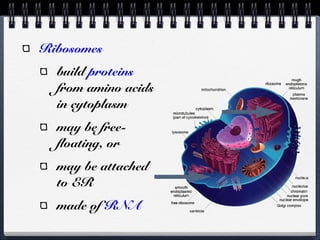
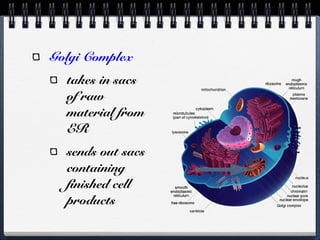
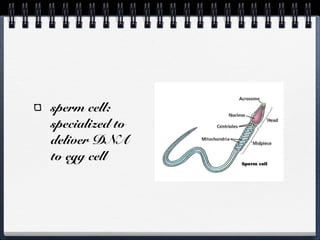
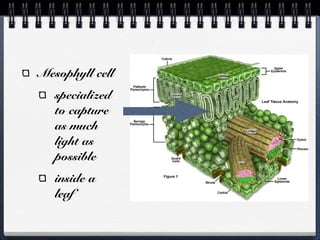
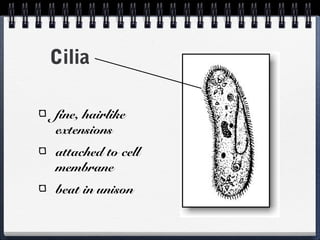
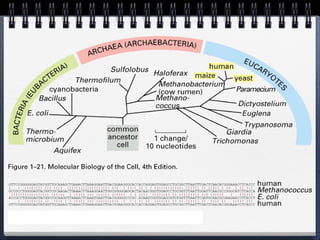
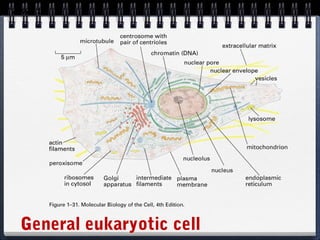
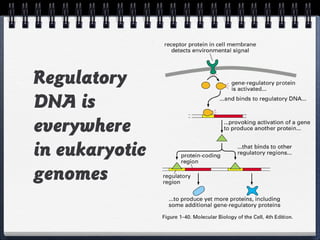
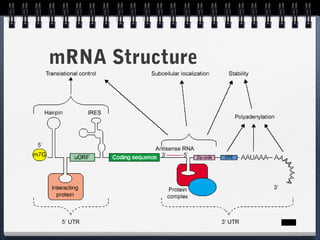
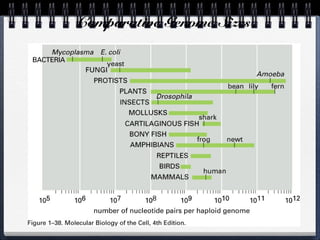
Cells can be either prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler, lacking membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex, containing membrane-bound organelles. Endosymbiotic theory proposes that eukaryotic organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved from prokaryotic cells living endosymbiotically within eukaryotes. Prokaryotes have circular DNA while eukaryotes have linear DNA packaged into chromosomes. There are several ways new genes can be generated from existing genes, such as mutation, duplication, segment shuffling, and horizontal transfer.