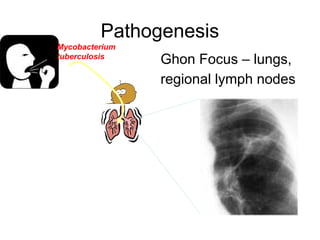
This document provides an overview of tuberculosis (TB), including its definition, causes, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, investigations, types, treatment regimens, and relationship to HIV/AIDS. TB is caused by mycobacteria, commonly Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which can affect any organ but typically affects the lungs. It is transmitted via airborne droplets from someone with active pulmonary TB. Primary infection may result in latent TB or active TB, depending on immune response. Symptoms vary based on location of infection. Diagnosis involves chest x-ray, sputum smear, and Mantoux test. Treatment involves a combination of bactericidal and bacteriostatic drugs. Multi-drug resistant TB can develop if treatment is not completed