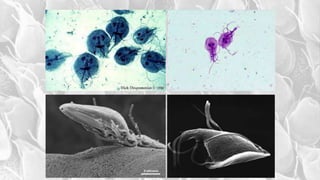
This document discusses Giardia lamblia, a unicellular parasite that causes giardiasis. Some key points:
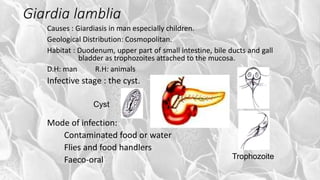
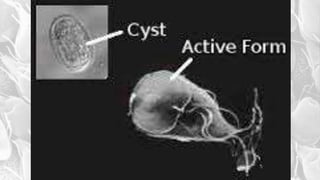
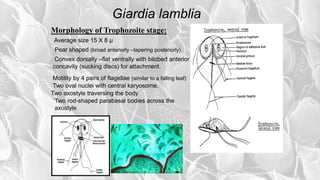
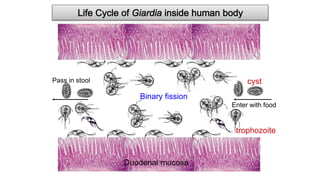
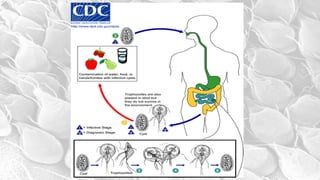
- G. lamblia was first observed by Van Leeuwenhoek in 1681 and causes traveler's diarrhea or beaver fever. It inhabits the small intestine as a trophozoite attached to the mucosa.
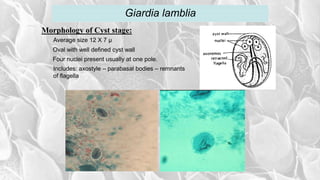
- The infective stage is the cyst, which is ingested through contaminated food or water or from contact with infected flies or food handlers. The cyst contains 4 nuclei and can survive outside the host.
- Symptoms of giardiasis include diarrhea, flatulence, and greasy stool. The infection is common in children. The