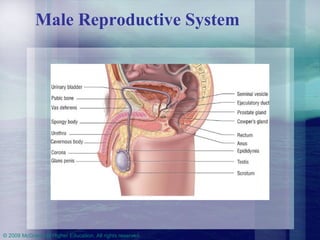
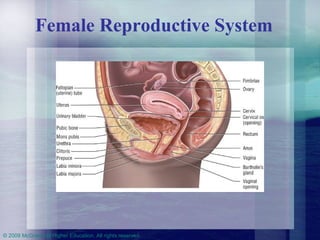
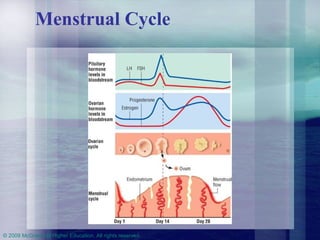
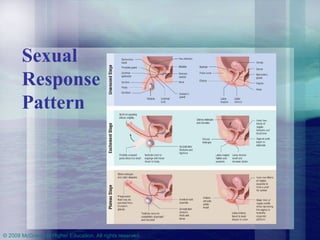
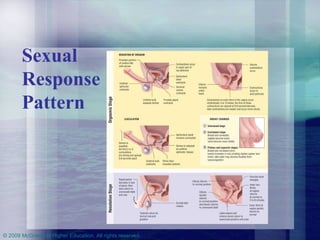
This chapter discusses the biological and psychosocial bases of human sexuality. It covers topics like genetic and gonadal development of sex, puberty, gender identity, male and female reproductive anatomy and functions, the human sexual response pattern, orientations, and healthy relationships. It provides information about sexuality across the lifespan from childhood to aging.