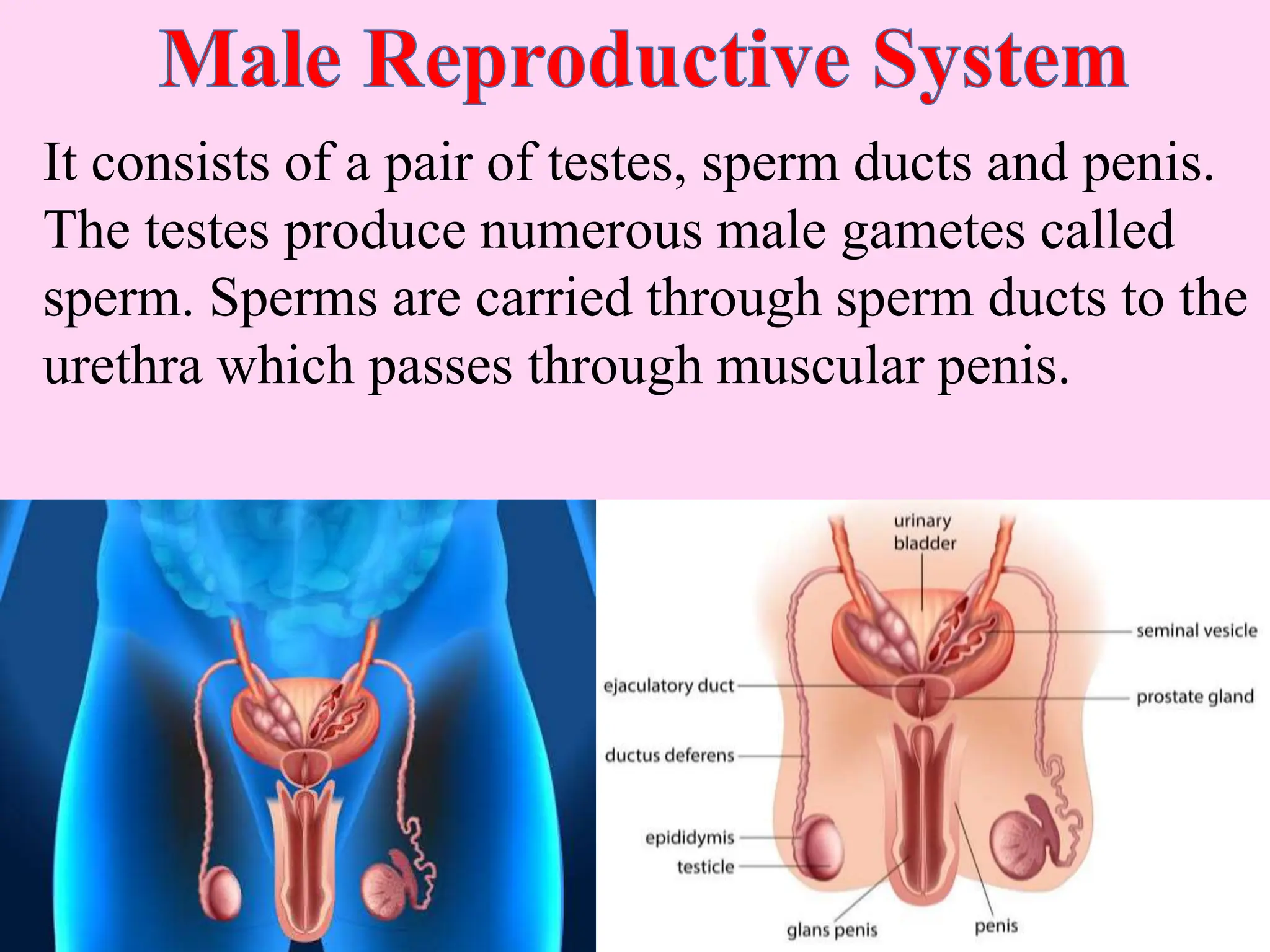
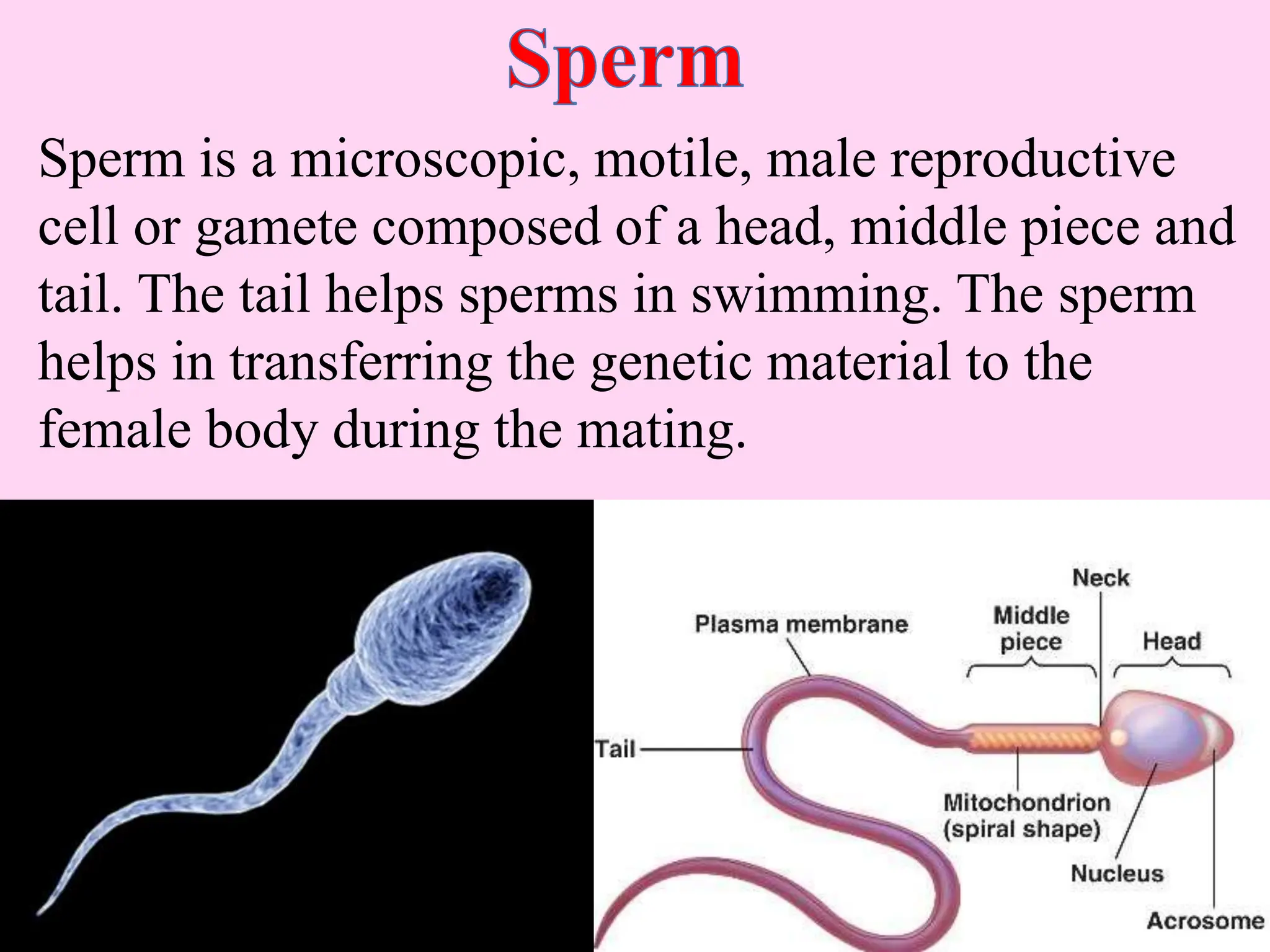
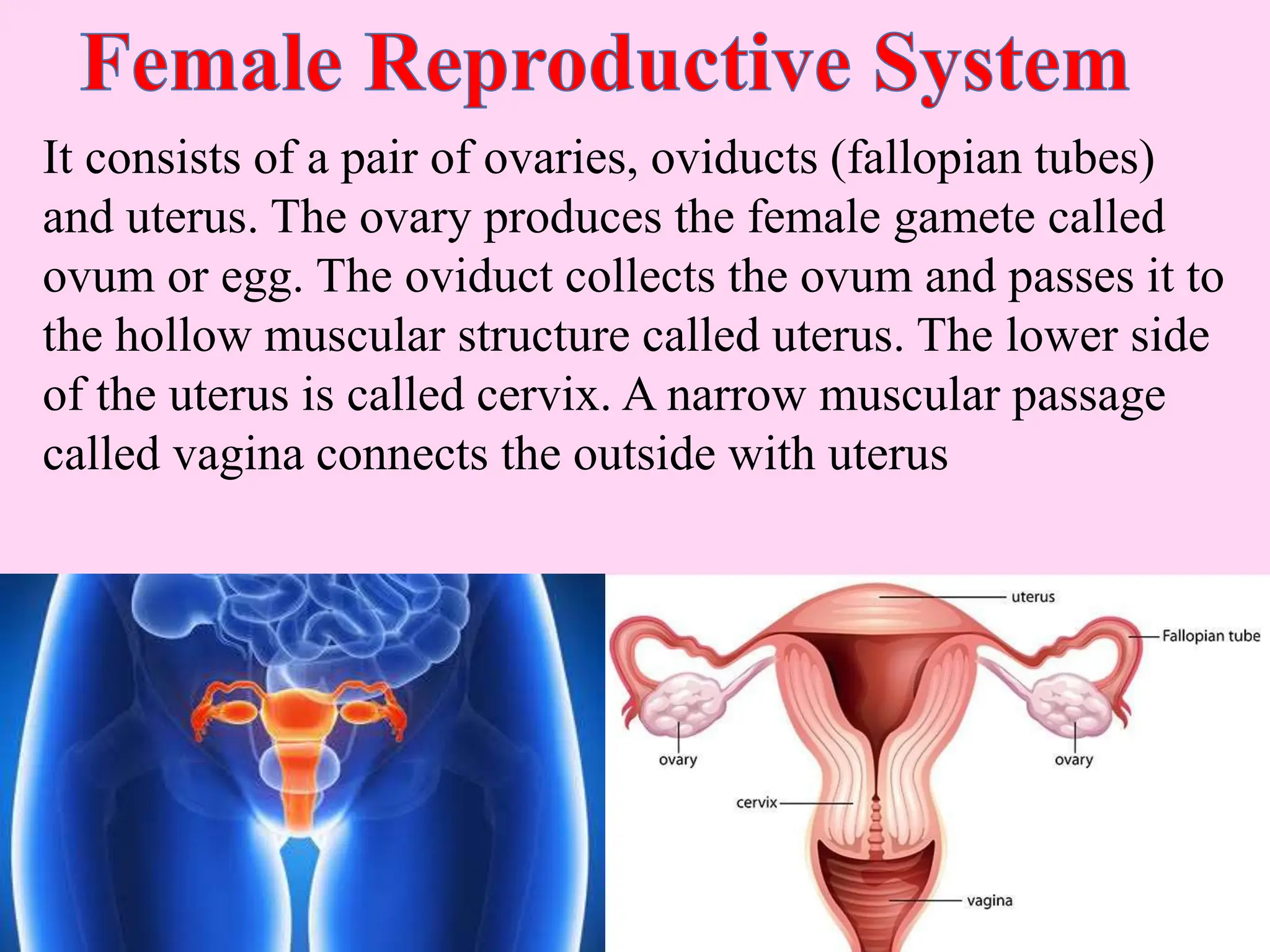
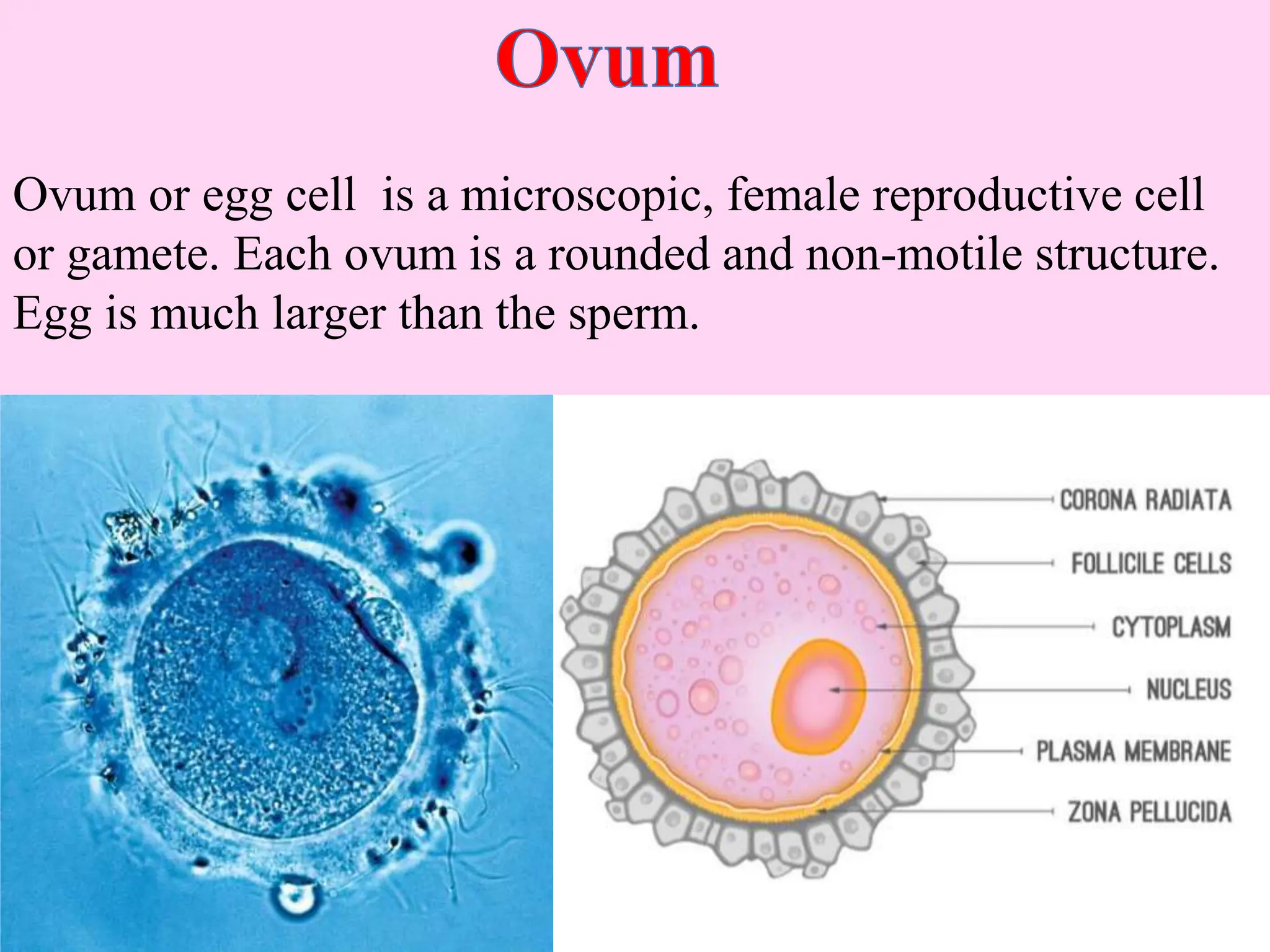
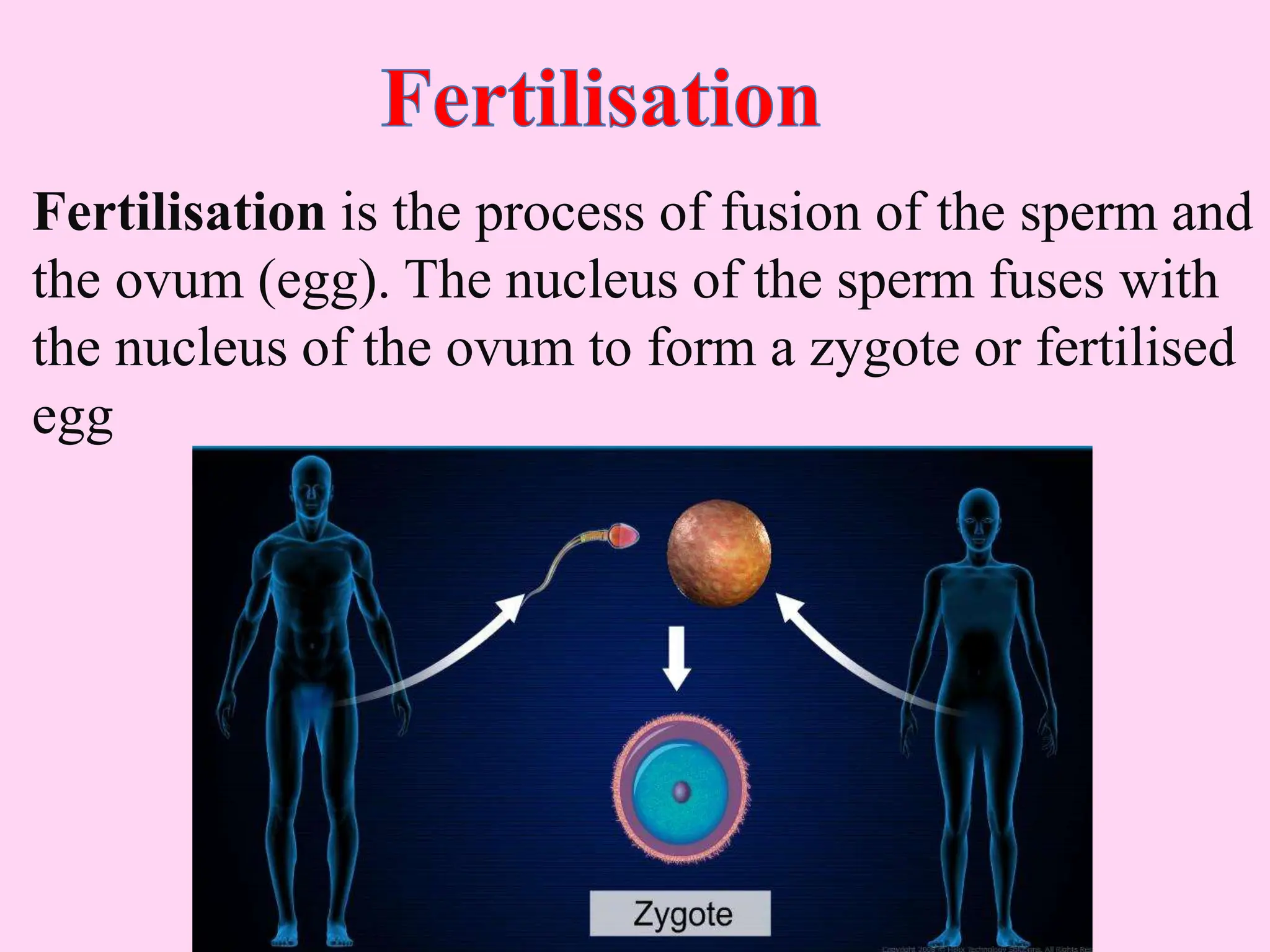
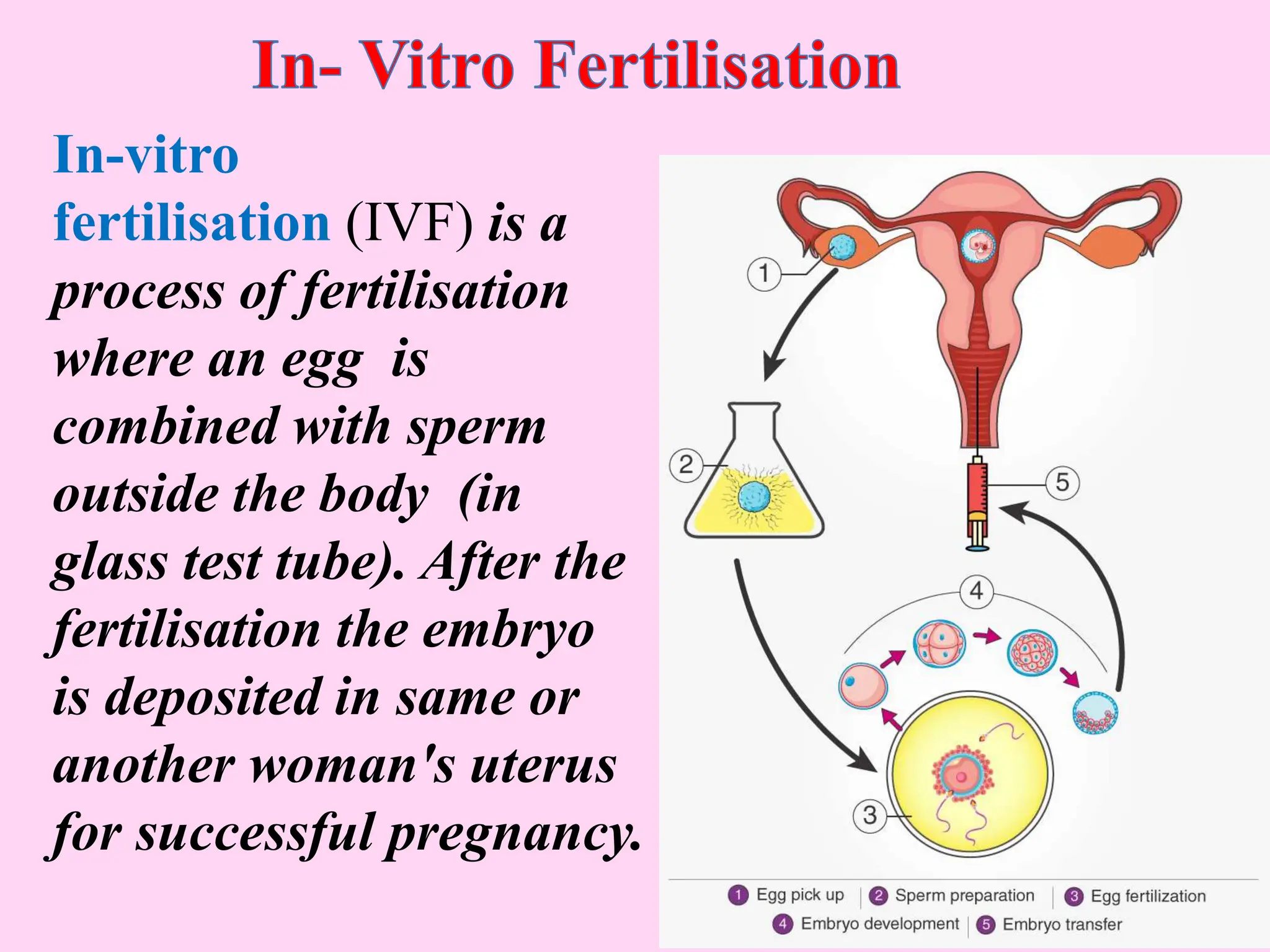
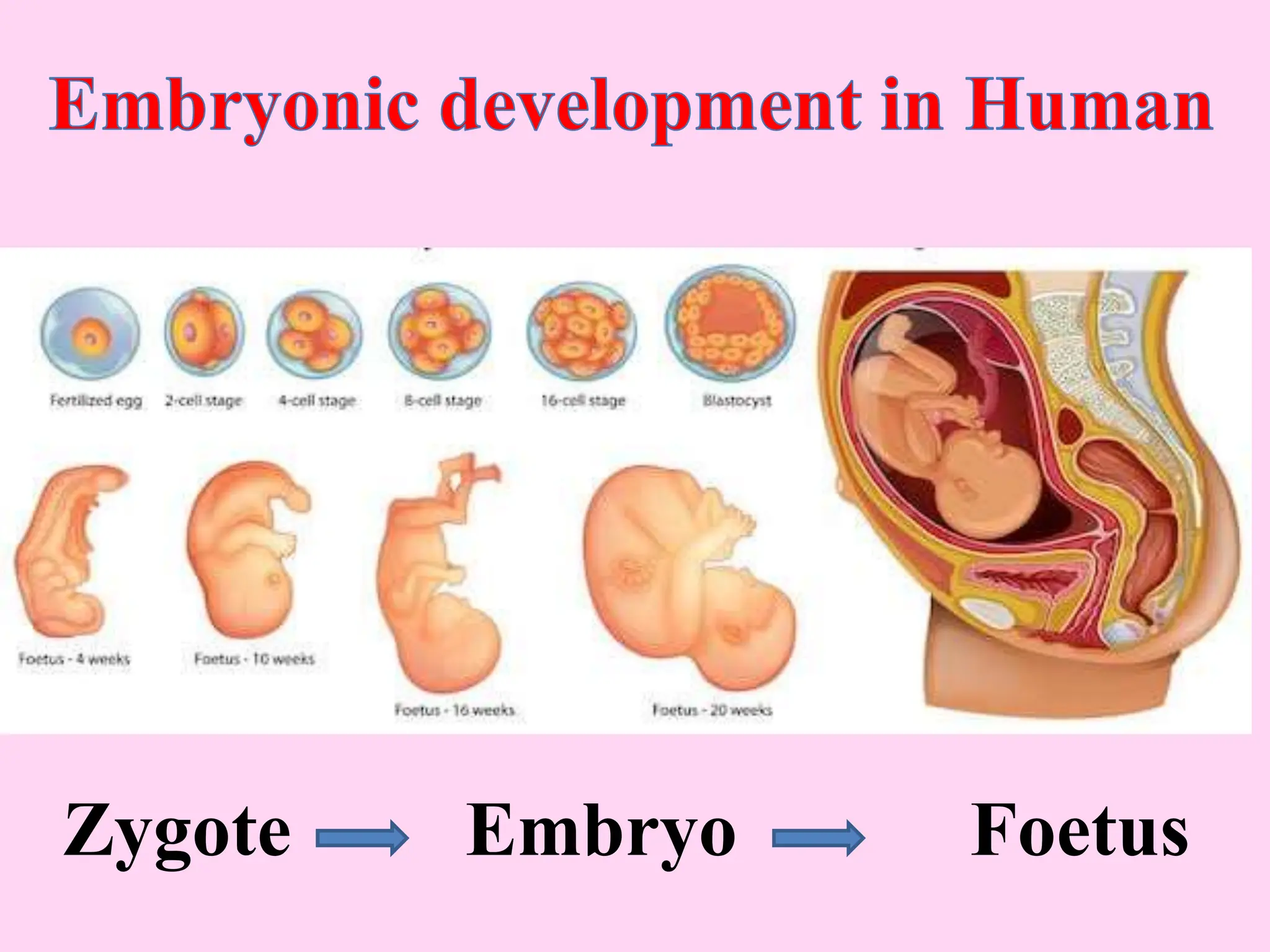
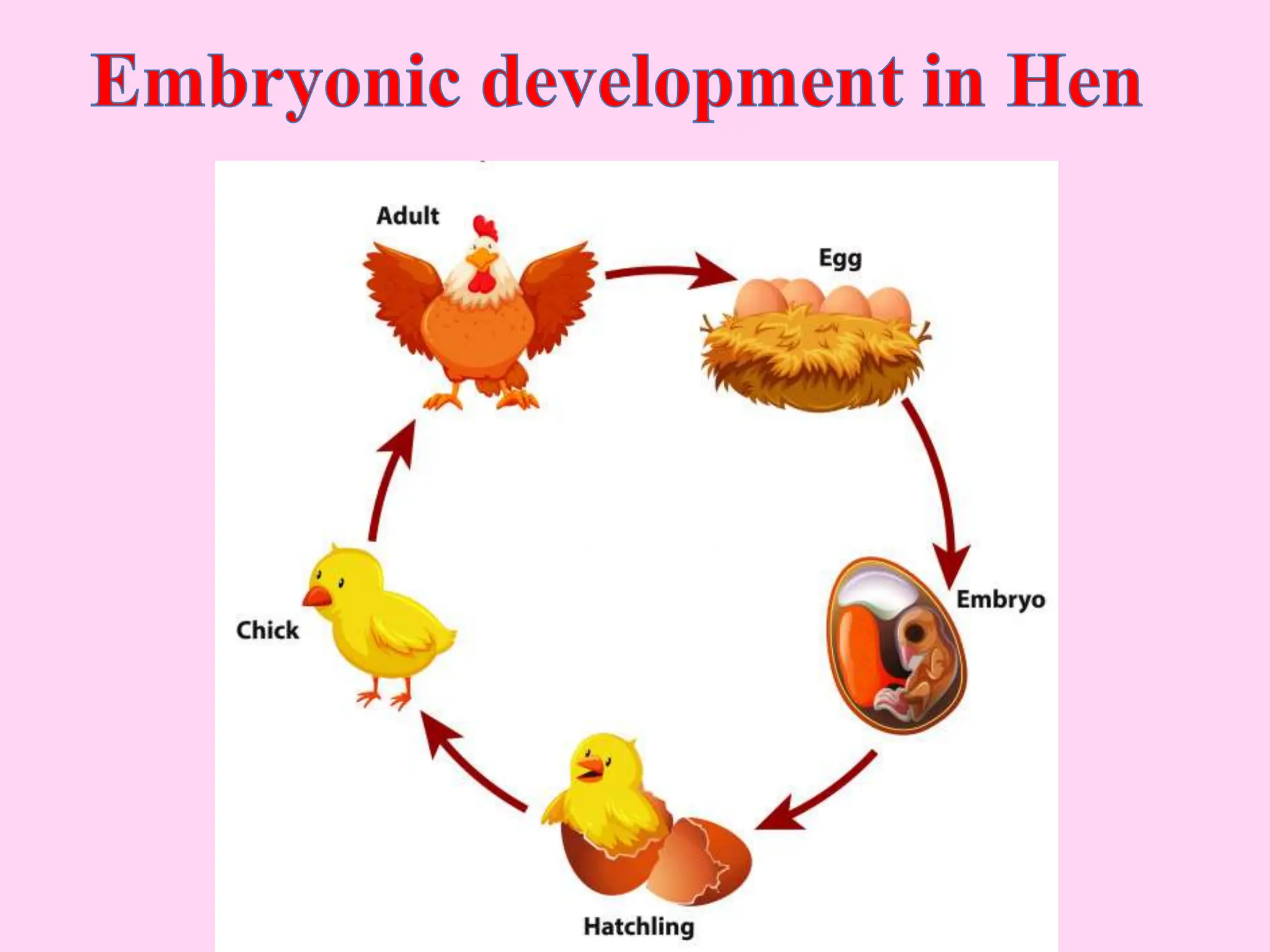
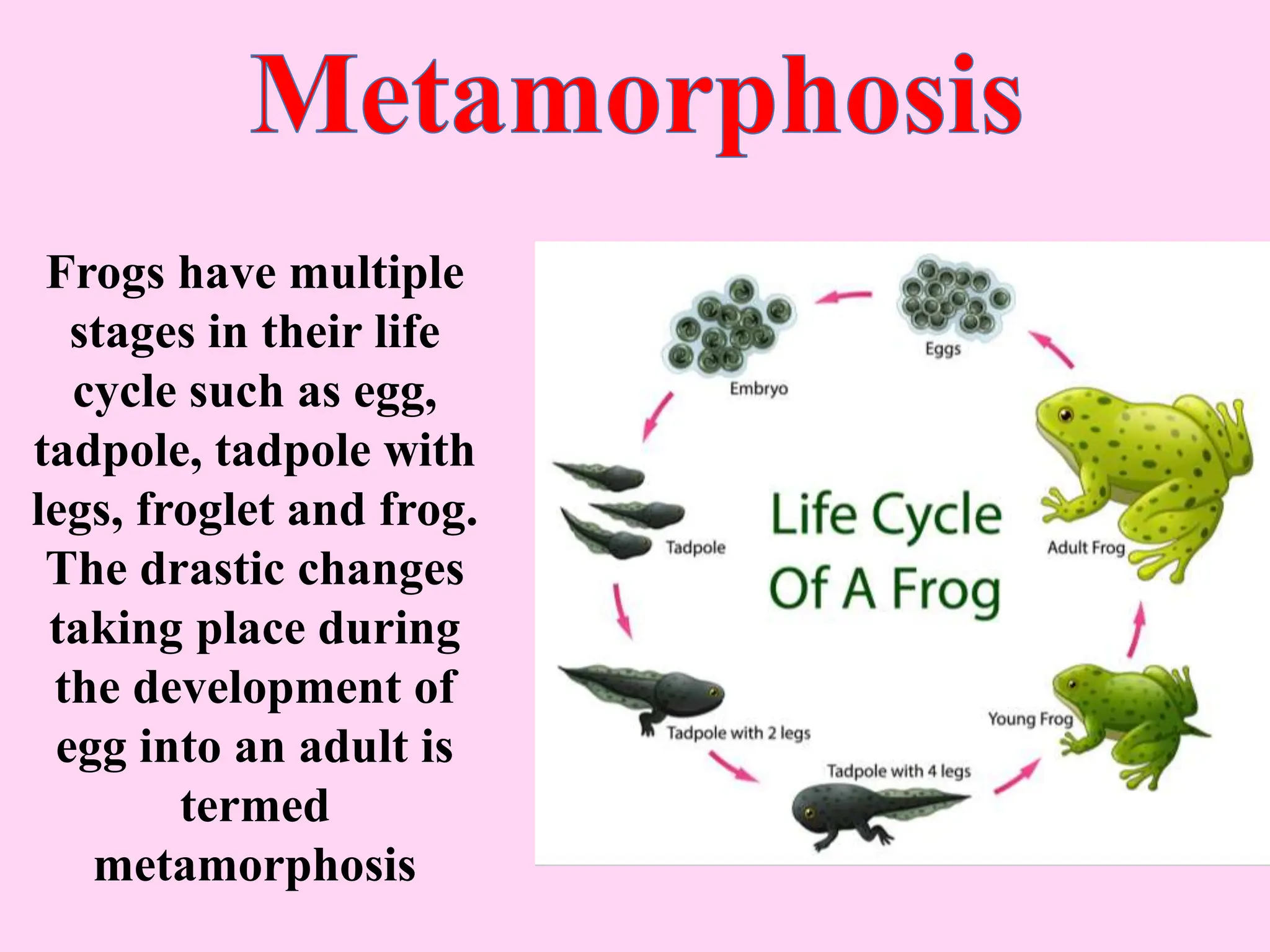
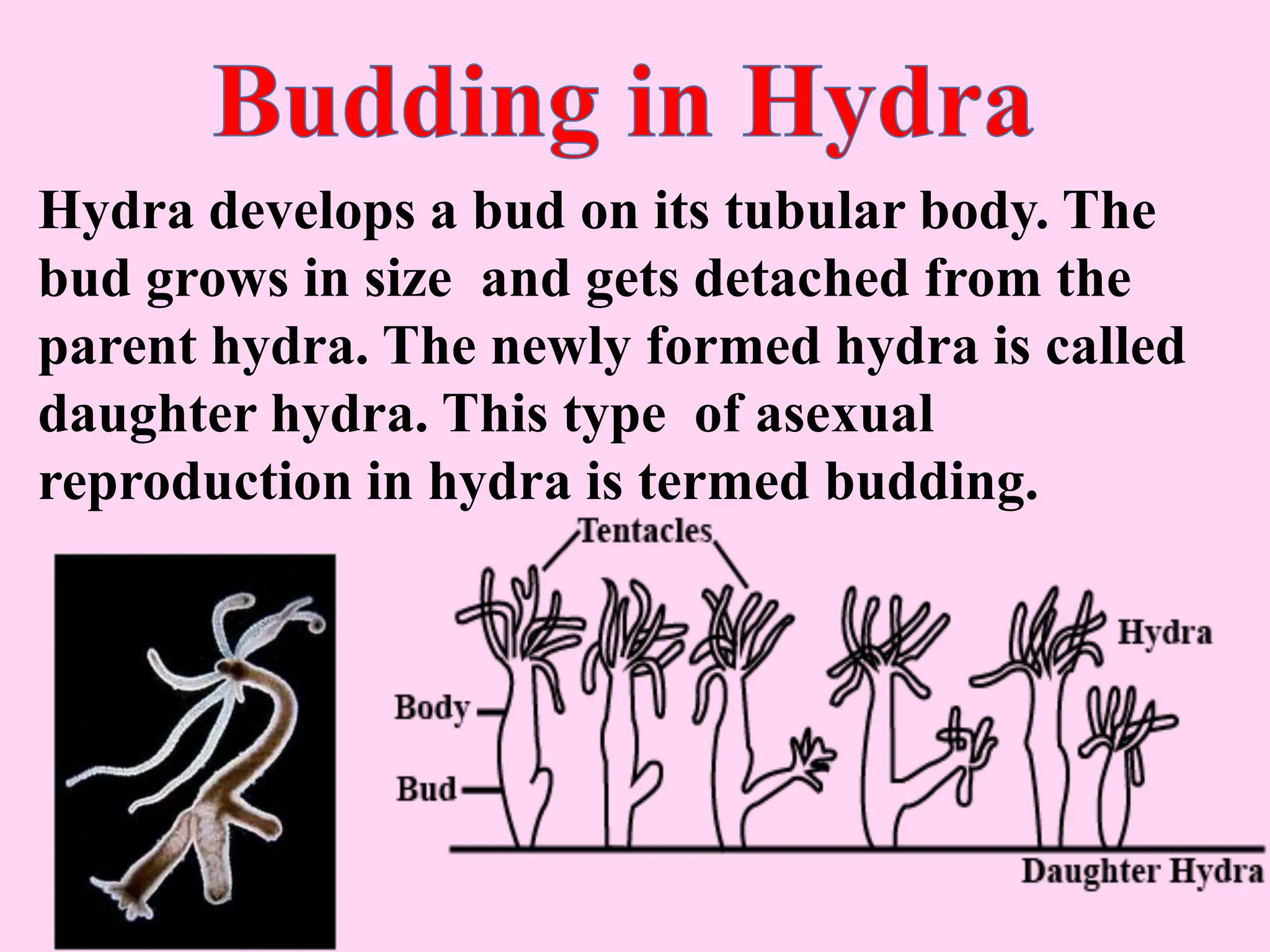
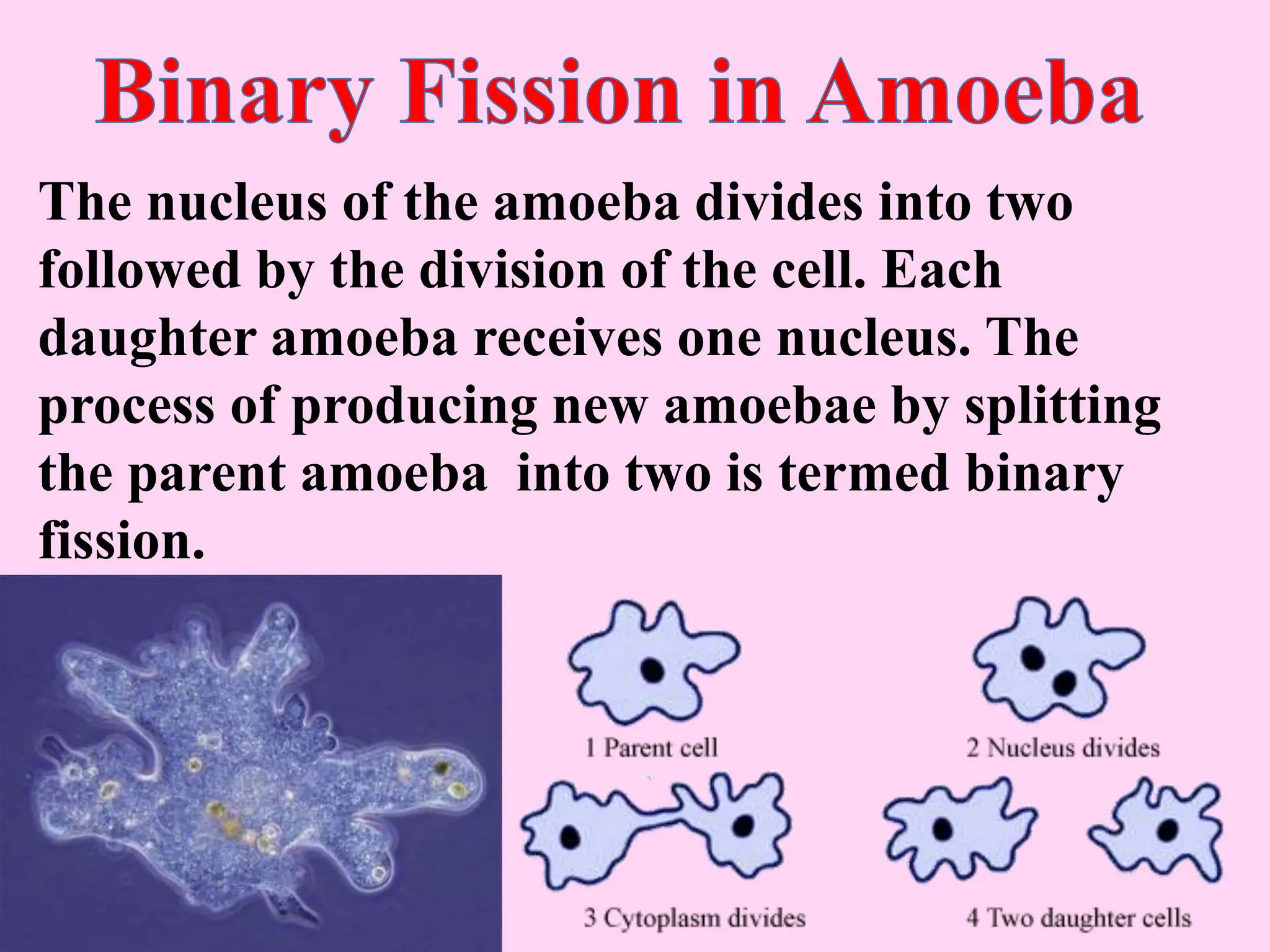
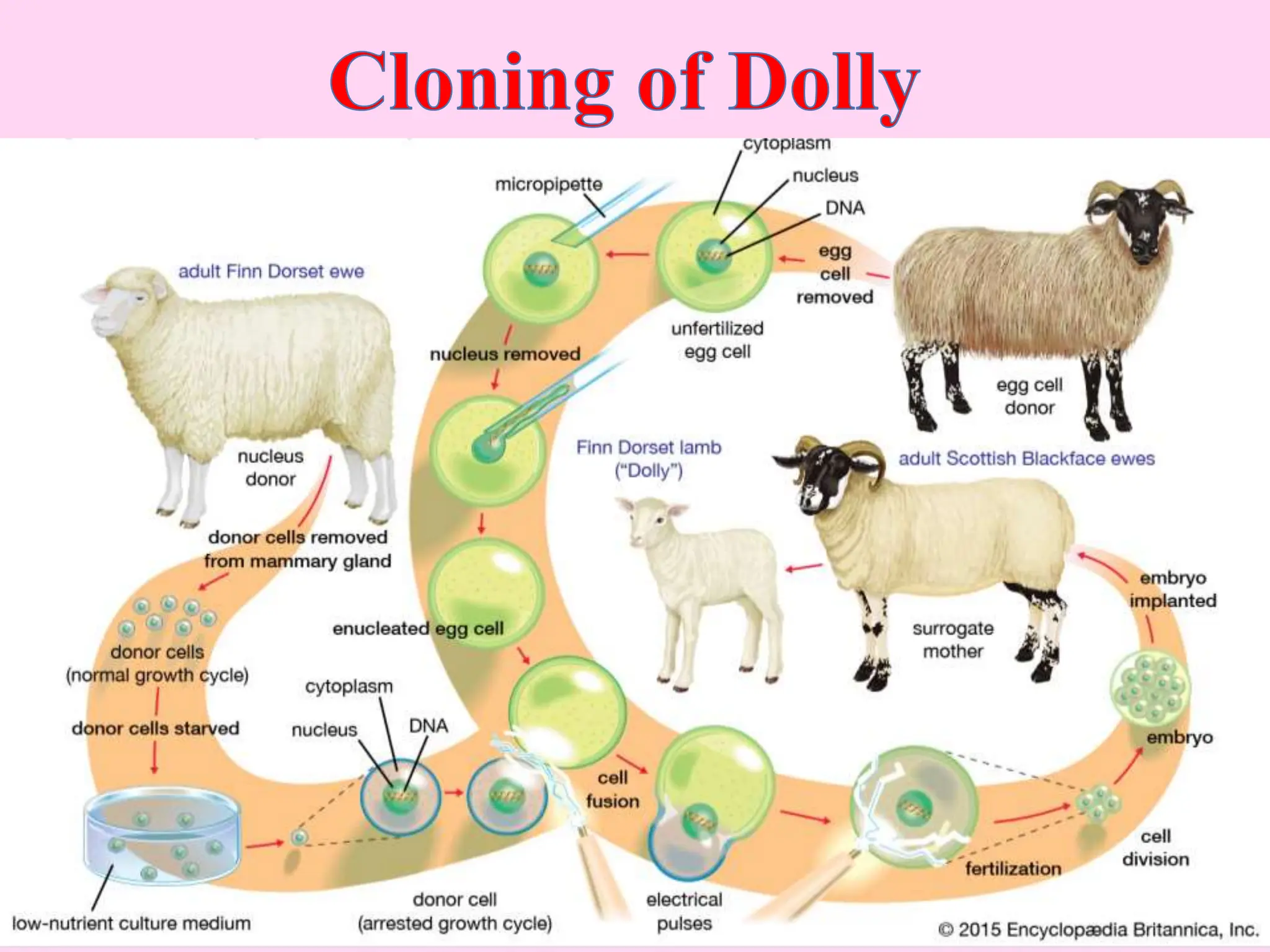
This document outlines key concepts around sexual and asexual reproduction that students will learn, including: differentiating between sexual and asexual reproduction; the male and female reproductive systems; internal and external fertilization; viviparous and oviparous animals; embryonic development; and examples of asexual reproduction like budding and binary fission. Students will learn these concepts through reading, drawing diagrams, observing frog development, and applying the knowledge in daily life.