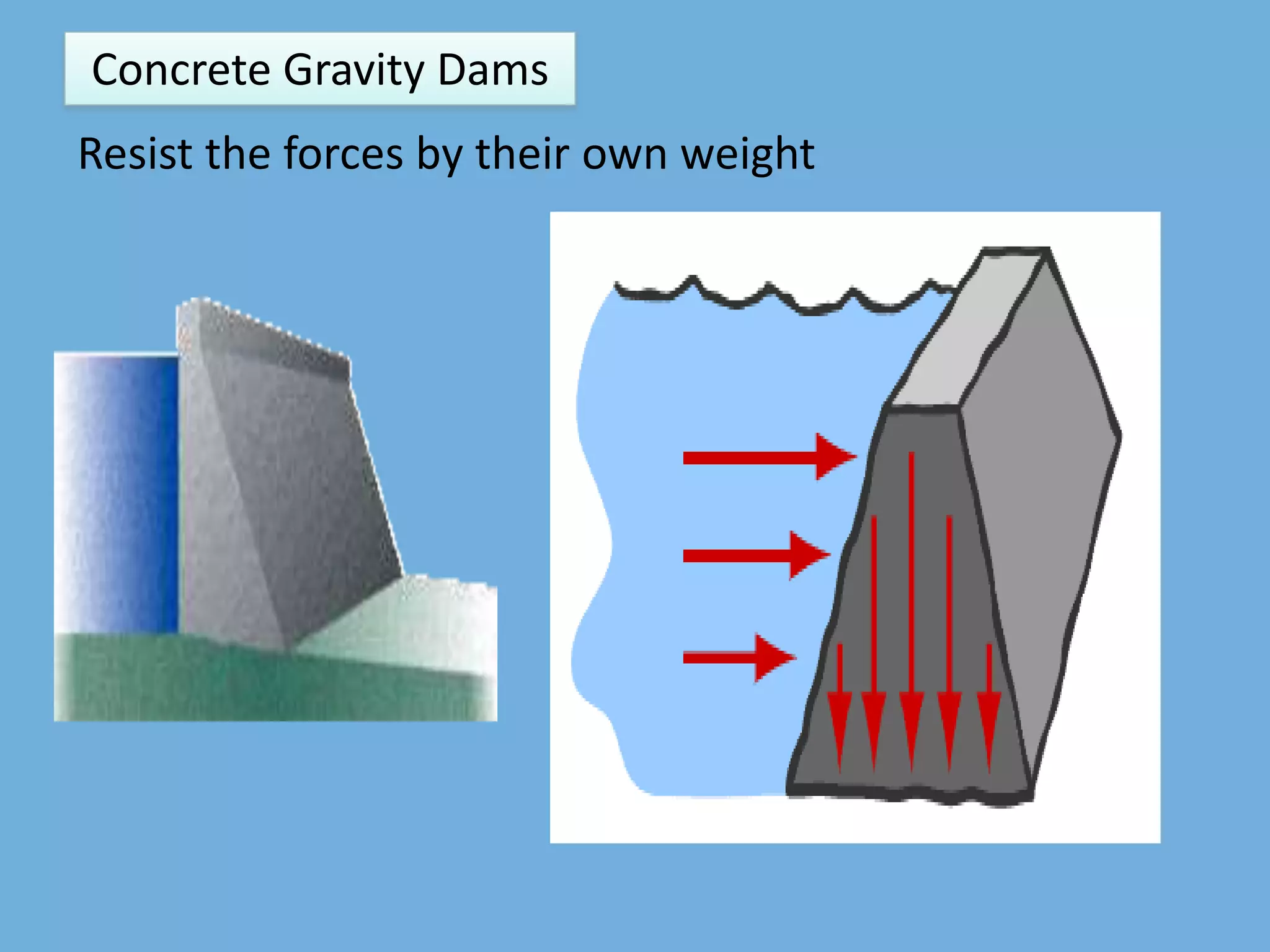
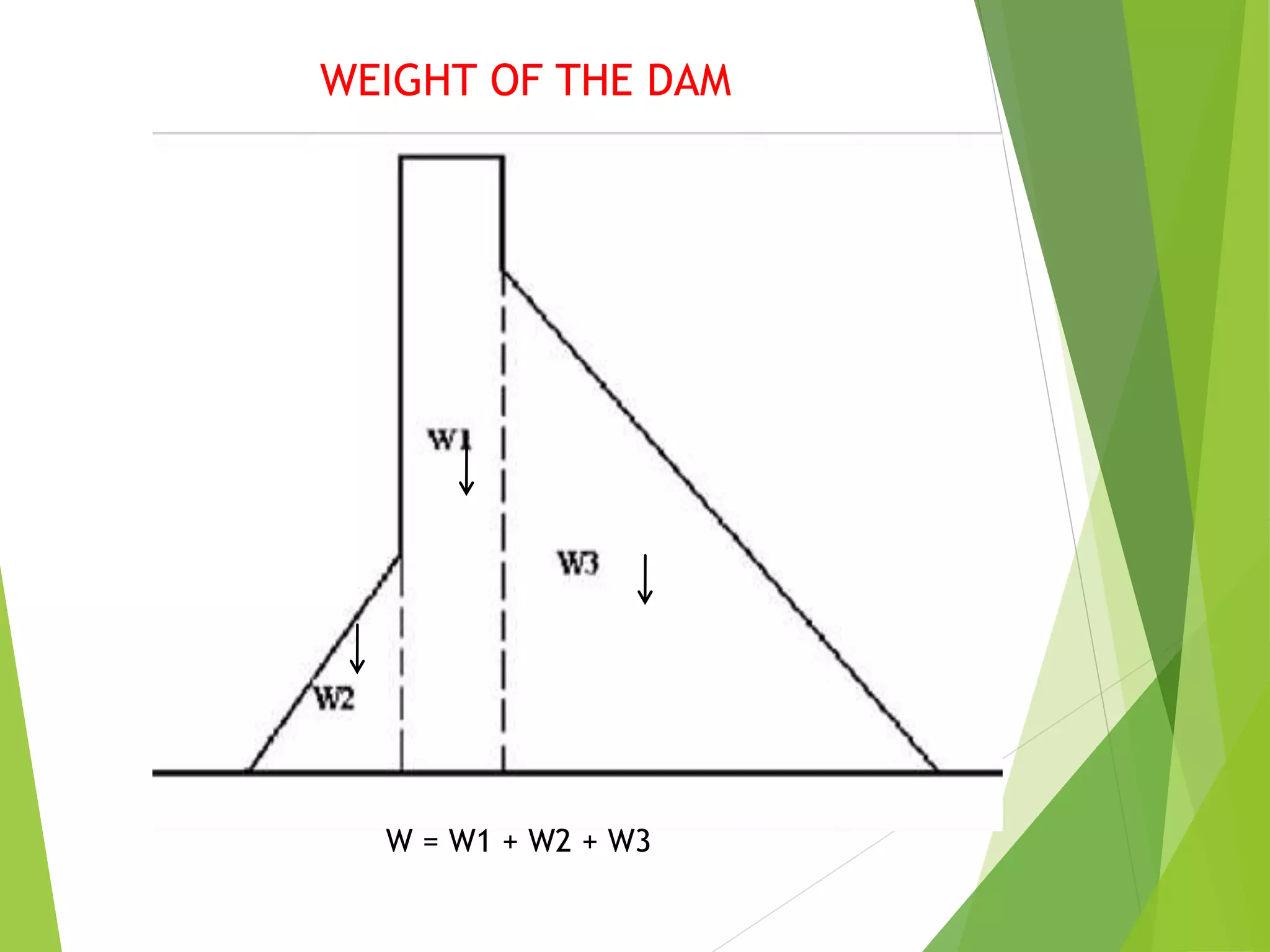
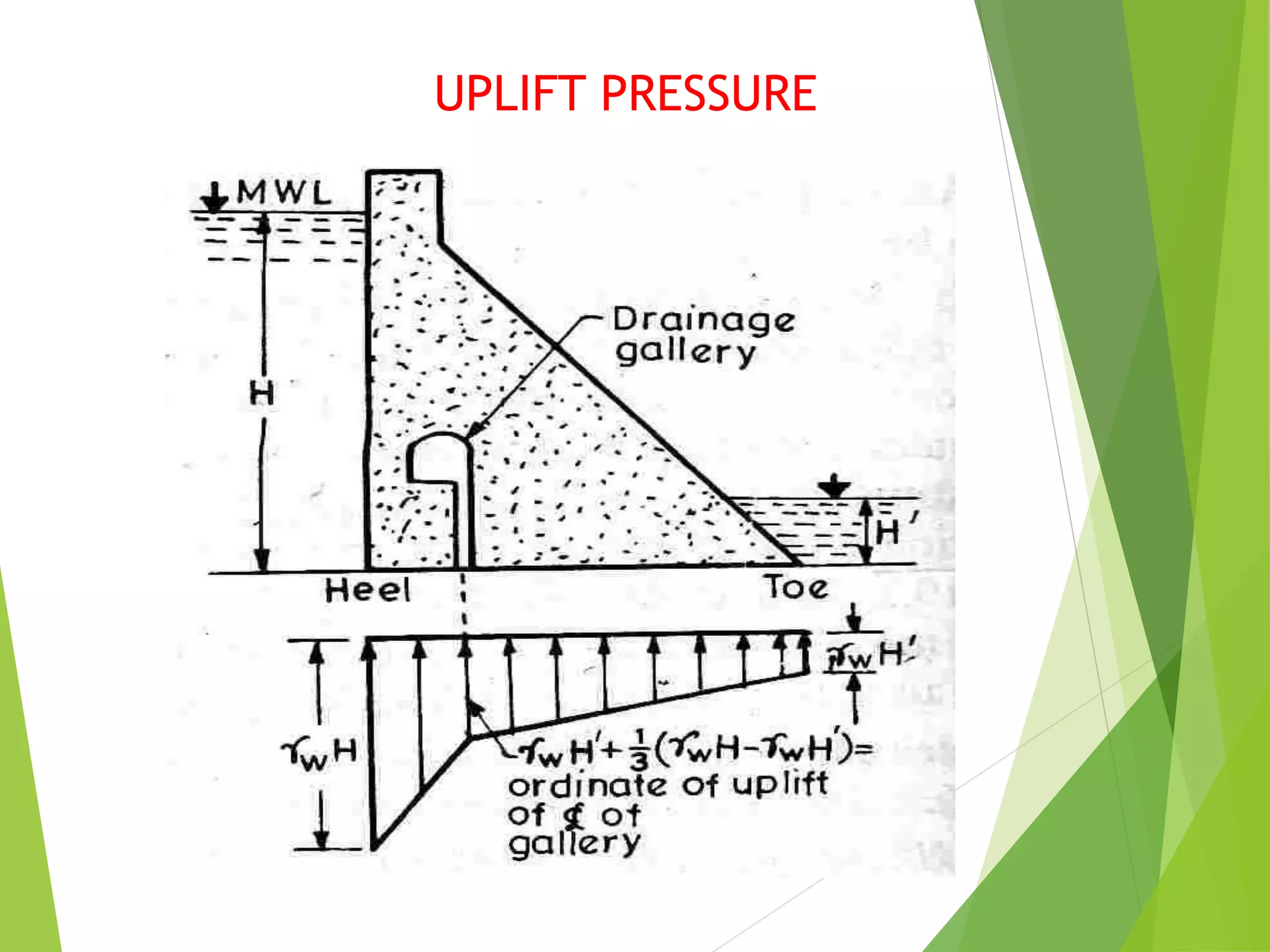
A gravity dam resists external forces through its own weight. It is a solid, durable structure constructed of masonry or concrete. Forces acting on a gravity dam include water pressure, the weight of the dam, uplift pressure, silt pressure, wave pressure, ice pressure, and pressure from earthquake forces. Water pressure is the major external force and varies with depth, while the weight of the dam is the main resisting force.