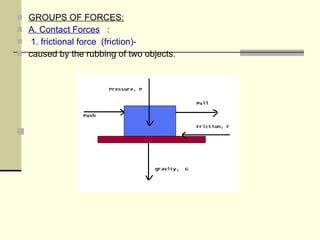
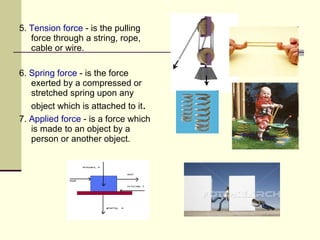
Force is defined as a push or pull that can cause an object's motion to change. It is measured in Newtons (N), with 1N being the force needed to accelerate 1kg of mass by 1m/s^2. There are two main types of forces - contact forces like friction and tension which require touching objects, and action-at-a-distance forces like gravity and magnetism which act without direct contact. Force is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction.