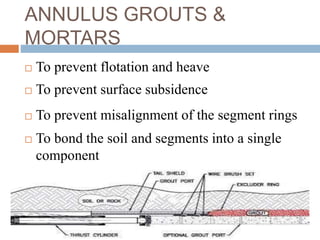
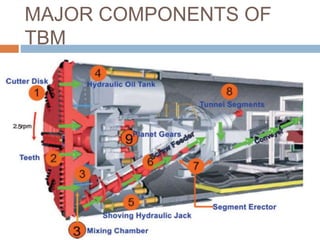
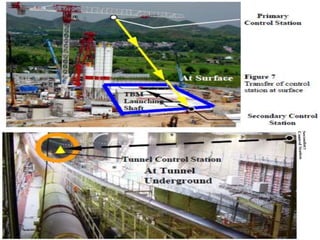
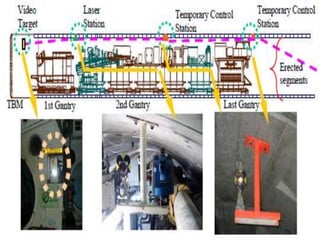
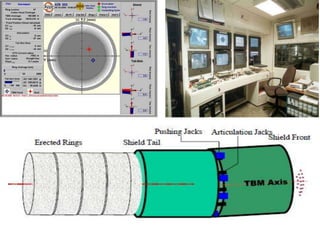
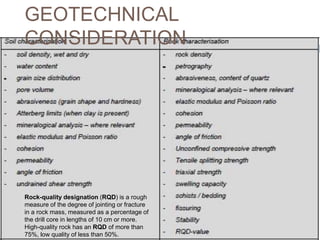
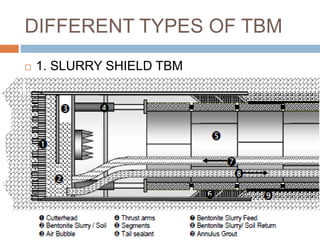
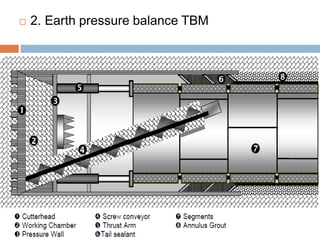
The document discusses tunnel boring machines (TBMs) and their use in tunnel construction. It describes some of the key components of a TBM, including the tunnel lining process using precast concrete segments. It also discusses the importance of surveying activities to guide TBM operations and transfer control stations. Geotechnical considerations like rock quality designation are important for TBM tunneling. The main types of TBMs covered are slurry shield and earth pressure balance machines. Annulus grouts and mortars are also discussed for bonding segments and preventing issues during tunneling.





![slurry test programmed will generally include the above parameters[ 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tunnelingbytunnelboringmachine-160418152822/85/Tunneling-by-tunnel-boring-machine-13-320.jpg)
![indicates typical particle size distributions for the use of EPBM[ 3 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tunnelingbytunnelboringmachine-160418152822/85/Tunneling-by-tunnel-boring-machine-15-320.jpg)