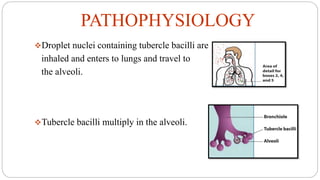
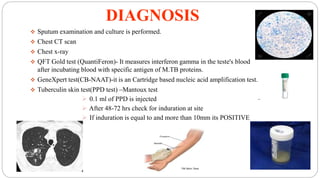
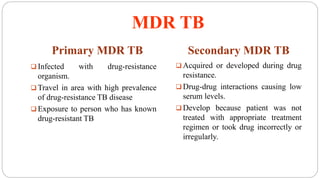
Tuberculosis is a chronic infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis that primarily affects the lungs. It spreads through the air and is one of the top infectious killers worldwide. Those at highest risk include those with weakened immune systems, living in areas with high TB rates, abusing alcohol or tobacco, or living with an infected individual. The bacteria are inhaled, travel to the lungs, and can spread throughout the body. Most infections remain latent without symptoms, but active disease can cause coughing, weight loss, fever and other signs. Diagnosis involves sputum tests, chest imaging and tuberculin skin tests. Treatment requires multiple antibiotic drugs over several months to prevent drug resistance. New vaccines and drug










![REFERNCES
Cardona PJ. Pathogenesis of tuberculosis and other mycobacteriosis.
Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2018 Jan;36(1):38-46. English, Spanish.
doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2017.10.015. Epub 2017 Dec 2. PMID: 29198784
Strausz J. Tuberkulózis 2006 [Tuberculosis 2006]. Orv Hetil. 2007 May
6;148(18):829-31. Hungarian. doi: 10.1556/OH.2007.28057. PMID:
17468065
KD Tripathi
Koch A, Mizrahi V. Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Trends Microbiol. 2018
Jun;26(6):555-556. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2018.02.012. Epub 2018 Mar 23.
PMID: 29580884
https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-
new-drug-treatment-resistant-forms-tuberculosis-affects-
lungs#:~:text=The%20U.S.%20Food%20and%20Drug,(TB)%20of%20th
e%20lungs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/37a494sxrxehayof0tky-signature-cfef839f3486d76b908efffabd96075e95529f3a58231101569a5b0a5e72d3f4-poli-210726212018/85/TUBERCULOSIS-14-320.jpg)
