Embed presentation
Downloaded 47 times


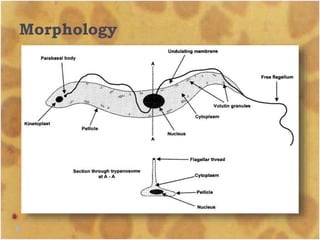
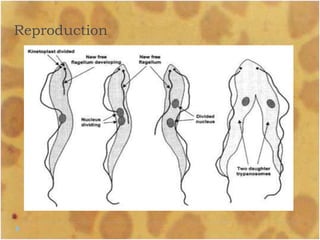
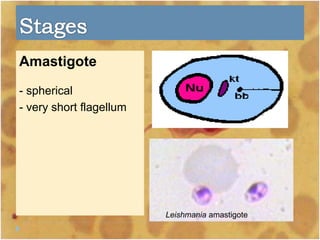
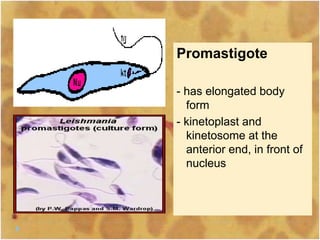
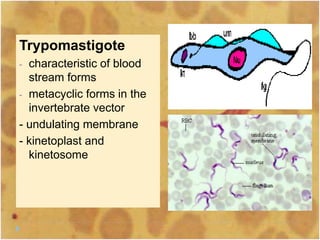
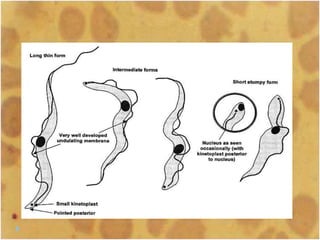
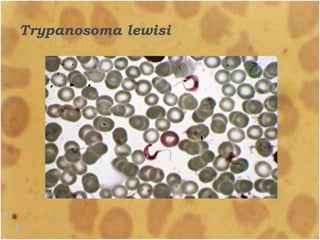
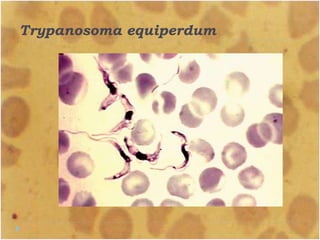
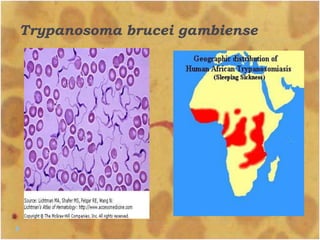
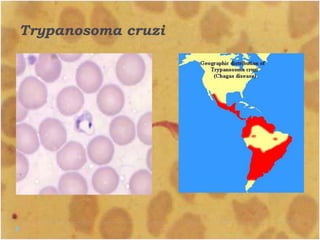
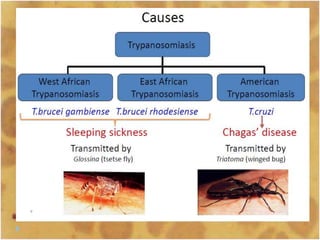
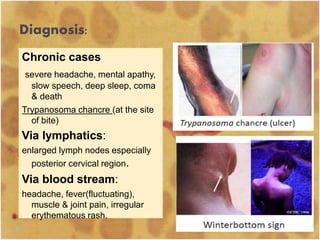
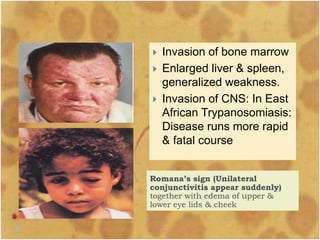
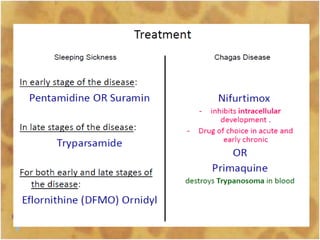
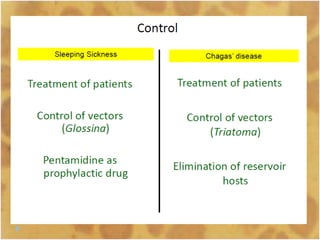
This document discusses the genus Trypanosoma, which are single-celled parasitic protozoa that cause serious diseases in humans and animals. It describes their morphology and life cycles. Trypanosoma have a single nucleus, flagellum, and rounded or leaf-like body. They exist in three main forms: amastigotes which are spherical, promastigotes which are elongated, and trypomastigotes which are found in the bloodstream. Examples mentioned are T. lewisi, T. equiperdum, T. brucei gambiense, and T. cruzi. Symptoms in humans are provided for the different stages of infection, such as headaches, fever, and


















