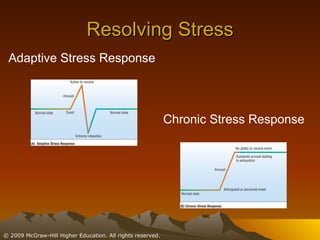
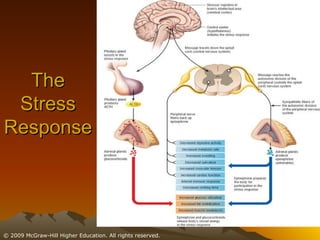
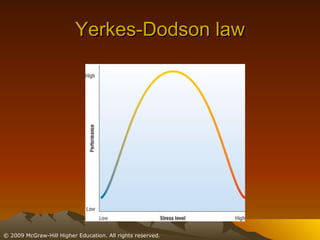
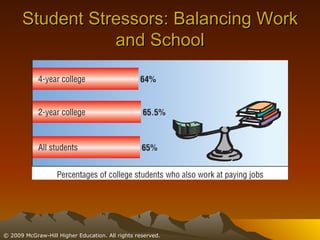
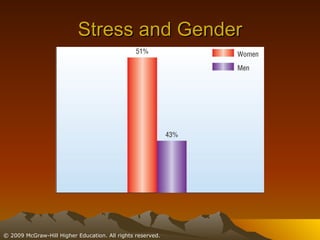
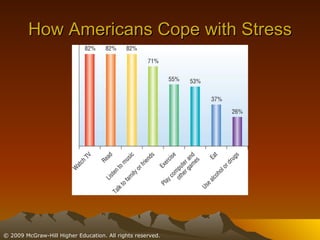
This chapter discusses stress, its causes and effects, and ways to manage it. It defines stress as a physiological and psychological state caused by stressors or disruptive events. There are two types of stress - eustress which enhances life, and distress which diminishes it. When stressed, the body undergoes the fight or flight response involving the brain, nervous system, and adrenal glands. Stress can be resolved through adaptive responses or become chronic. Prolonged stress can deplete the body's resources and damage physical and mental health. Moderate stress can be motivating, but too much has negative health impacts. The chapter outlines student, job, technological, and environmental stressors and recommends lifestyle habits, relaxation techniques