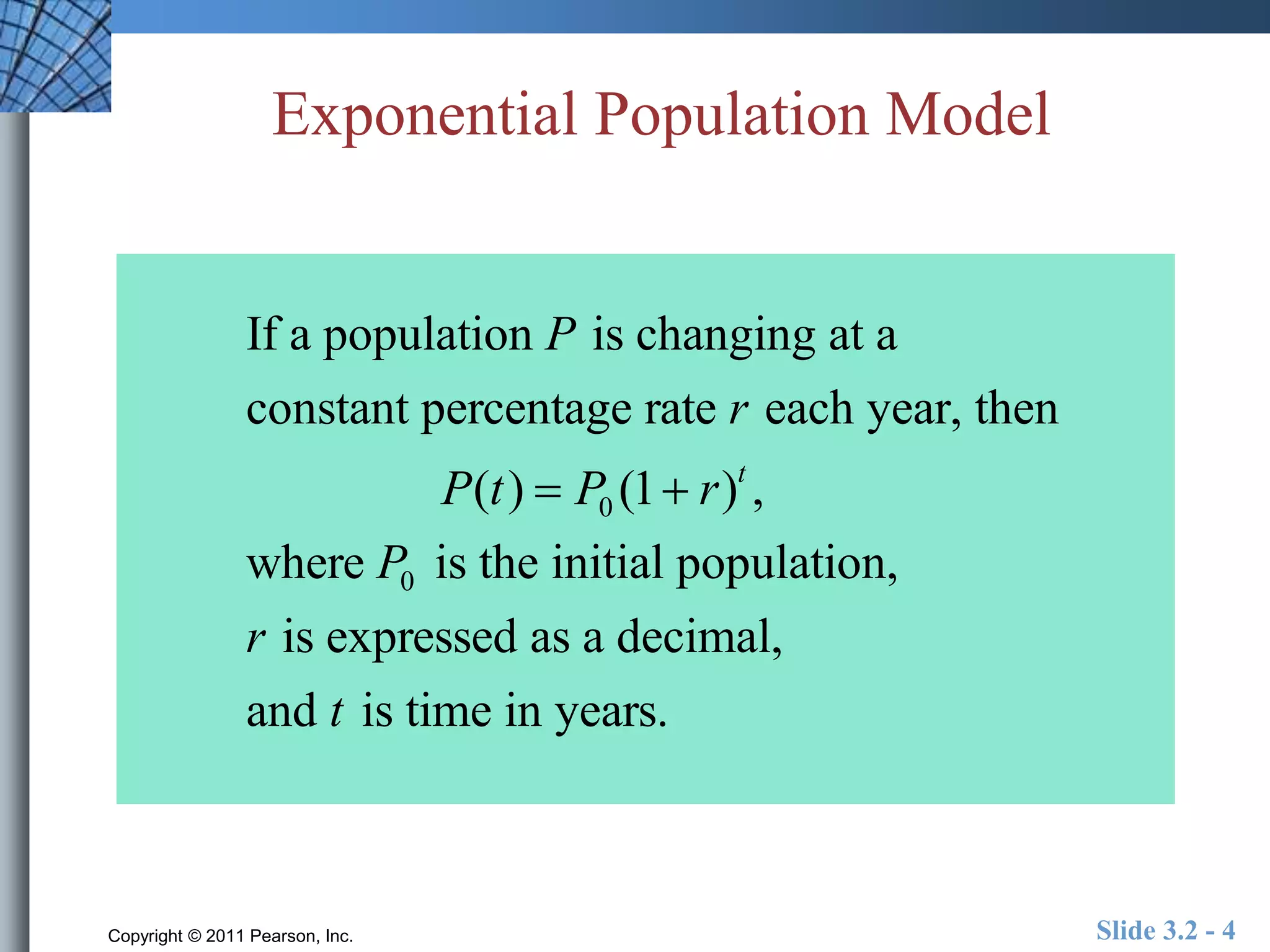
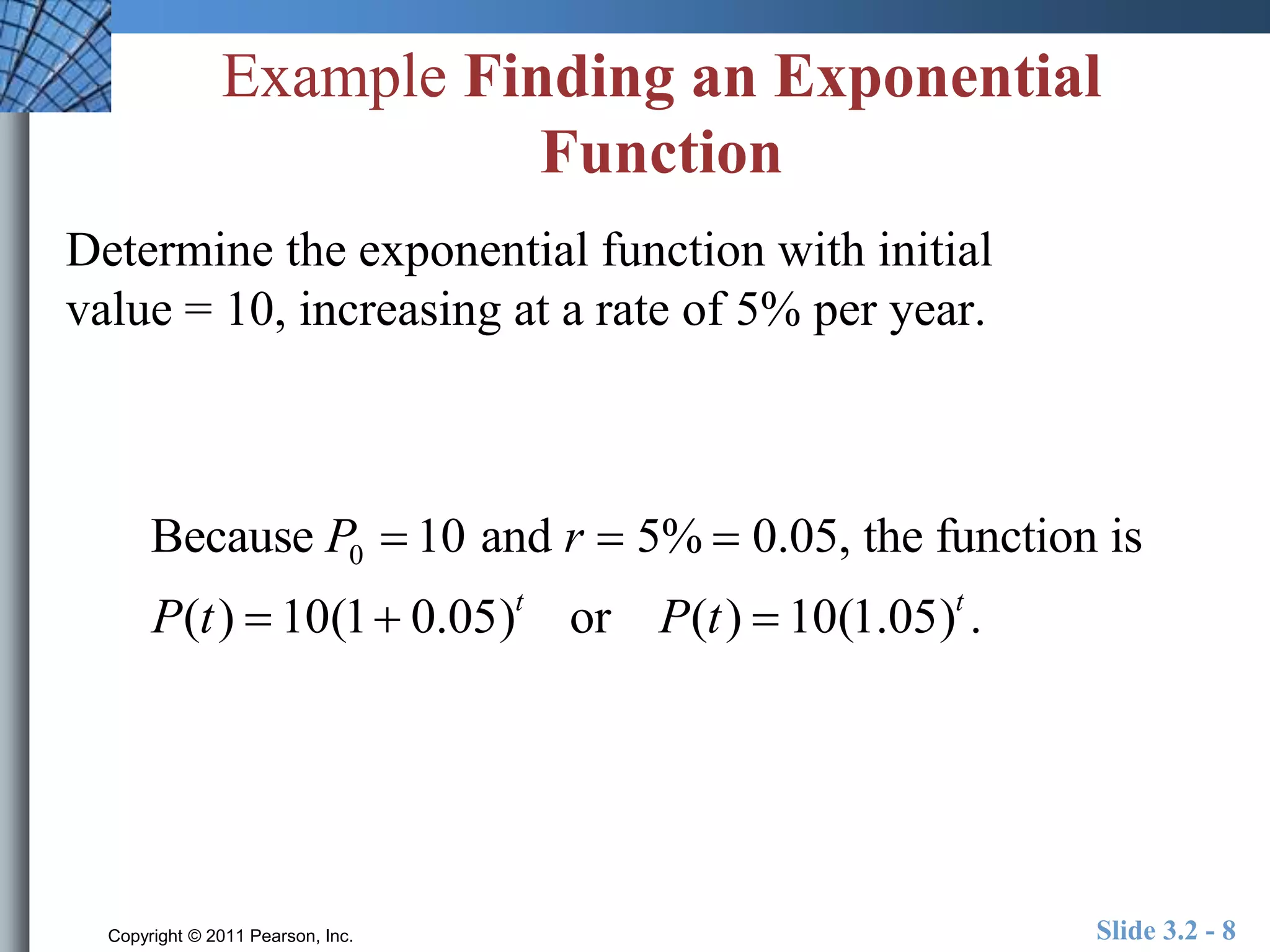
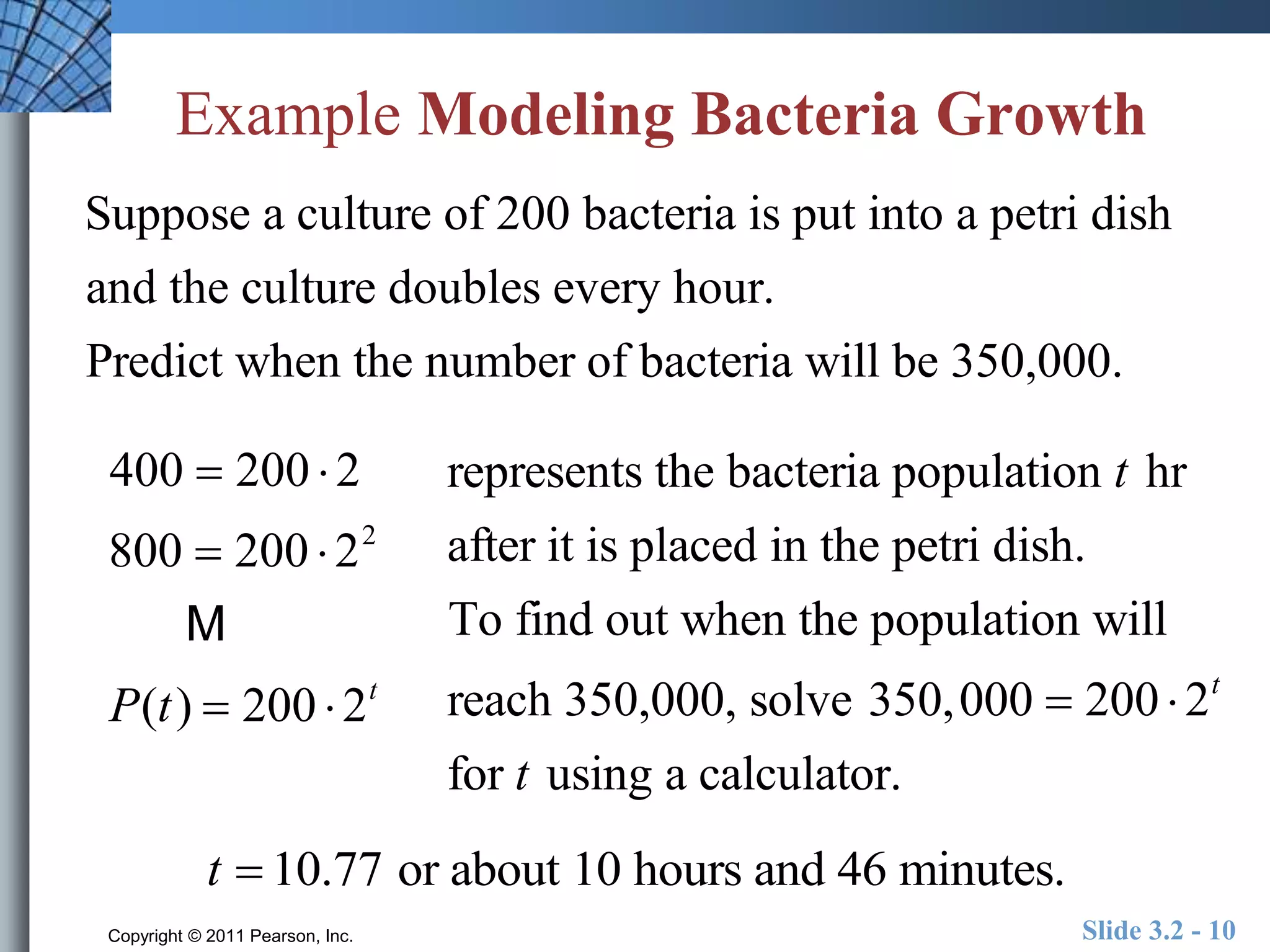
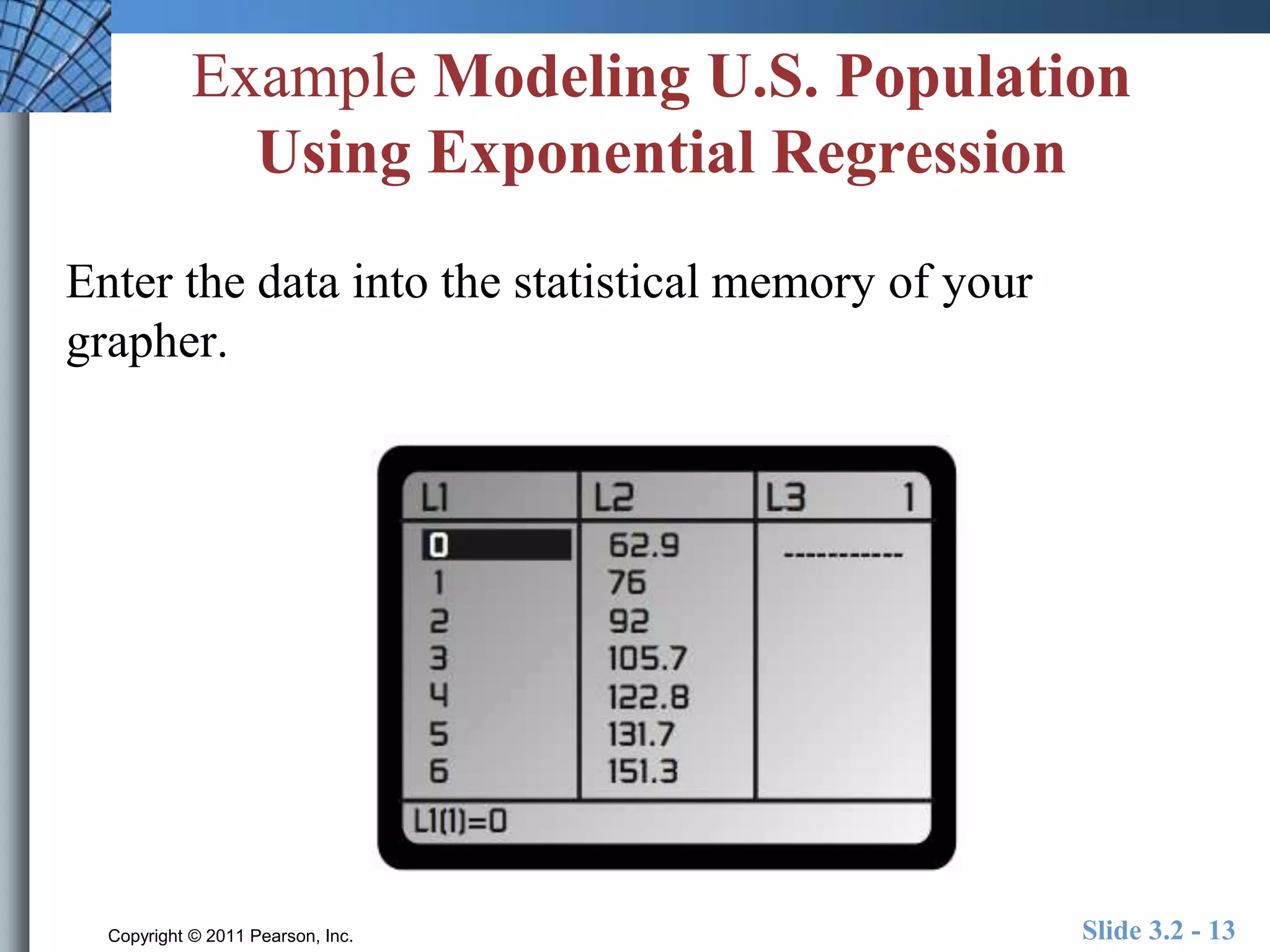
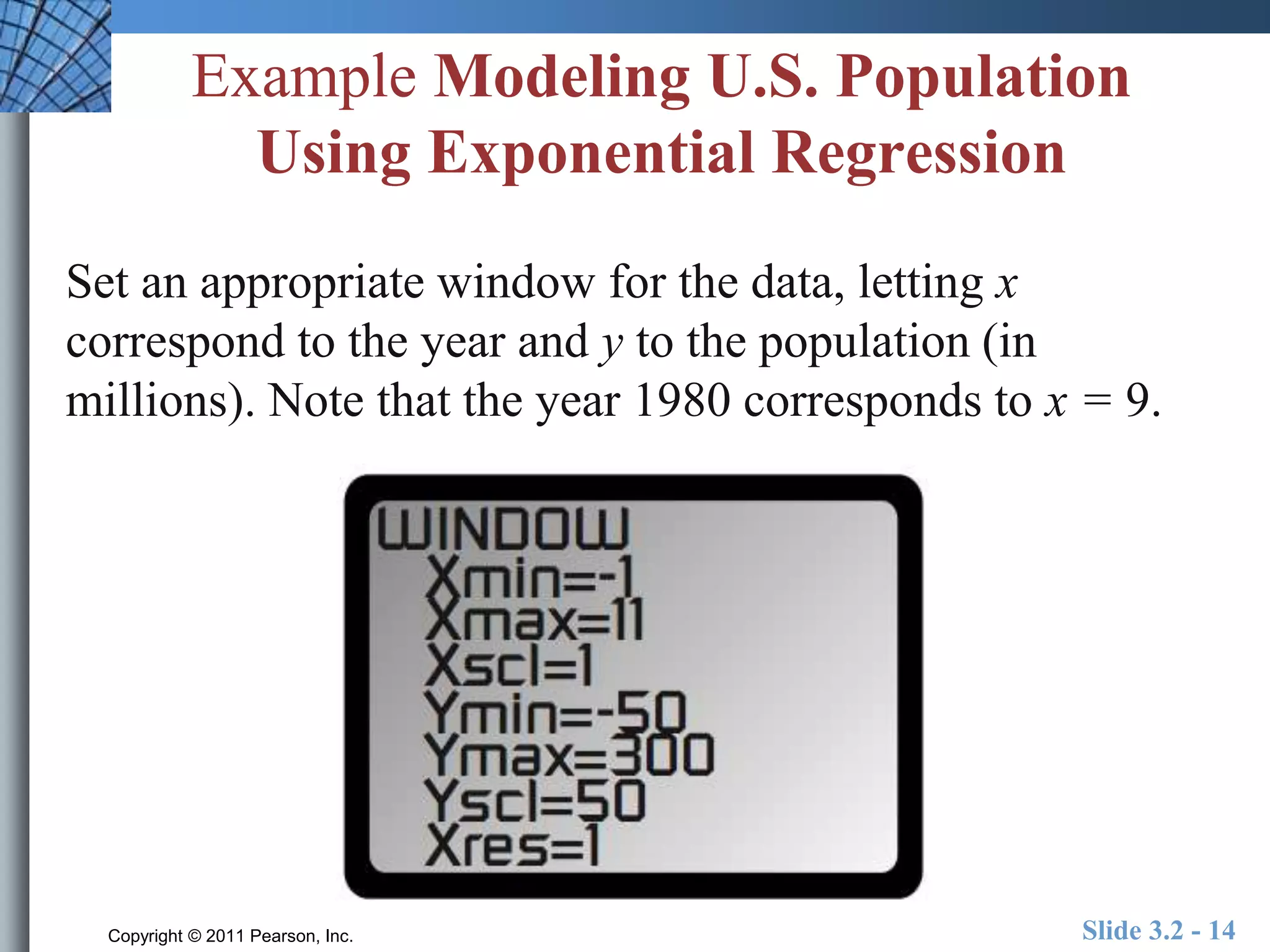
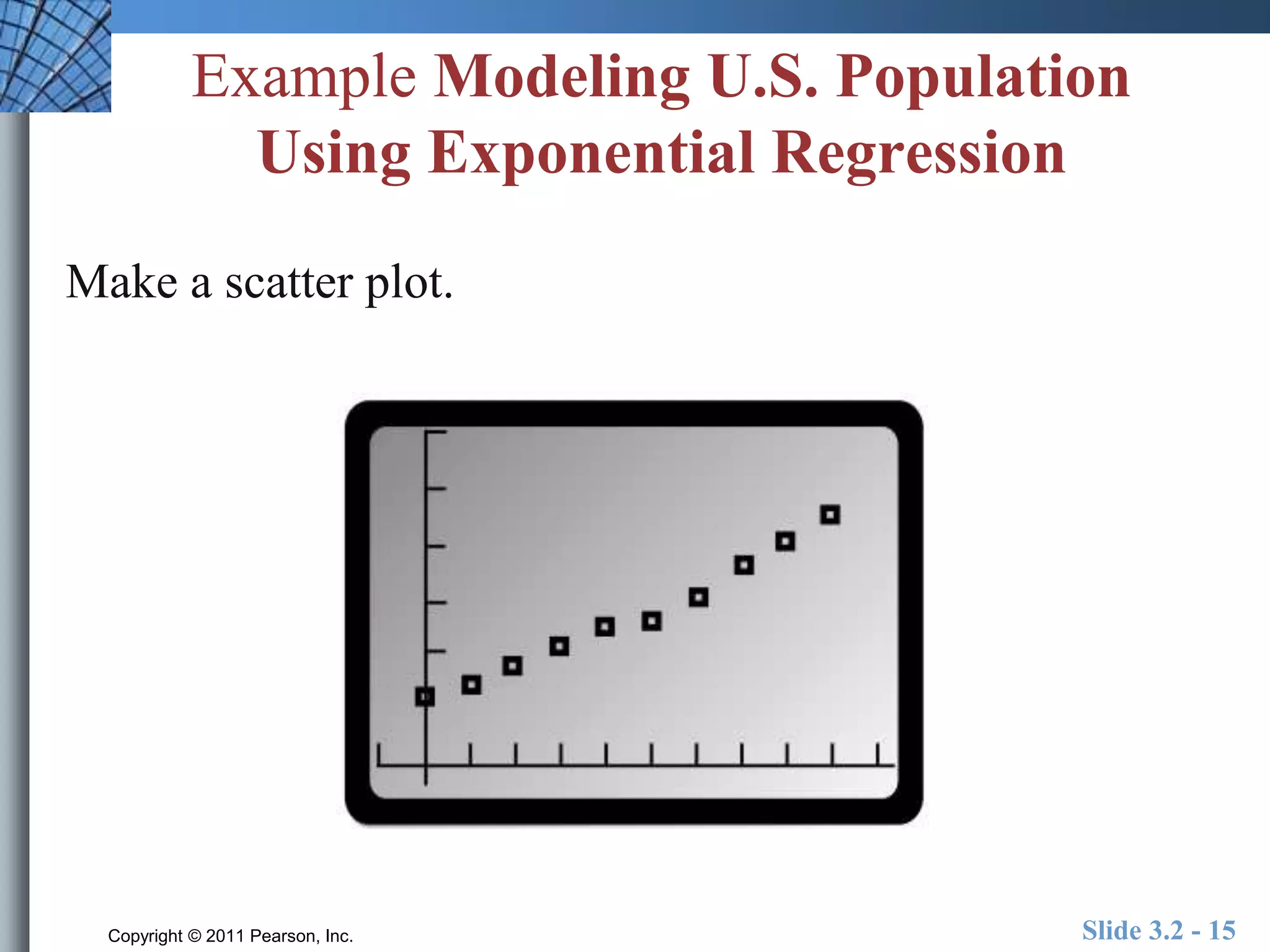
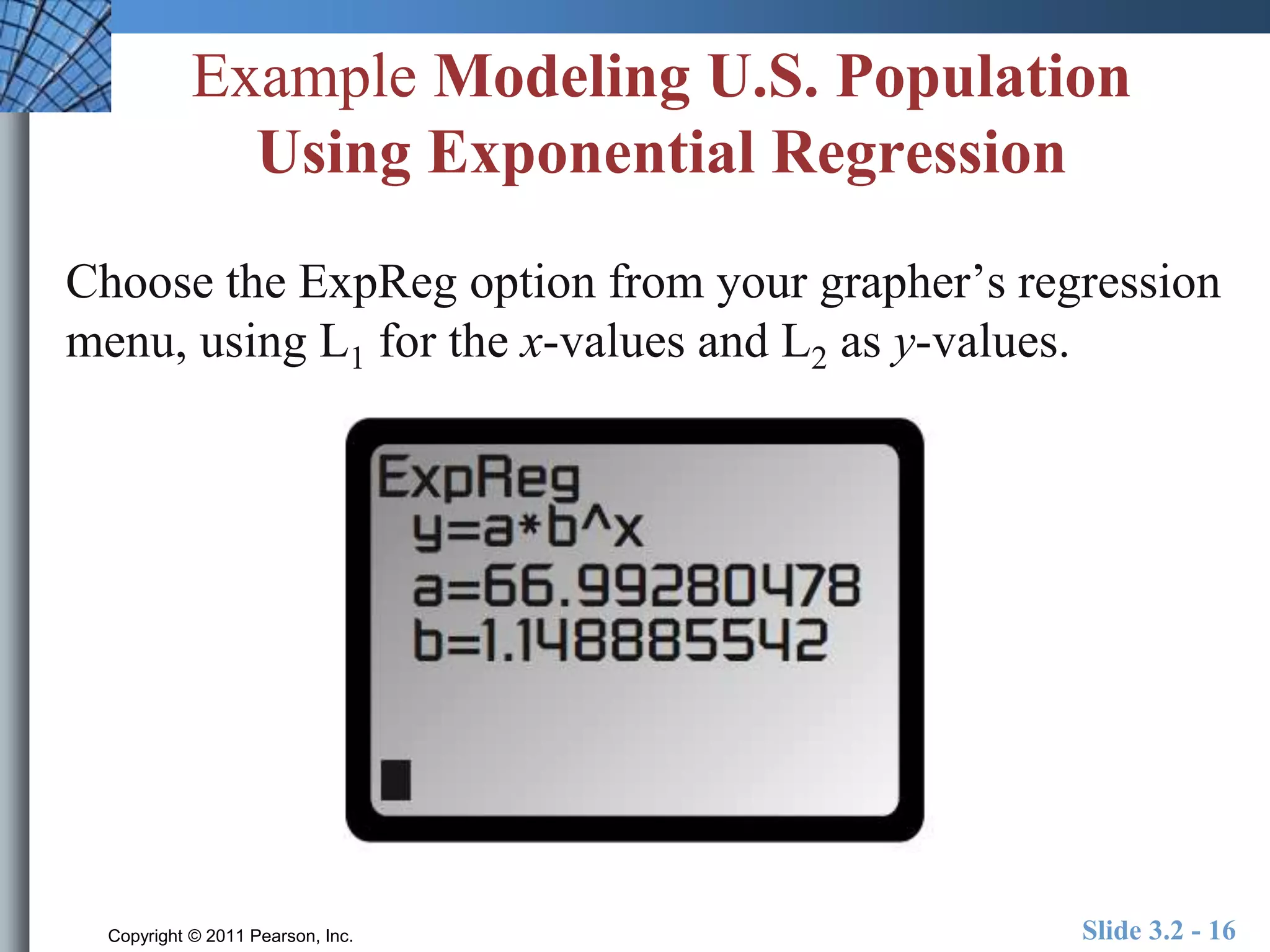
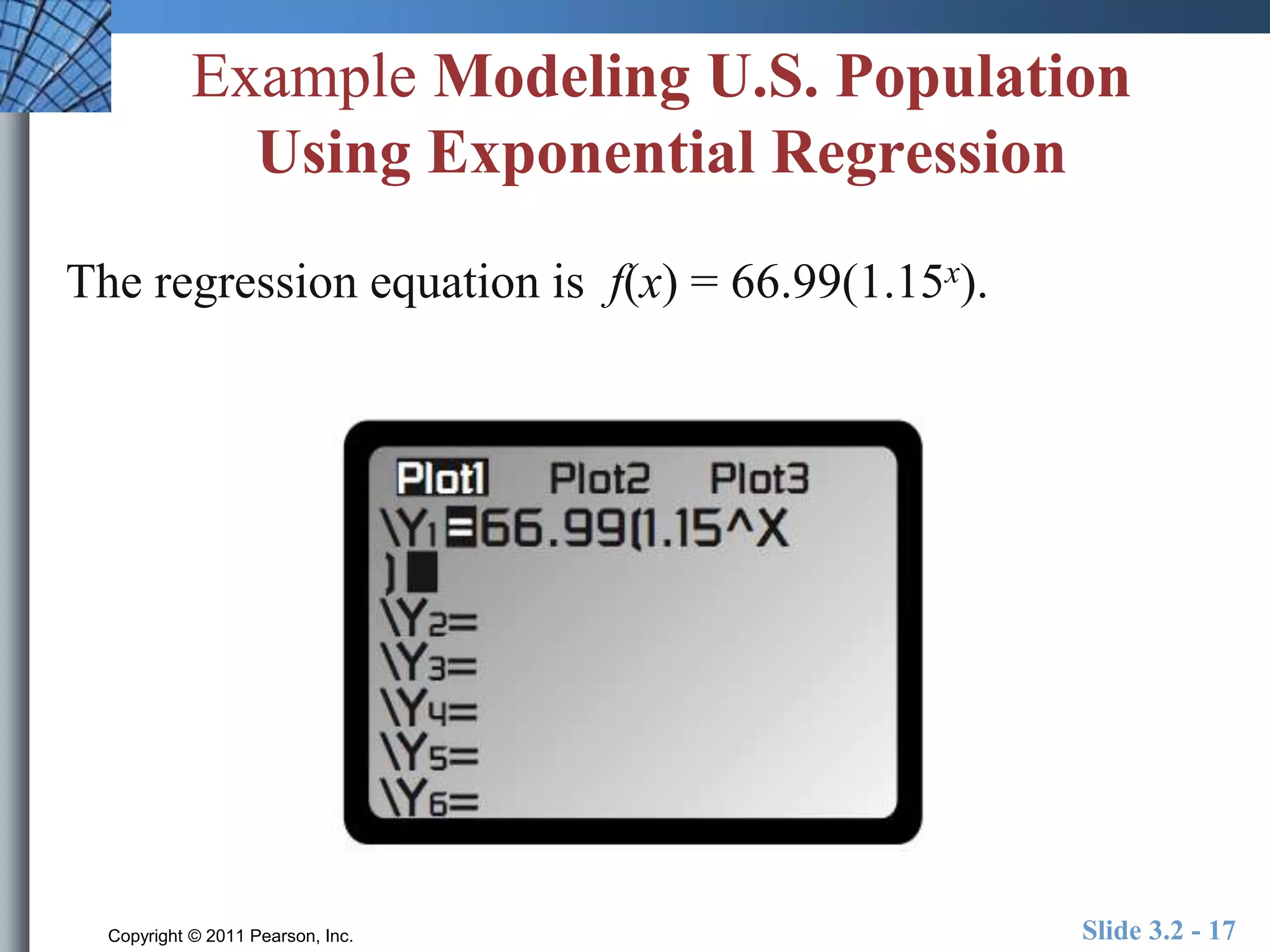
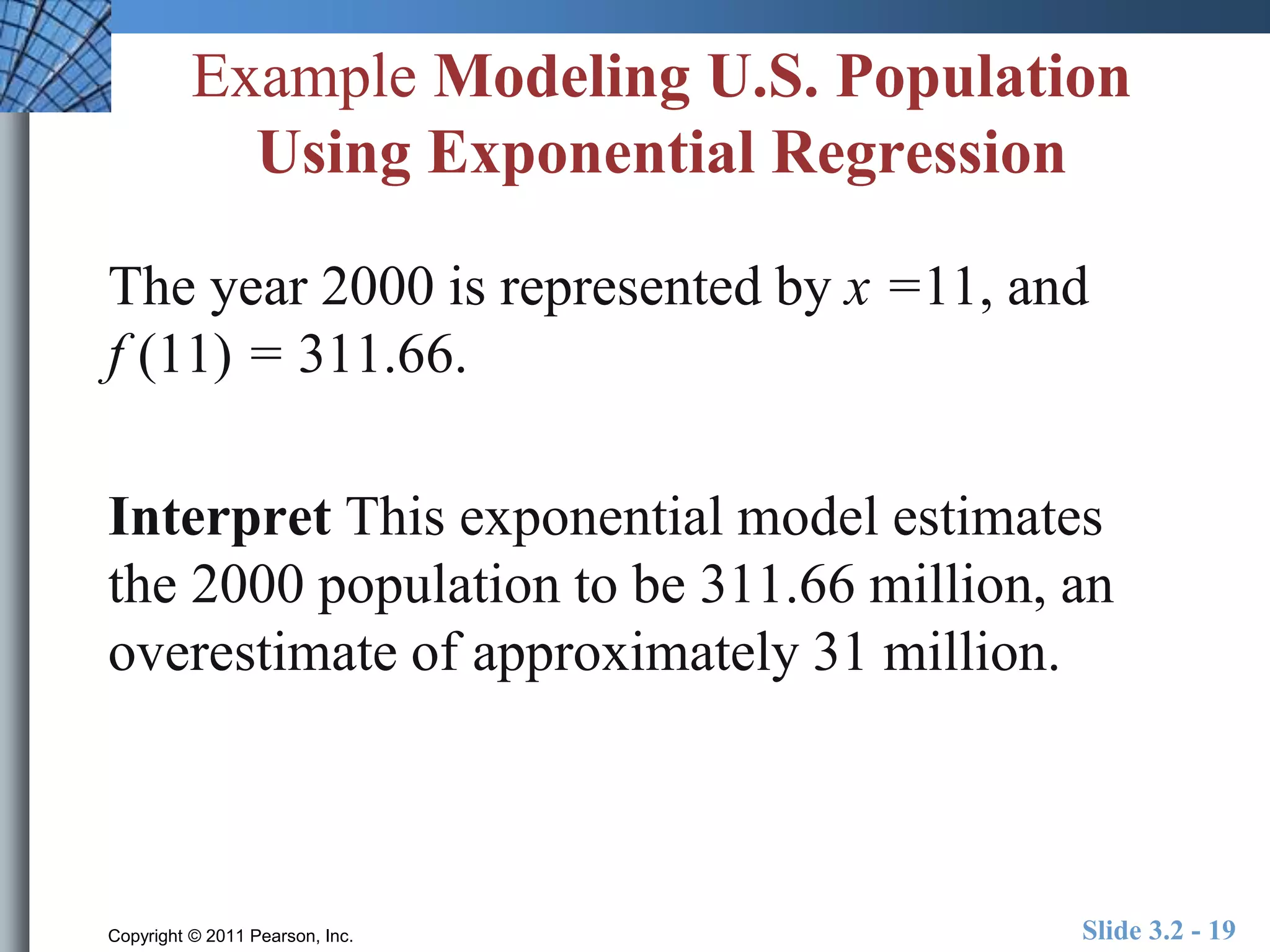
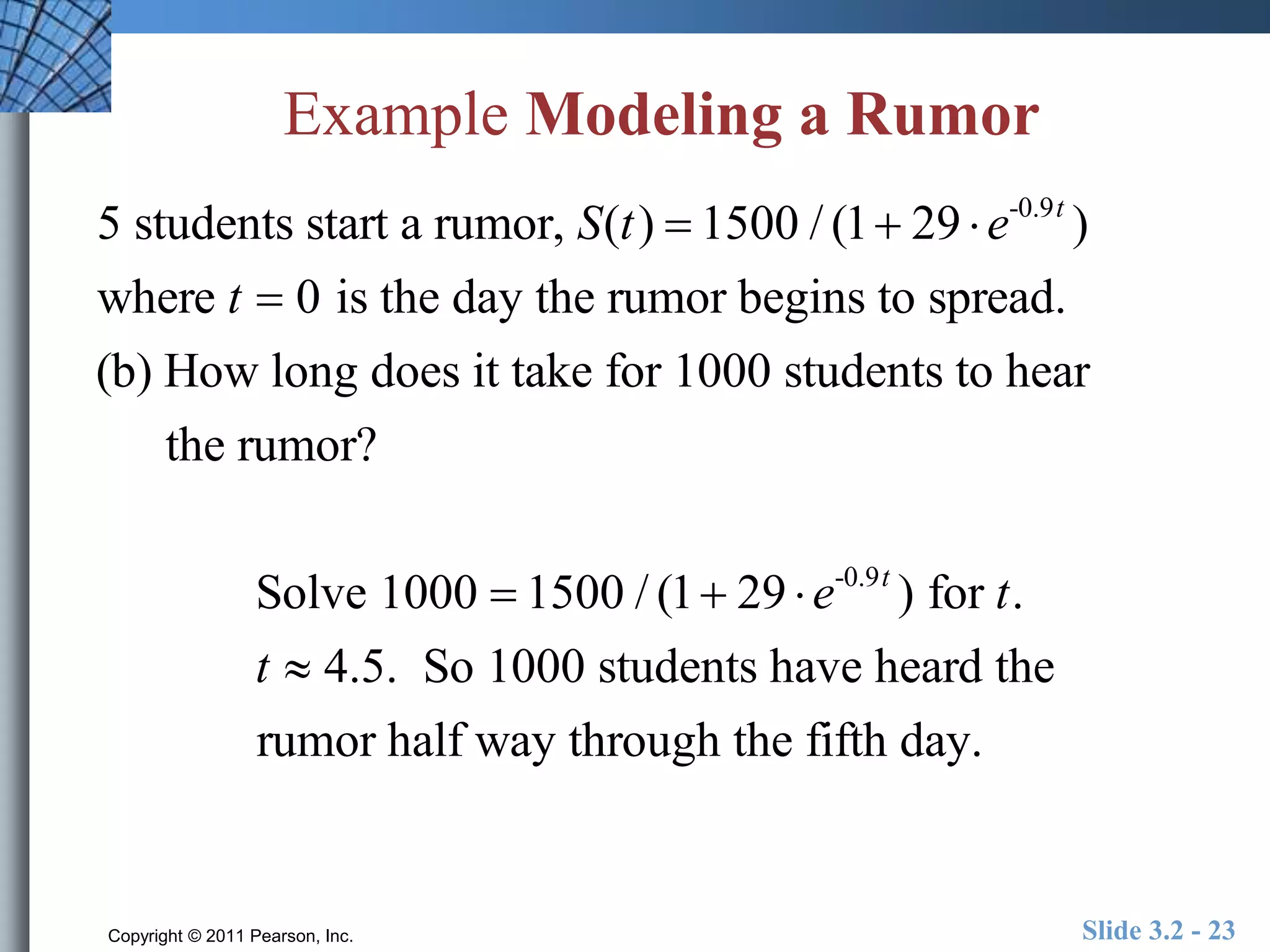
This document discusses exponential and logistic modeling. Exponential functions can model unrestricted growth, while logistic functions model restricted growth like disease spread. Constant percentage rate and exponential population models are presented. Examples show determining growth rates from functions, modeling bacteria growth, and using regression to model US population growth exponentially over time. Logistic modeling is also discussed through an example of modeling rumor spread through a school.