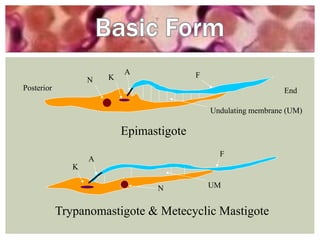
Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense is a protozoan parasite and causative agent of East African sleeping sickness in humans. It is transmitted by the tsetse fly and progresses from an initial chancre at the site of the tsetse bite to invasion of the central nervous system. Clinical signs include headaches, fever, and changes in behavior and motor function that can lead to coma and death if untreated. Diagnosis involves microscopic examination of blood, lymph, or cerebrospinal fluid to demonstrate the presence of the parasite. Treatment depends on the stage of infection, but may include pentamidine, suramin, eflornithine, or melarsoprol. Control efforts also focus on