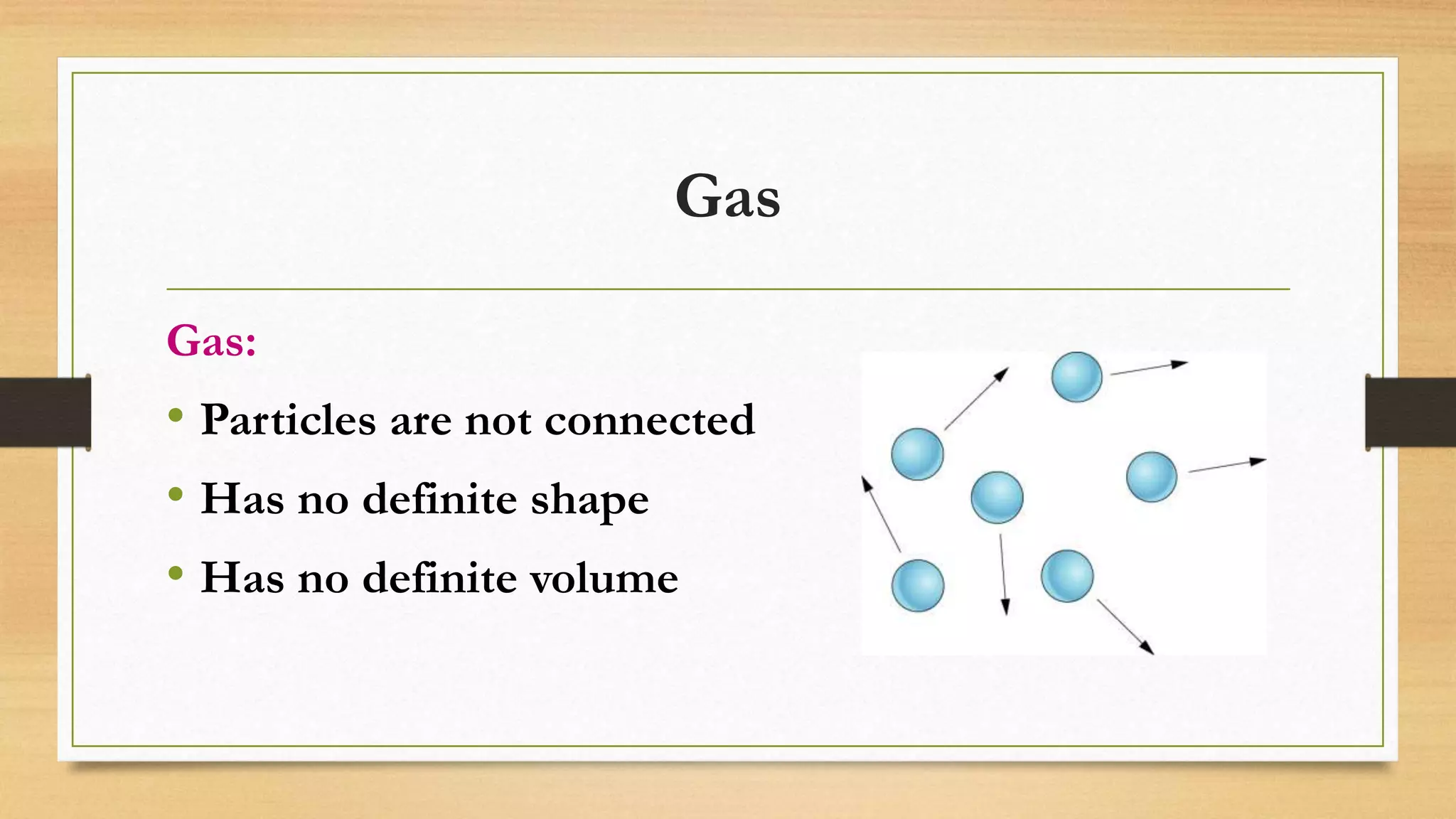
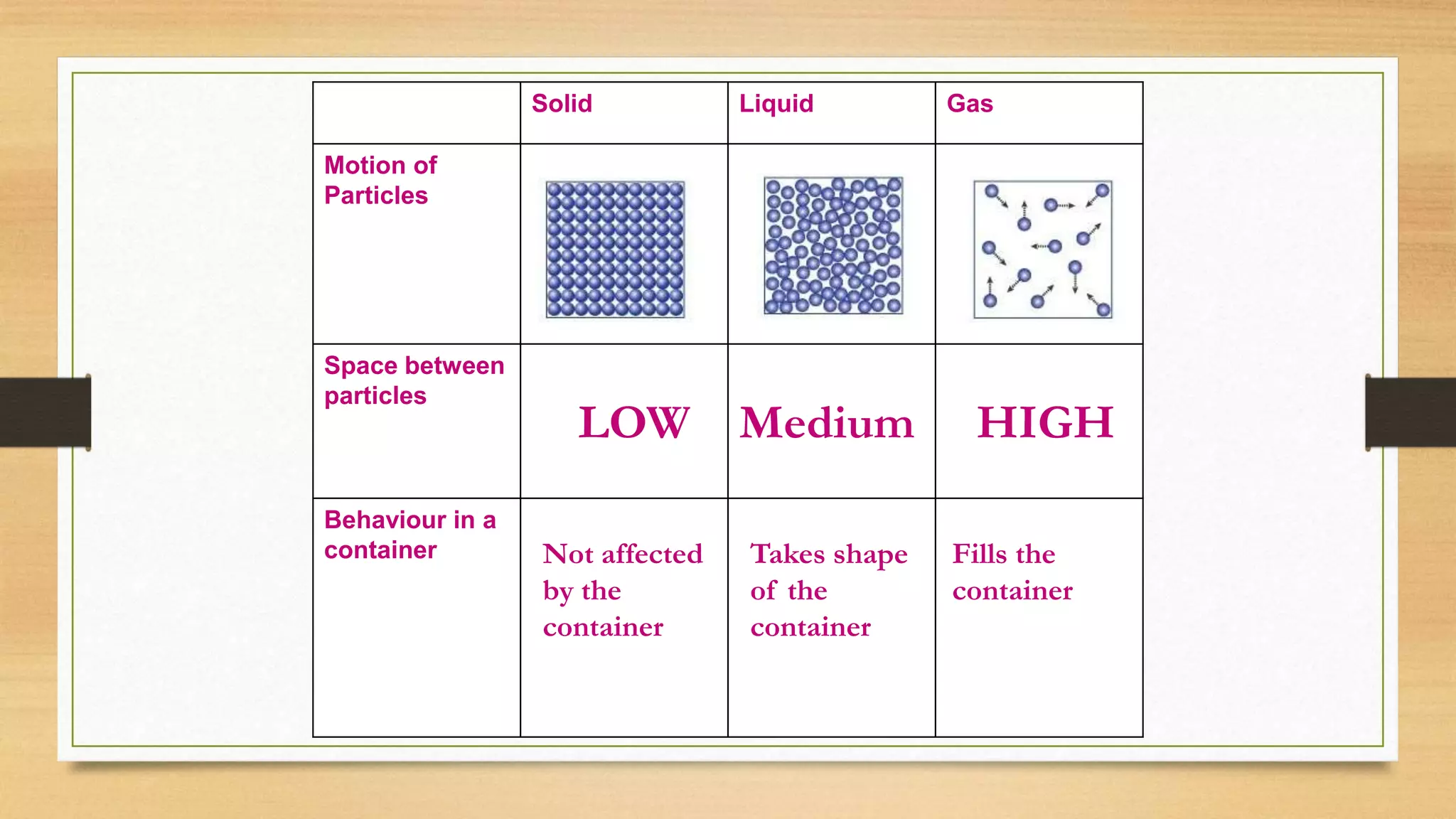
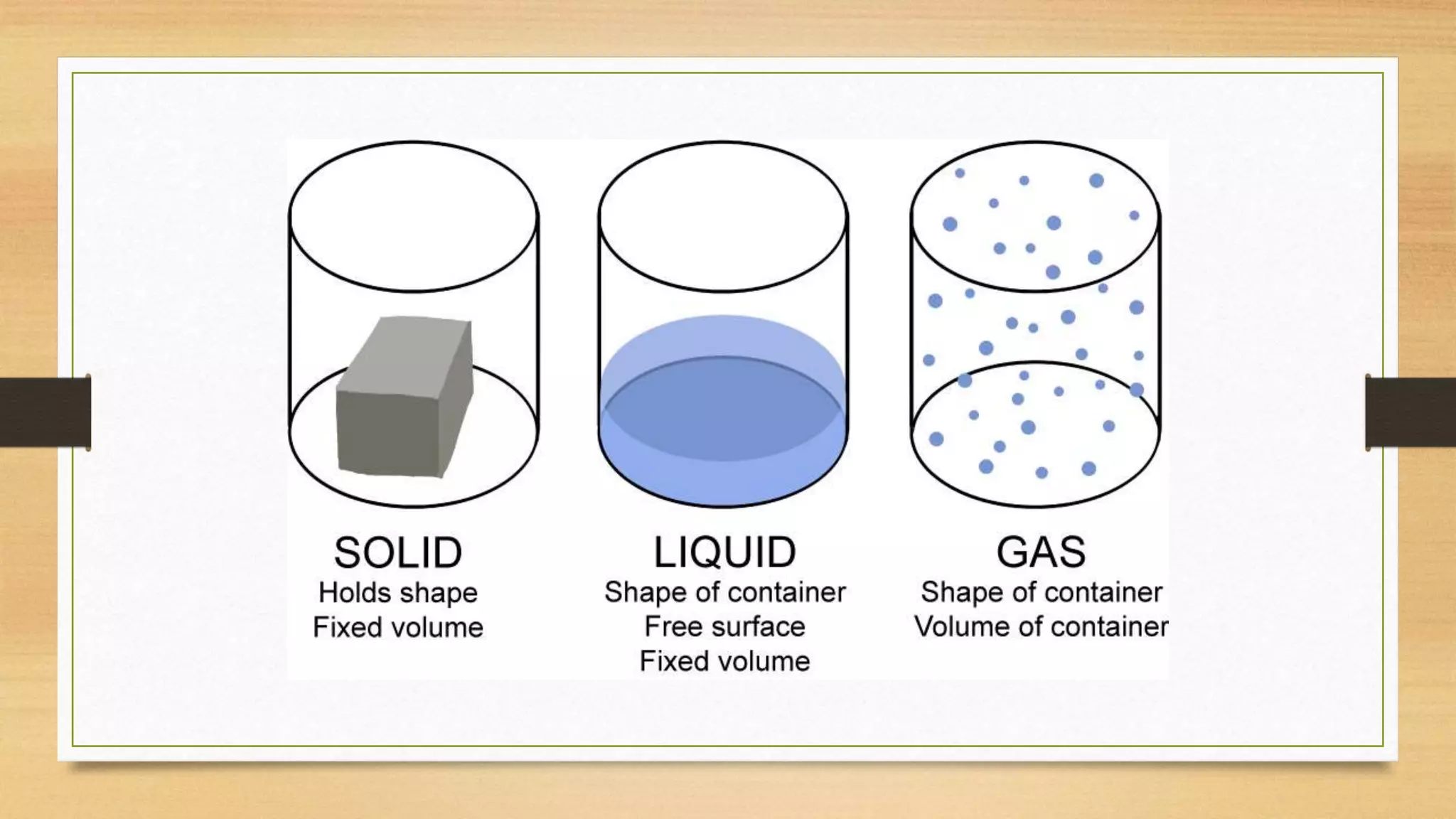
The document discusses the particle model of matter (PMOM), which states that all matter is made up of tiny particles that are in constant motion. The PMOM explains that there are three main states of matter - solid, liquid, and gas - which differ based on how close or far apart the particles are and how they behave. Solids have particles very close together with a definite shape and volume, liquids have particles loosely attached that take the shape of their container but have a definite volume, and gases have particles not connected that fill their container without a definite shape or volume.










