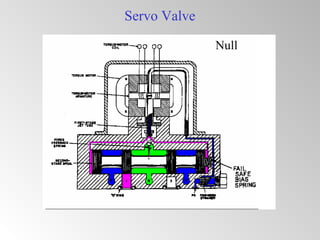
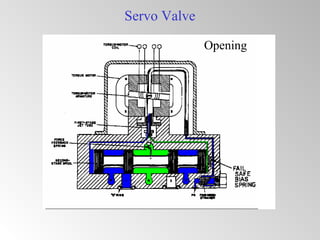
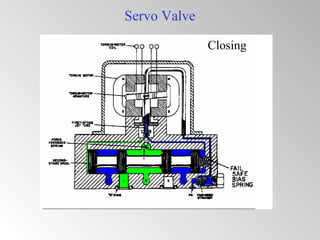
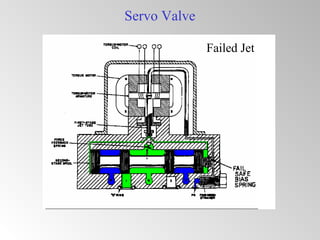
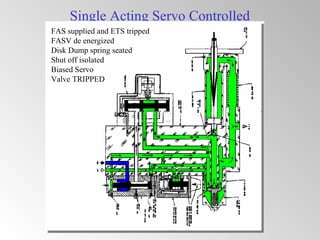
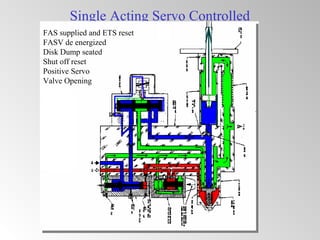
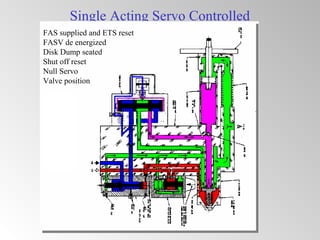
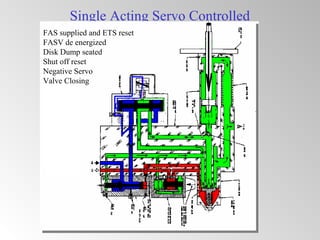
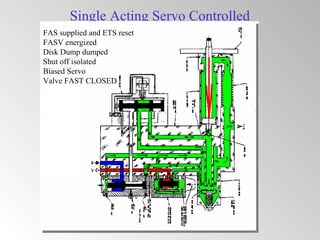
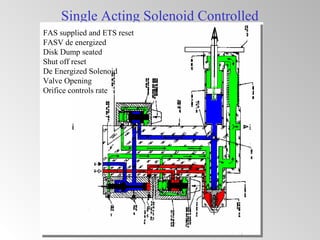
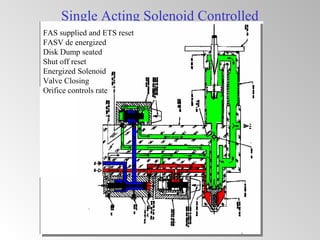
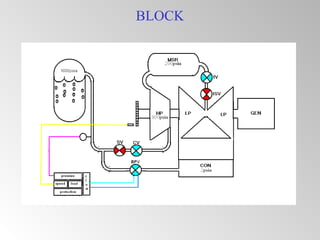
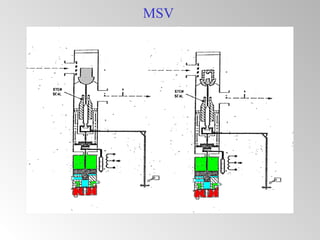
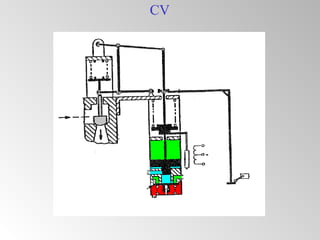
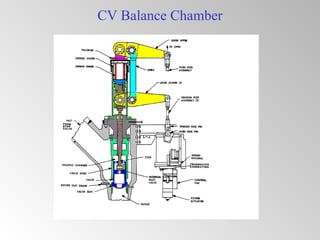
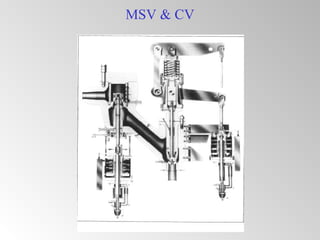
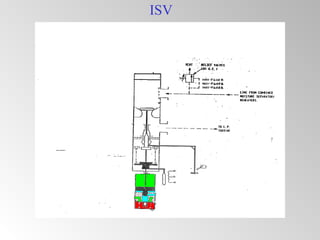
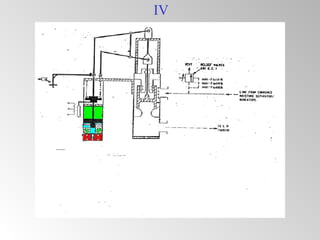
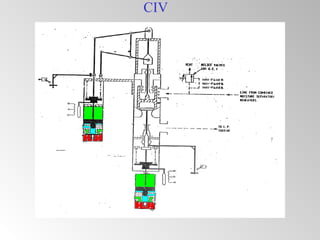
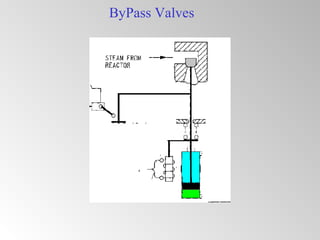
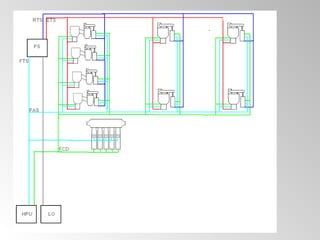
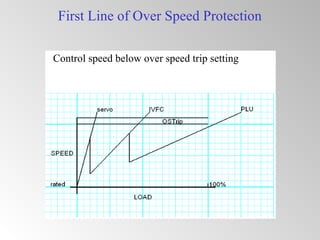
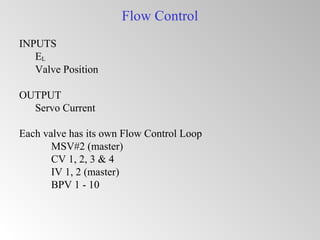
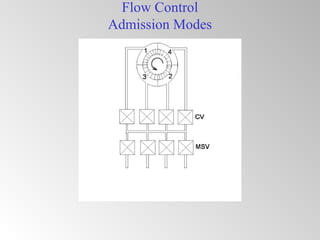
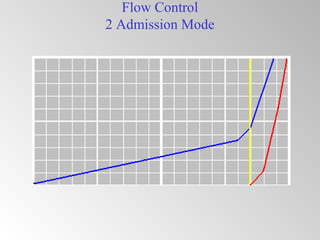
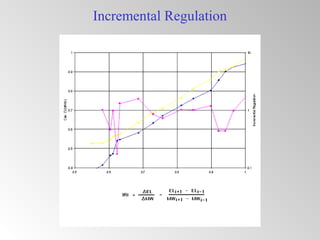
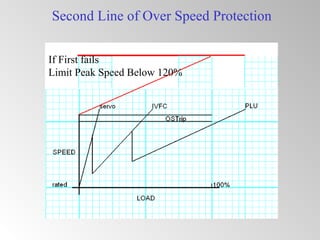
The document discusses steam turbine governor systems and controls. It describes how governors regulate steam flow to maintain desired turbine speed even as load torque changes. It also describes emergency controls to reduce steam flow if load is lost to prevent overspeed, or trip the turbine if speed cannot be controlled. The document then summarizes various turbine control components, including hydraulic and electronic controls, valves, actuators and their functions in speed control, load control, flow control and overspeed protection.