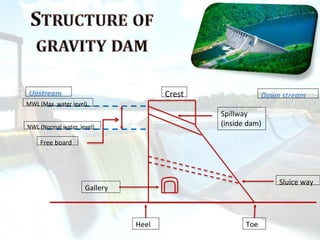
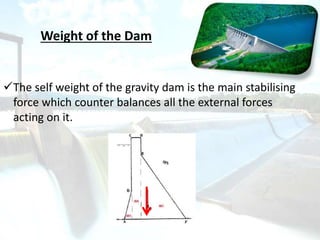
Gravity dams are rigid concrete dams that rely entirely on their weight to maintain stability. They are built with a triangular cross-section to transfer loads directly to strong rock foundations. Famous gravity dams discussed include the Bhakra Dam in India and Fontana Dam in the US. Advantages are that they are durable, allow heights over 700 feet, and have low maintenance costs. However, they require competent foundations and construction is complex. Forces like water pressure, uplift, and earthquakes must be addressed through design to prevent failures by overturning, sliding, tension, or crushing.