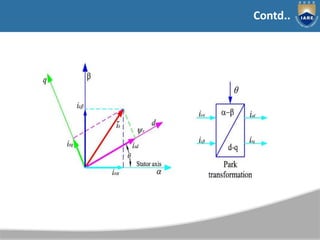
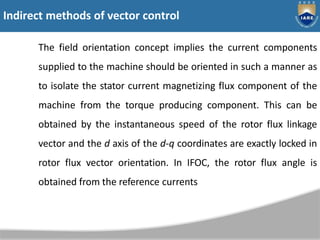
The document discusses various methods of speed control for induction motors, including rotor resistance control. Rotor resistance control involves connecting a variable external resistance to the rotor circuit of a wound rotor induction motor to control its speed. This is done by varying the effective rotor resistance using a chopper. The torque-speed characteristics show that increasing rotor resistance increases slip and reduces motor speed at constant torque. However, rotor resistance control is not suitable for squirrel cage motors and has low efficiency due to losses in the external resistance.