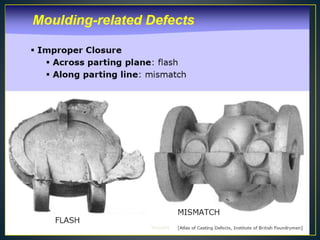
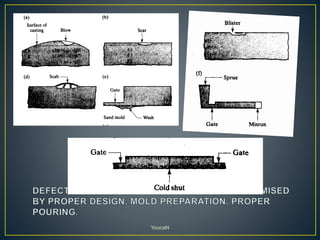
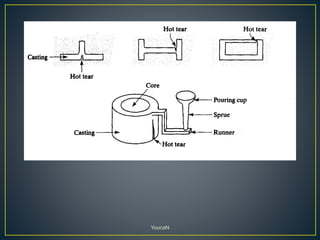
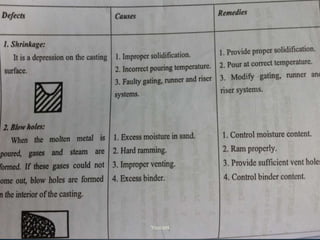
The document discusses various casting defects such as blows, blisters, scars, washes, cuts, sinks, shrinkage cavities, pinholes, blowholes, hot tears, and misruns. Blows are large cavities caused by gases displacing molten metal, while blisters are shallow blows covered by a thin layer of metal. Washes are low projections on drag faces that decrease in height. Pinholes and blowholes are small gas pockets on or just below casting surfaces. Hot tears are cracks from stresses during solidification. Misruns occur when cavities are incompletely filled.