Ocean properties
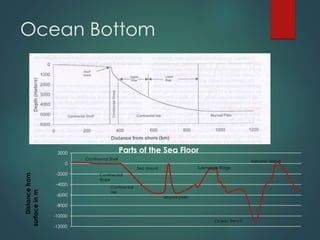
- 1. Ocean Bottom -12000 -10000 -8000 -6000 -4000 -2000 0 2000 Parts of the Sea Floor Distancefrom surfaceinm Continental Shelf Continental Slope Continental rise abyssal plain Sea mount Submarine Ridge Ocean Trench Volcanic Island
- 2. Water Properties Highly Incompressible Extremely Large Heat capacity and Thermal conductivity Largely Opaque to Electromagnetic Energy in the Visible part of Spectrum Largely opaque to Electromagnetic Energy in the Radio and Radar Frequency Range Extremely Transparent to Acoustic Energy
- 3. Dissolved salts in sea water (atoms): 55.3 % Chlorine 30.8 % Sodium 3.7 % Magnesium 2.6 % Sulfur 1.2 % Calcium 1.1 % Potassium
- 4. Fresh Water Density Water behaves like normal fluid expanding when heated and contracting when cooled between 100°C and 4°C Water expands from 4°C to 0°C thus giving maximum density at 4°C At 0°C water changes to solid phase forming ice crystals with a volume increase of about 9%. Thus ice floats This change in property gives rise to vertical circulation of water
- 5. Temperature in the ocean The Sun hits the surface layer of the ocean, heating the water up. Wind and waves mix this layer up from top to bottom, so the heat gets mixed downward too. The temperature of the surface waters varies mainly with latitude. The polar seas (high latitude) can be as cold as -2 degrees Celsius (28.4 degrees Fahrenheit) while the Persian Gulf (low latitude) can be as warm as 36 degrees Celsius (96.8 degrees Fahrenheit). Ocean water, with an average salinity of 35 psu, freezes at -1.94 degrees Celsius
- 6. Temperature cont… Thermocline- a distinct zonation of waters based on temperature. In large bodies of water this is a natural process occurring between the air and wind influenced surface waters, which have relatively rapidly changing temperatures, with the colder, more constant temperature deeper waters.
- 7. Salinity and Density Density of water increases with increase in salinity – 1.025 at 20°C with salinity of 35gm/Kg (35‰) Temperature of Maximum density decrease from 4°C with increase in salinity Freezing Temperature decrease from 0°C with increase in salinity T(ρ max) in°C = 3.95-0.200S-0.0011S² T(freezing) in°C = -0.003-0.0527S-0.00004S²
- 8. Salinity cont… Halocline- vertical zone in the oceanic water column in which salinity changes rapidly with depth, located below the well-mixed, uniformly saline surface water layer. Especially well developed haloclines occur in the Atlantic Ocean, in which salinities may decrease by several parts per thousand from the base of the surface layer to depths of about one kilometre (3,300 feet). In higherノ
- 10. Variation of temperature of max density and freezing with temperature
- 11. Freezing of Sea Water It would seem that at 35‰ salinity, the maximum density would occur in solid phase thus freezing water at bottom of the sea This does not happen Salt is precipitated as the temperature approaches freezing point thus making the ice of fresh water only with increased salinity just below the formed ice This leads to a denser fluid strata just below the formed ice on the sea surface. This leads to a type of vertical circulation
- 12. Energy Spectrum of incident radiation at ocean depth
- 13. Speed of sound in water
- 14. Why is Ocean Circulation Important? Transport ~ 20% of latitudinal heat Equator to poles Transport nutrients and organisms Influences weather and climate Influences commerce
- 15. Sailors have know about ocean currents for centuries Sailors have know that “rivers” flow in the seas since ancient times. They used them to shorten voyages, or were delayed by trying to stem them. If navigators do not correct to deflection by currents, they may be far away from where they think they are and meet disaster. Fridtjof Nansen scientifically observed ice pack drift for two years and recorded it in 1893-96. This was later put to theory by Ekman Another systematic study of currents was done by Maury based on logbooks in the US Navy’s Depot of Charts and Instruments. His charts and “Physical Geography of the Sea” assisted navigators worldwide.
- 16. Surface Currents - The upper 100 to 200 meters of the ocean Deep Water Currents – Mainly Geostrophic flow (98% of volume) Bottom Current Ocean Currents
- 18. Physical properties of the atmosphere: Water vapor •Cool air cannot hold much water vapor, so is typically dry •Warm air can hold more water vapor, so is typically moist •Water vapor decreases the density of air
- 19. Physical properties of the atmosphere: Density • Warm, low density air rises • Cool, high density air sinks • Creates circular- moving loop of air (convection cell)
- 21. The Coriolis effect • The Coriolis effect – Is a result of Earth’s rotation – Causes moving objects to follow curved paths: • In Northern Hemisphere, curvature is to right • In Southern Hemisphere, curvature is to left – Changes with latitude: • No Coriolis effect at Equator • Maximum Coriolis effect at poles
- 22. The Coriolis effect on Earth • As Earth rotates, different latitudes travel at different speeds • The change in speed with latitude causes the Coriolis effect
- 23. Earth’s Rotation and Variation of Tangential Velocities
- 24. Surface Currents Forces 1. Solar Heating (temp, density) 2. Winds 3. Coriolis
- 25. Winds and surface water Wind blowing over the ocean can move it due to frictional drag. Waves create necessary roughness for wind to couple with water. One “rule of thumb” holds that wind blowing for 12 hrs at 100 cm per sec will produce a 2 cm per sec current (about 2% of the wind speed)
- 26. Wind-Driven and Density-Driven Currents Wind-driven currents occur in the uppermost 100 m or less Density differences causes by salinity and temperature produce very slow flows in deeper waters.
- 27. Top-down drag Wind acts only on the surface water layer. This layer will also drag the underlying water, but with less force. Consequently, there is a diminution of speed downward and Turbulent mixing. Direction of movement is also influenced by the Coriolis Effect and Ekman Spiral
- 28. Ekman spiral Ekman spiral describes the speed and direction of flow of surface waters at various depths Factors: Wind Coriolis effect
- 29. Ekman transport Ekman transport is the overall water movement due to Ekman spiral Ideal transport is 90º from the wind Transport direction depends on the hemisphere
- 30. Ekman Transport Water flow in the Northern hemisphere- 90o to the right of the wind direction Depth is important
- 31. Geostrophic Flow Surface currents generally mirror average planetary atmospheric circulation patterns
- 33. Currents in the “Real” Ocean Currents rarely behave exactly as predicted by these theoretical explanations due to factors such as Depth—shallow water does not permit full development of the Ekman spiral Density—deeper currents moving in different directions influence the overlying surface movement
- 34. Eddy Warm core ring 1. Rotates clockwise 2. Found on the landward side of the current Cold core ring (cyclonic eddy) 1. Rotates counterclockwise 2. Forms on the ocean side of the current A circular movement of water formed along the edge of a permanent current In an average year, 10-15 rings are formed 150-300 km in diameter Speed 1 m/sec
- 36. Upwelling and downwelling Vertical movement of water () Upwelling = movement of deep water to surface Hoists cold, nutrient-rich water to surface Produces high productivities and abundant marine life Downwelling = movement of surface water down Moves warm, nutrient-depleted surface water down Not associated with high productivities or abundant marine life
- 37. Circulation As water becomes cold it sinks, which causes the under water currents in the oceans. This mixes the layers of water which allow food from the surface to reach the bottom. This along with upwelling and downwelling (the upward and downward motion of sub- surface water toward the surface and bottom of the ocean. This is often a source of cold, nutrient-rich water. Strong upwelling occurs along the equator where easterly winds are present. Upwelling also can occur along coastlines). This increases the productivity ( the amount of carbon available to the system as a result of photosynthesis) of the marine ecosystem.
- 38. Circulation Cont… circulation of surface waters of the ocean are driven by winds, the circulation of the deep waters are driven by density differences. Circulation in the depths of the ocean is referred to as thermohaline circulation. The deep ocean is layered with the densest water on bottom and the lightest water on top. Water tends to move horizontally throughout the deep ocean, moving along lines of equal density. Vertical circulation is limited because it is easier for water to move along lines of constant density than across them.
- 39. Surface and Deep-Sea Current Interactions Unifying concept: “Global Ocean Conveyor Belt” http://seis.natsci.csulb.edu/rbehl/ConvBelt.htm
- 40. White sections represent warm surface currents. Purple sections represent deep cold currents
