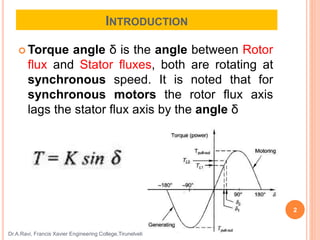
This document discusses synchronous motor drives and variable frequency control methods. Synchronous motors have higher efficiency than induction motors but are generally more expensive. Variable frequency control can be done through true synchronous mode using an open-loop system or self-controlled mode using a closed-loop system. Methods like V/F control, margin angle control, and power factor control are explored. Voltage source inverters and current source inverters are also discussed for feeding synchronous motors.