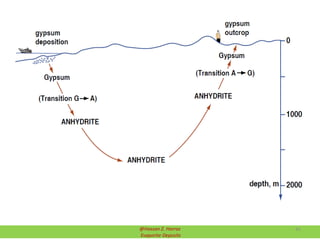
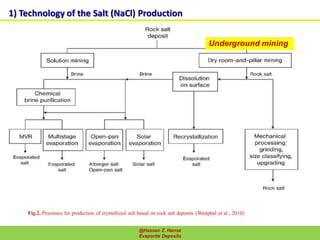
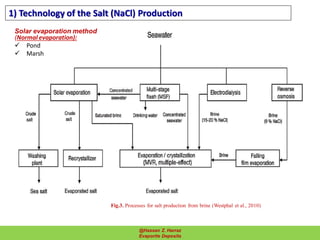
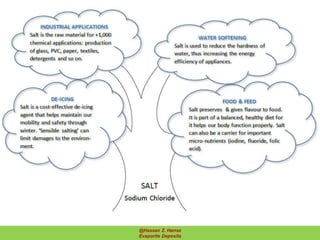
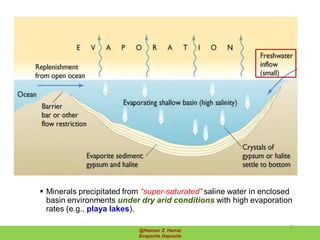
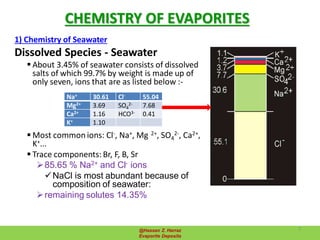
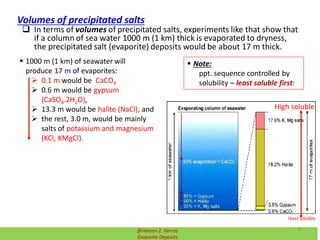
Evaporite deposits are mineral sediments that form from saline solutions through evaporation, primarily in arid environments. These deposits serve as indicators of paleoclimate and are formed mainly from sea-water, with significant occurrences from the Permian and Miocene periods, displaying varying mineral compositions. Production methods include surface, underground, and solution mining, and they have important economic significance due to their mineral content, including potassium and magnesium salts.

















![Order of precipitation of common compounds in Continental waters
(saline lakes) and Inland Brine Lakes evaporation:
1) CaCO3 and MgCO3 are the 1st to precipitate
2) CaSO4 precipitates …. All calcium are precipitated ( Leaving mostly Na
and Mg cations)
3) NaCO3 are precipitated next as:
3.1) Borax (Na2B4O7·10H2O or Na2[B4O5(OH)4]·8H2O)
3.2) Borates
3.3) Nitrates
3.4) Natron (Na2CO2.10H2O)
3.5) Trona (NaHCO3.Na2CO3.2H2O)
4) NaSO4 are precipitated
5) MgSO4 and Epsomite/ Epsom salts (MgSO4.7H2O) precipitated ….. left
NaCl
6) NaCl saltern is left. These are fairly common (Great Salt Lake)
7) MgCl2 and CaCl2 lakes are precipitated
Precipitationsequence
EVAPORATION SEQUENCE OF CONTINENTAL WATERS (Saline Lakes)
@Hassan Z. Harraz
Evaporite Deposits
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evaporitedeposits-181024102428/85/Evaporite-deposits-23-320.jpg)












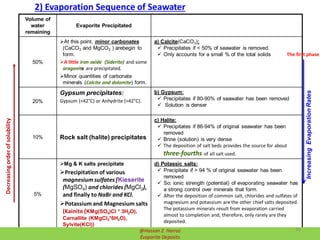
![Lakes Seawater
1) CalciteCaCO3 and Magnesite (MgCO3 ) 1) Calcite(CaCO3) and Dolomite (CaMg(CO3 )2
2) CaSO4 precipitates next. 2) Gypsum:
Gypsum precipitates:
Gypsum (<42°C) or Anhydrite (>42°C).
3) NaCO3 precipitates next as:
3.1) Borax (Na2B4O7·10H2O or
Na2[B4O5(OH)4]·8H2O)
3.2) Borates
3.3) Nitrates
3.4) Natron (Na2CO2.10H2O)
3.5) Trona (NaHCO3.Na2CO3.2H2O)
4) NaSO4 precipitates
5) MgSO4 and Epsomite/ Epsom salts
(MgSO4.7H2O) precipitates
3) Halite:
Precipitates if 86-94% of original seawater
has been removed
Brine (solution) is very dense
6) NaCl saltern is left. These are fairly
common (Great Salt Lake)
7) MgCl2 and CaCl2 are precipitates
4) Potassic salts:
Precipitate if > 94 % of original seawater
has been removed
So: ionic strength (potential) of
evaporating seawater has a strong control
over minerals that form
Compared between Evaporation Sequence of Seawater and Lakes
IncreasingEvaporationRates
Decreasingorderofsolubility
The
first
phase
@Hassan Z. Harraz Evaporite Deposits 38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evaporitedeposits-181024102428/85/Evaporite-deposits-38-320.jpg)