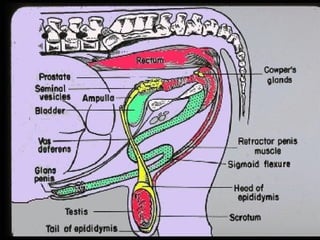
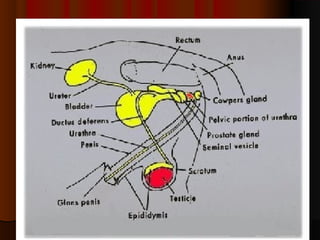
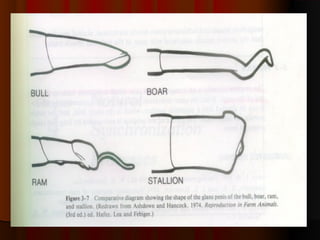
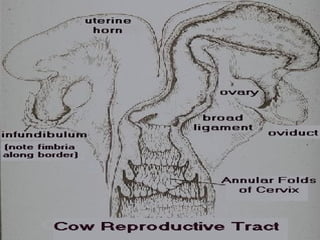
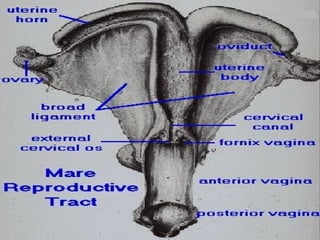
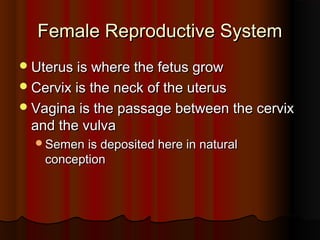
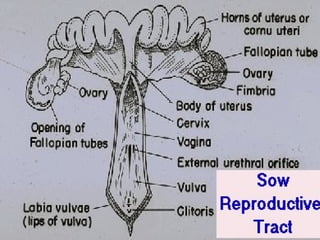
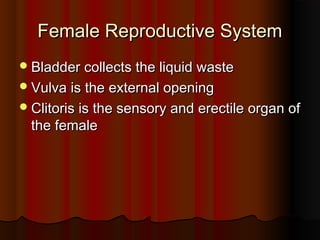
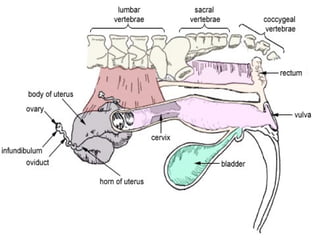
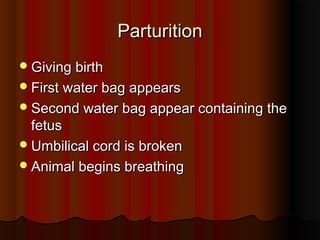
El documento detalla el proceso de reproducción animal, incluyendo la reproducción sexual y asexual, junto con la anatomía de los sistemas reproductivos masculino y femenino en diversas especies. Se abordan aspectos como la ovulación, la fertilización, el embarazo y el parto, así como los ciclos de celo en diferentes animales, y la producción de esperma y hormonas. También se menciona la importancia de ciertas condiciones y características, como la criptorchidismo, en la fertilidad animal.