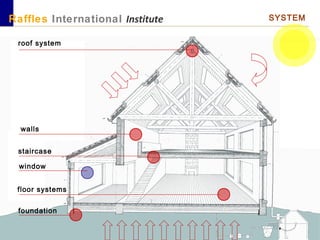
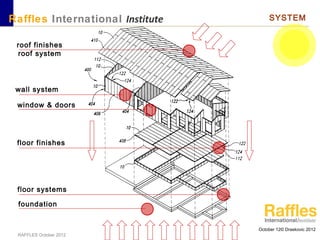
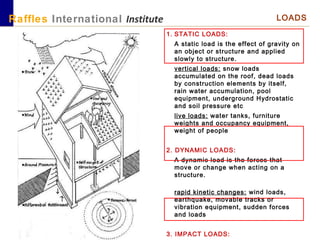
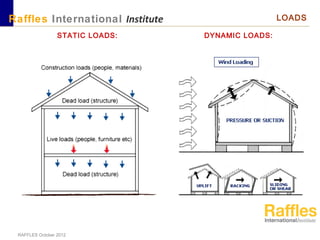
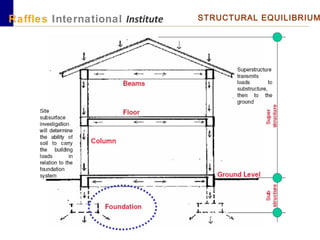
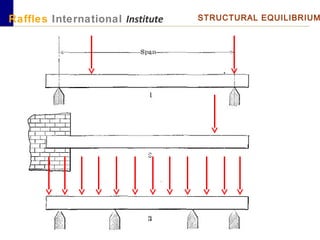
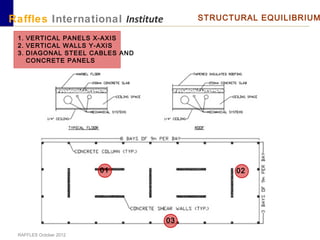
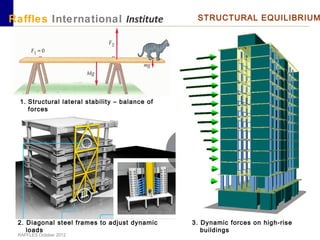
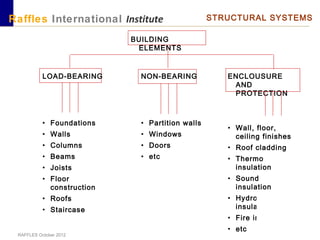
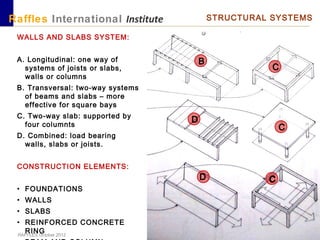
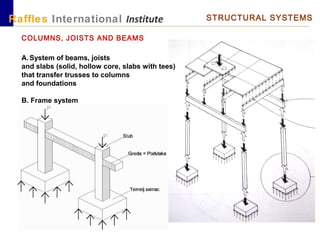
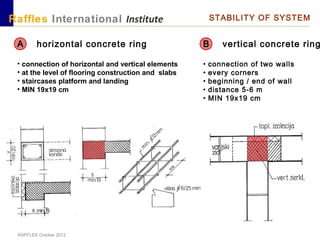
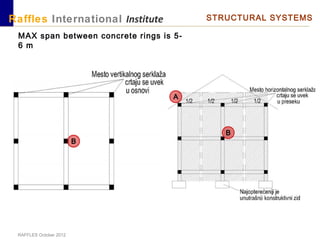
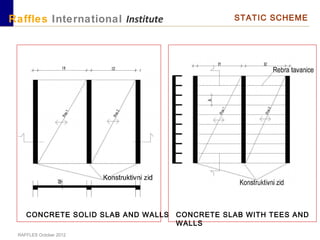
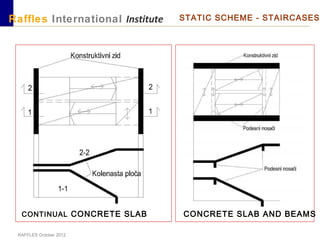
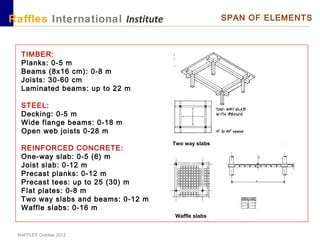
This document outlines the aims, schedule, and content for a Building Technology and Construction module. The module aims to teach students about load-bearing systems, construction documentation, and choosing appropriate structural solutions. Over 11 weeks, topics will include foundations, roofs, walls, floors, stairs, and finishes. Students will learn about building elements, structural systems, loads on buildings, and achieving structural equilibrium. They will complete modeling, drawing, and documentation assignments related to residential construction.