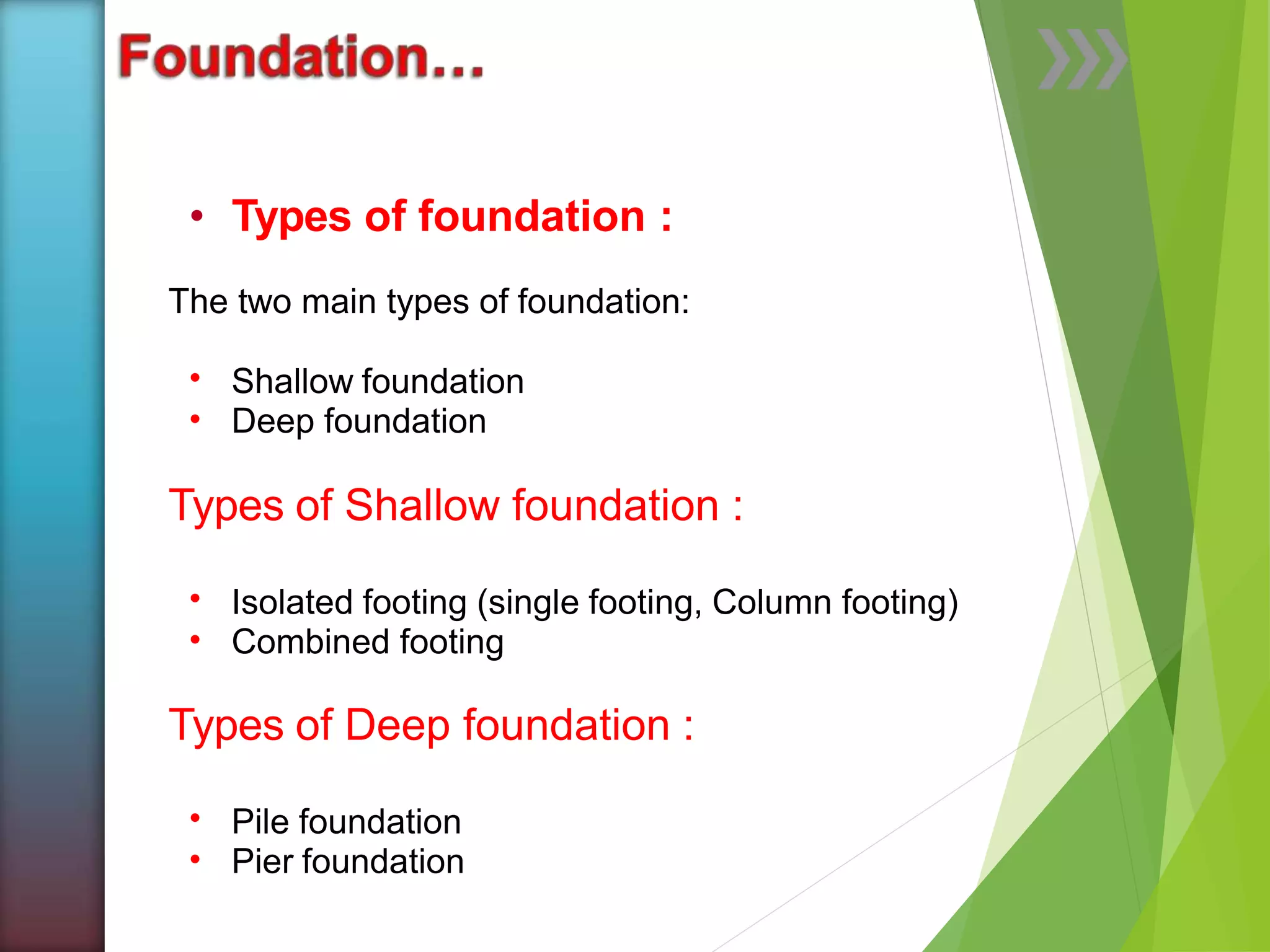
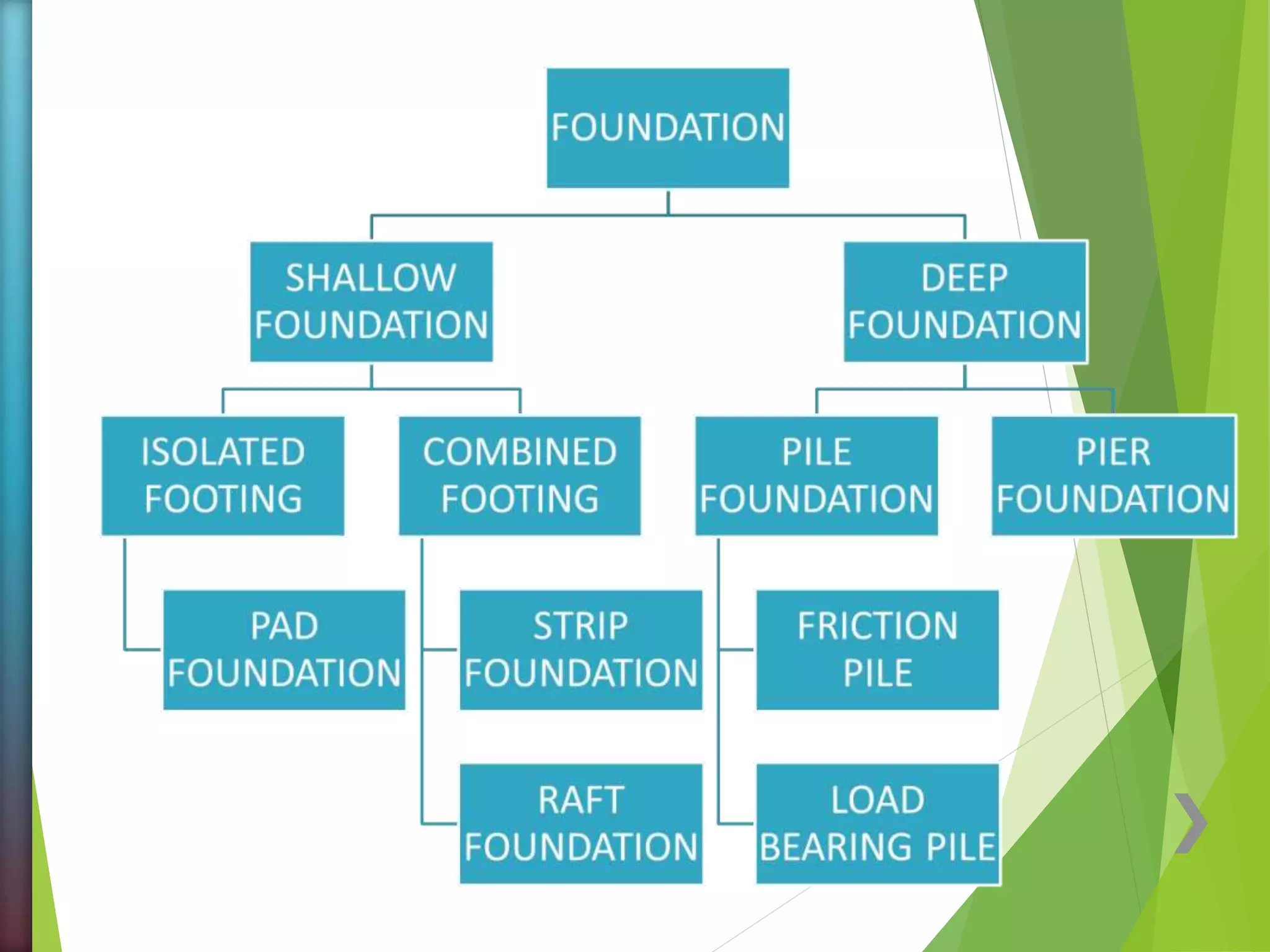
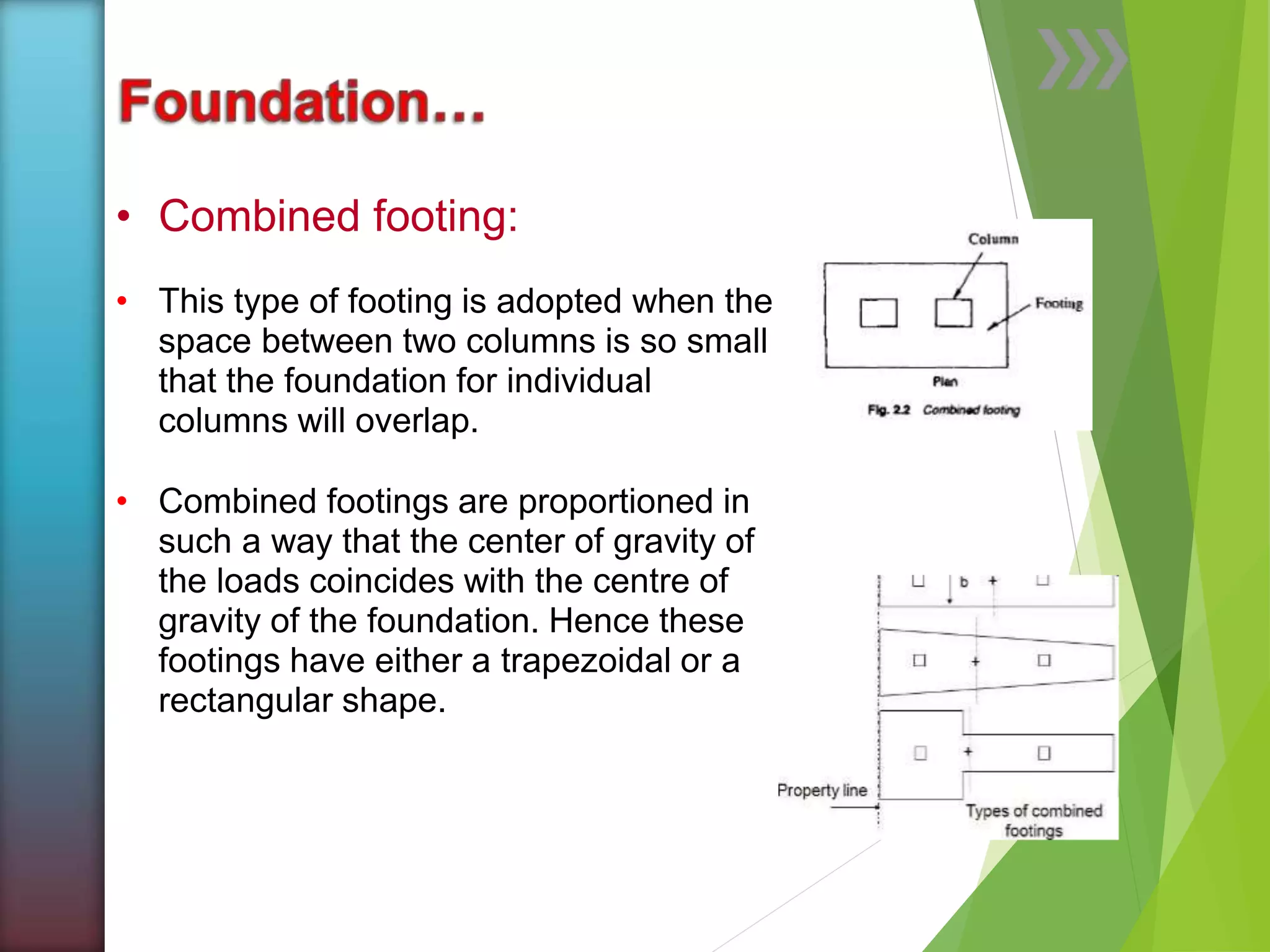
The document discusses foundations for structures. Foundations distribute the load from a structure across a larger area of soil, support the structure, and provide stability against forces like wind and rain. Foundation design depends on soil type, groundwater, structural requirements, site conditions, and cost. Shallow foundations have a depth less than the width and include isolated and combined footings. Deep foundations like piles and piers extend below the shallow depth and transfer load directly to a hard soil layer or bedrock. Piles support load through friction against the soil or by bearing directly on a firm layer, and can be made of materials like concrete, steel, or timber.