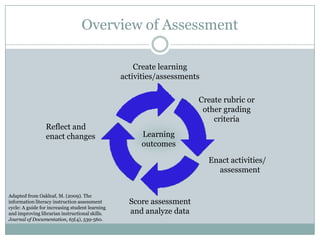
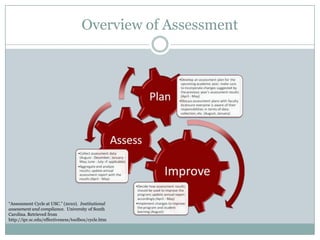
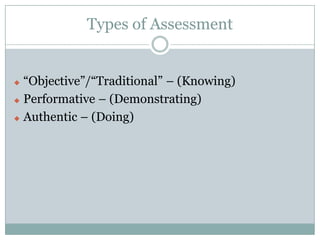
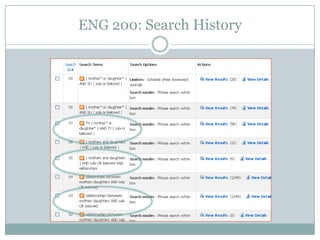
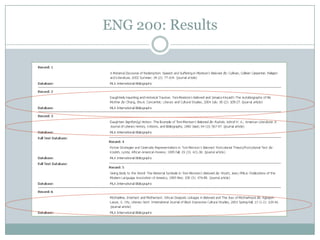
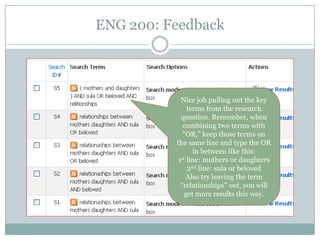
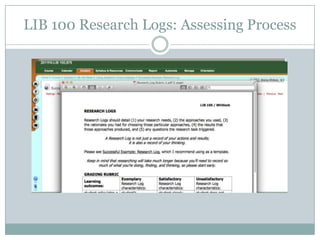
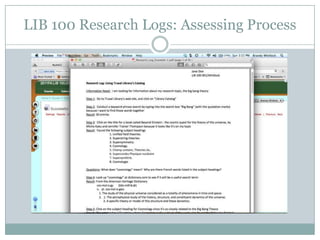
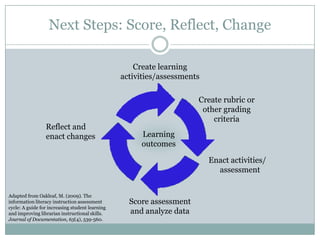
This document discusses assessment in information literacy instruction. It begins by outlining the learning outcomes of the session, which are to define key assessment terms, distinguish between objective, performative and authentic assessment measures, and prepare performative or authentic assessments for learning outcomes. The document then discusses why assessment is important for improving teaching and learning. It provides an overview of the assessment cycle and explains key steps like creating learning outcomes and activities, developing assessment tools, and using rubrics. Various assessment examples are provided and different types of assessments are defined. The document emphasizes using performative and authentic assessments to evaluate higher-order thinking. It concludes by recapping the assessment cycle and encouraging attendees to design their own assessment questions.