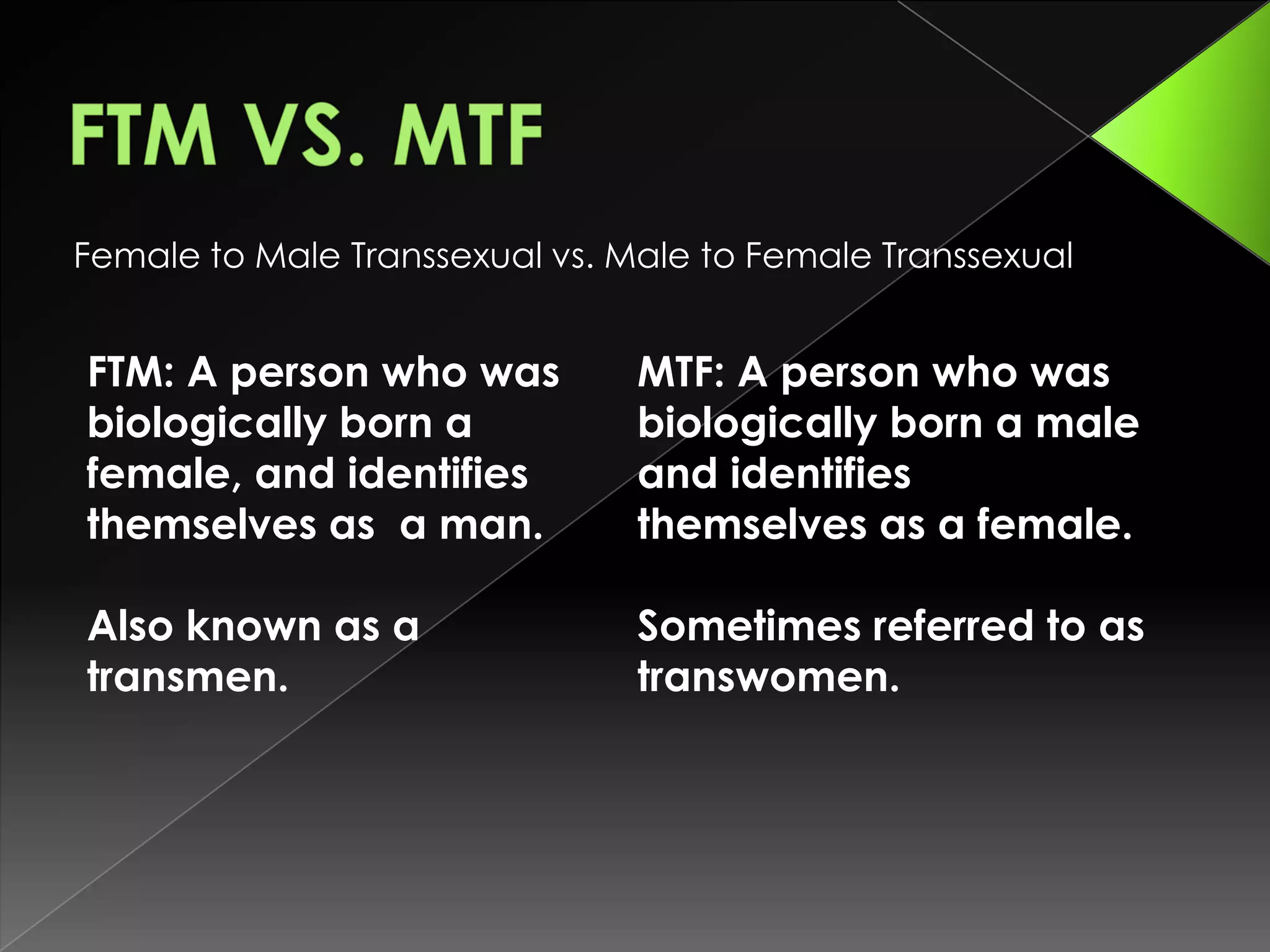
Sex, gender identity, and gender expression can exist on spectrums that are different than traditional norms. Gender identity refers to one's internal sense of self as male, female, both, or neither, which may or may not correspond to their sex assigned at birth. There are many terms used to describe various gender identities including transgender, transsexual, genderqueer, and more which challenge societal expectations of gender roles and expressions.