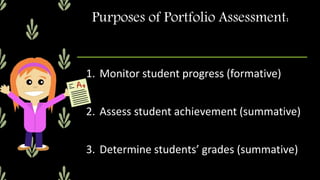
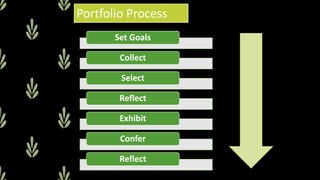
A portfolio is a collection of a student's work that is selected and organized to show student learning progress over time or showcase a student's best work. A portfolio can contain classwork, assessments, reflections, and other materials. It provides advantages as an assessment tool by allowing students to develop reflective skills and giving teachers documentation of student learning. However, portfolios also have disadvantages such as being time-consuming to create and store. There are different types of portfolios, including working, documentary, and showcase portfolios, that serve different purposes and contain various materials. Effective portfolio assessment involves collaboration between teachers, students, and parents using clear criteria.