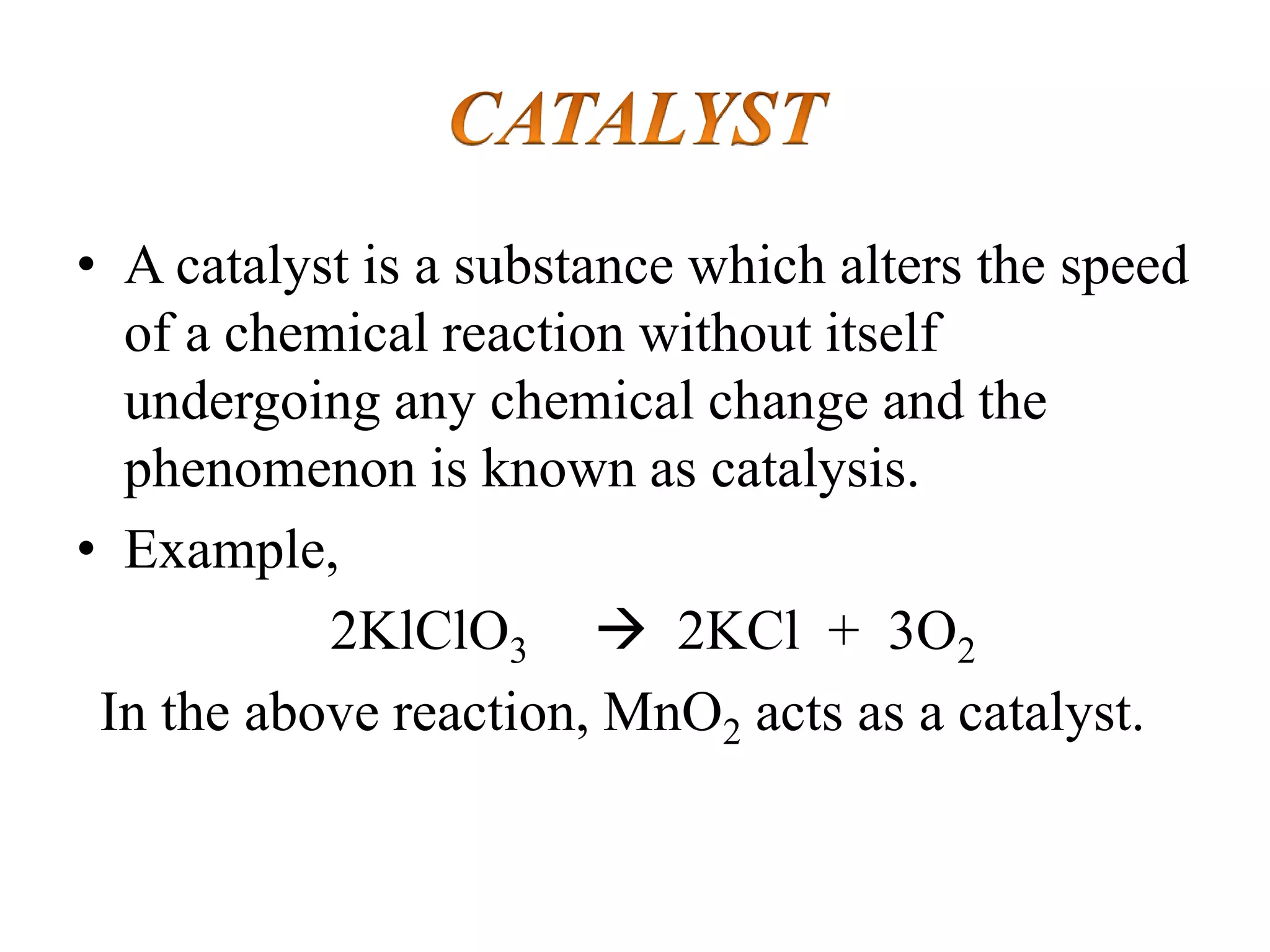
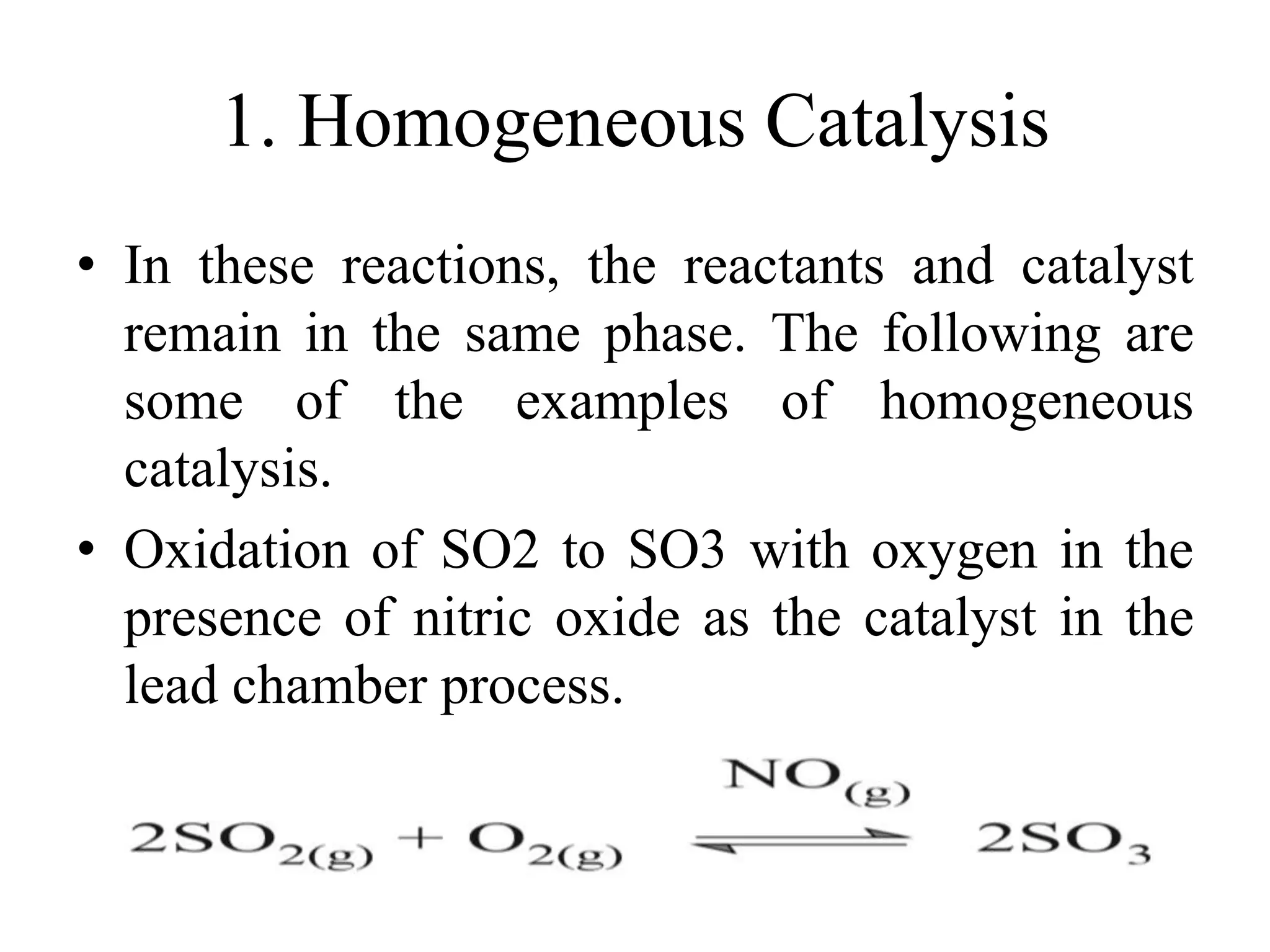
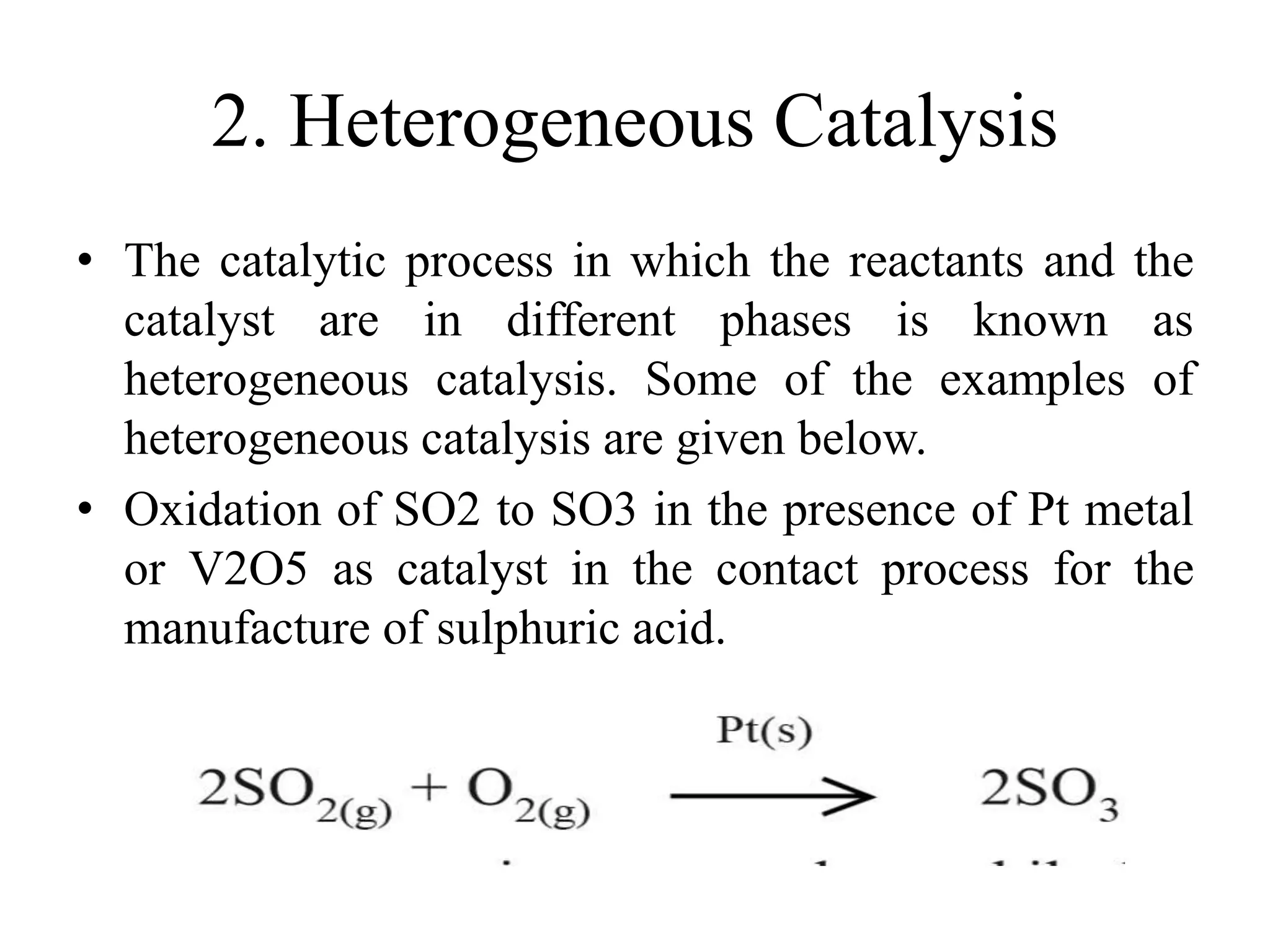
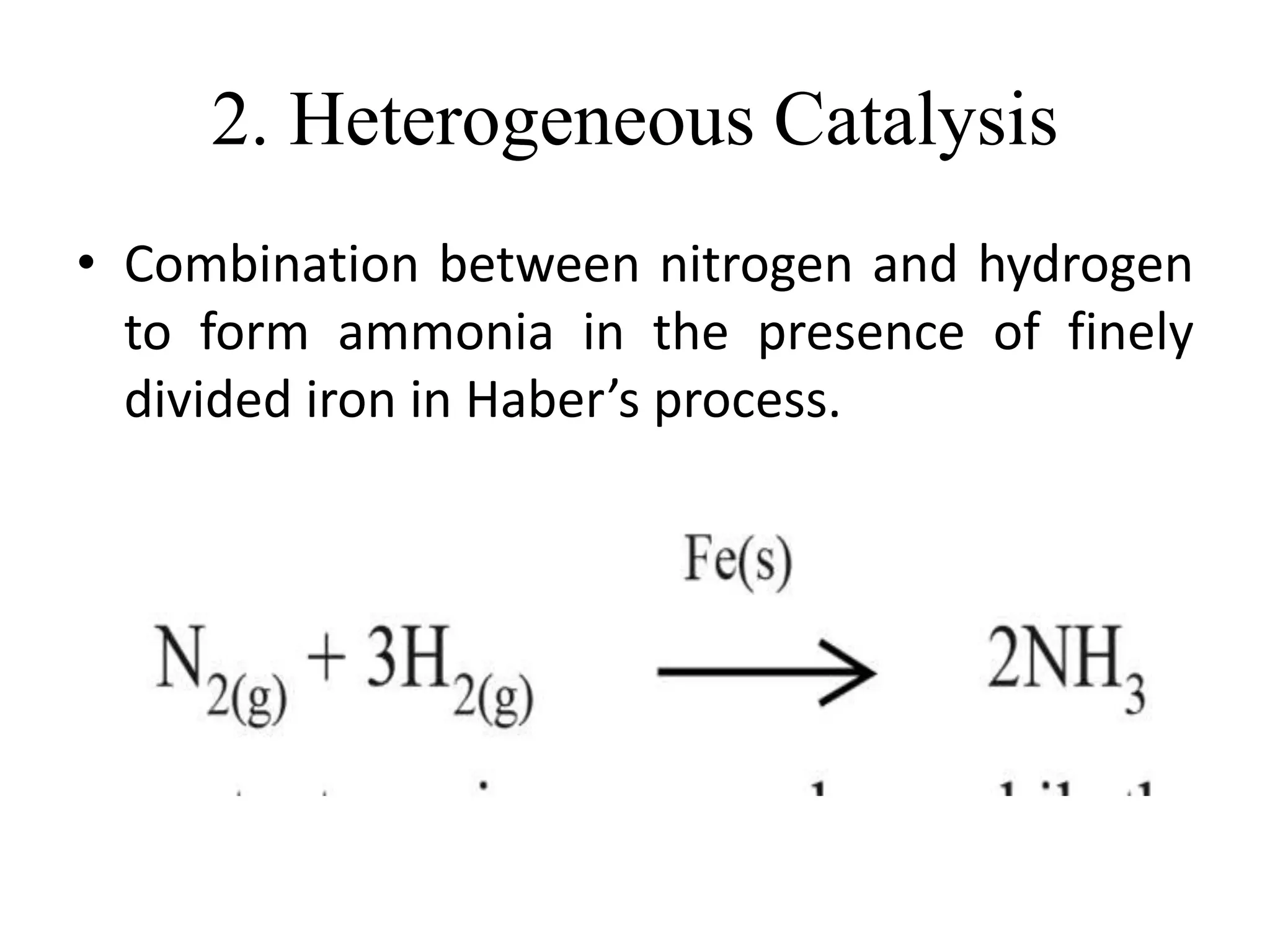
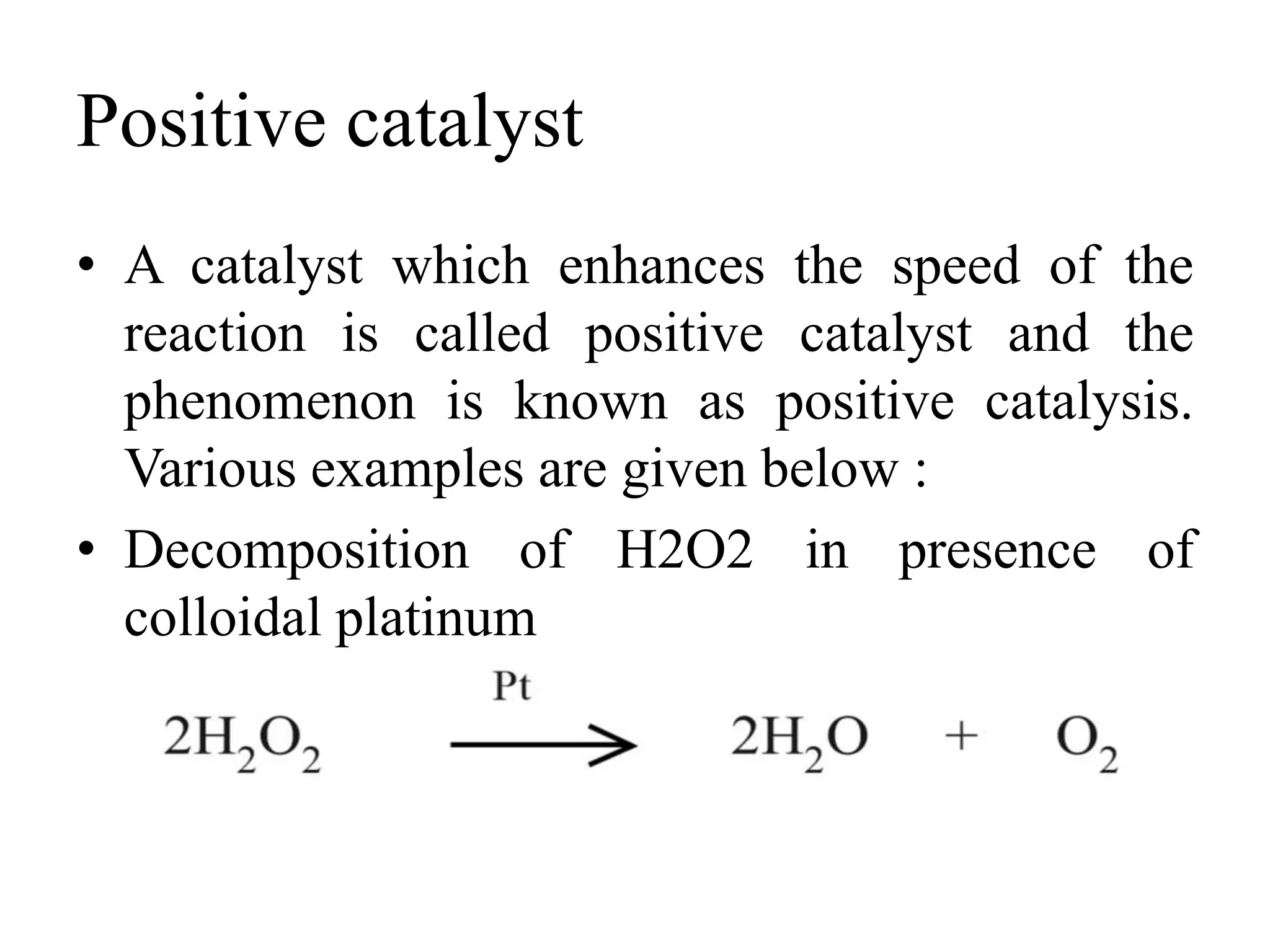
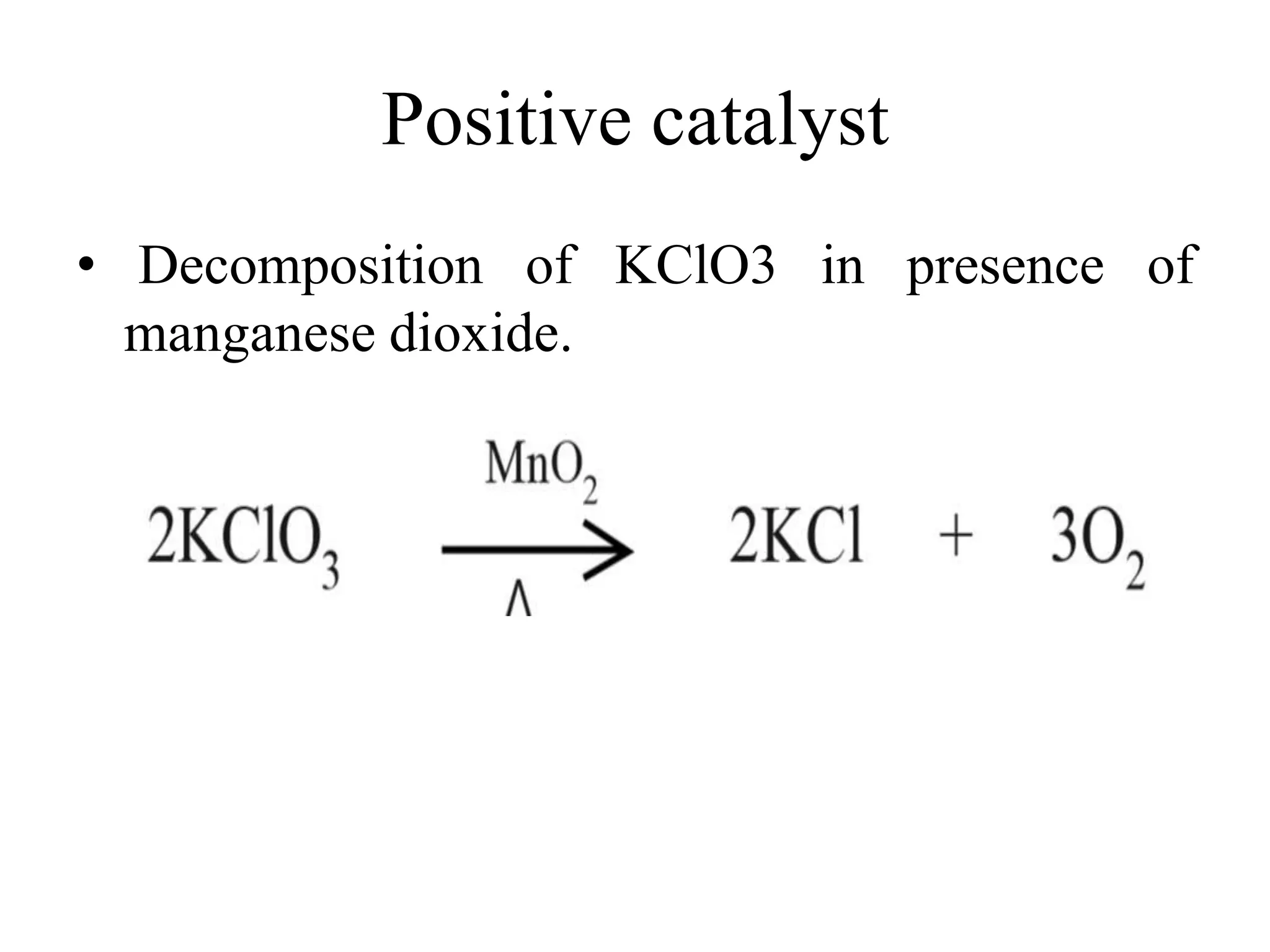
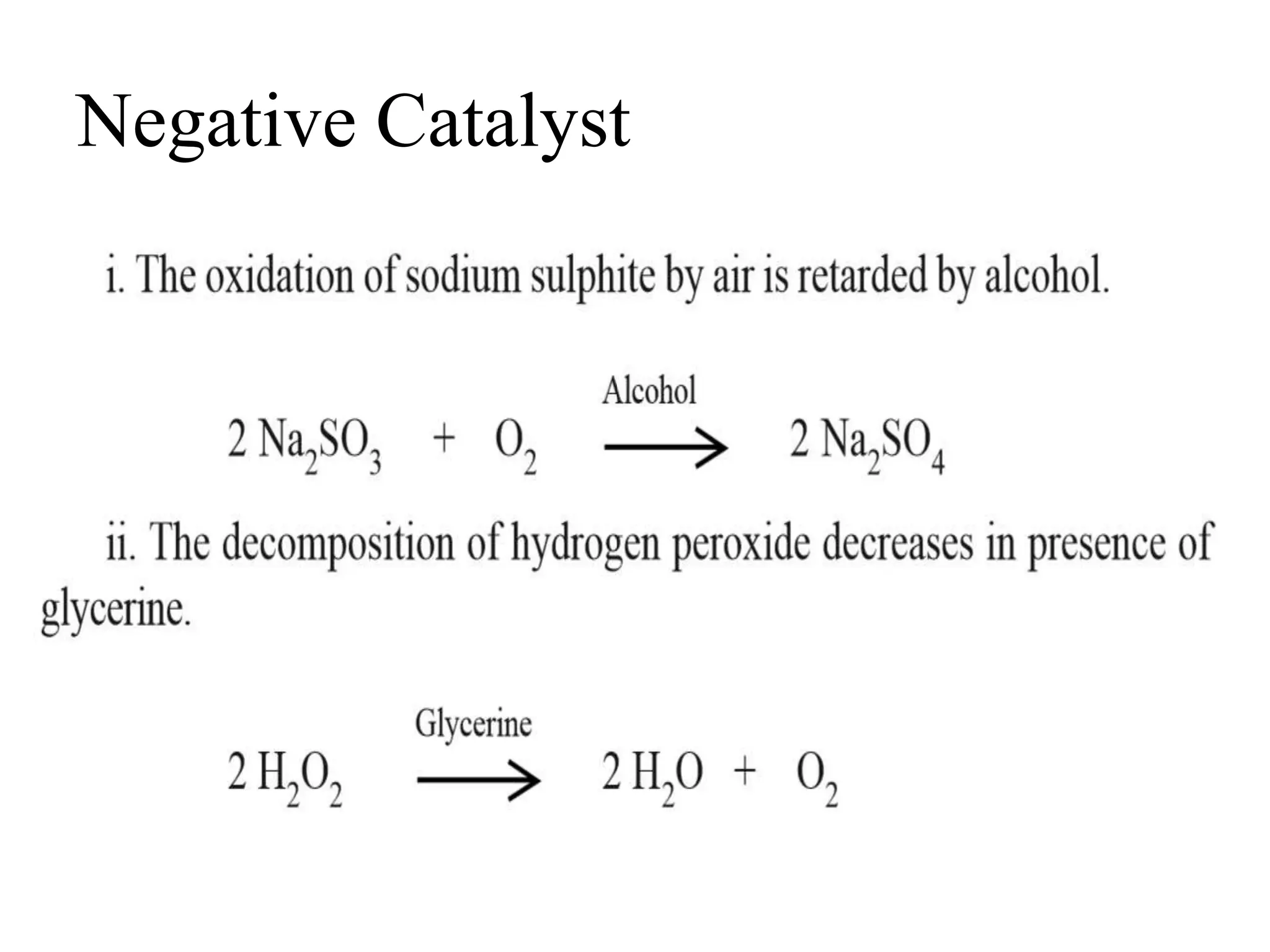
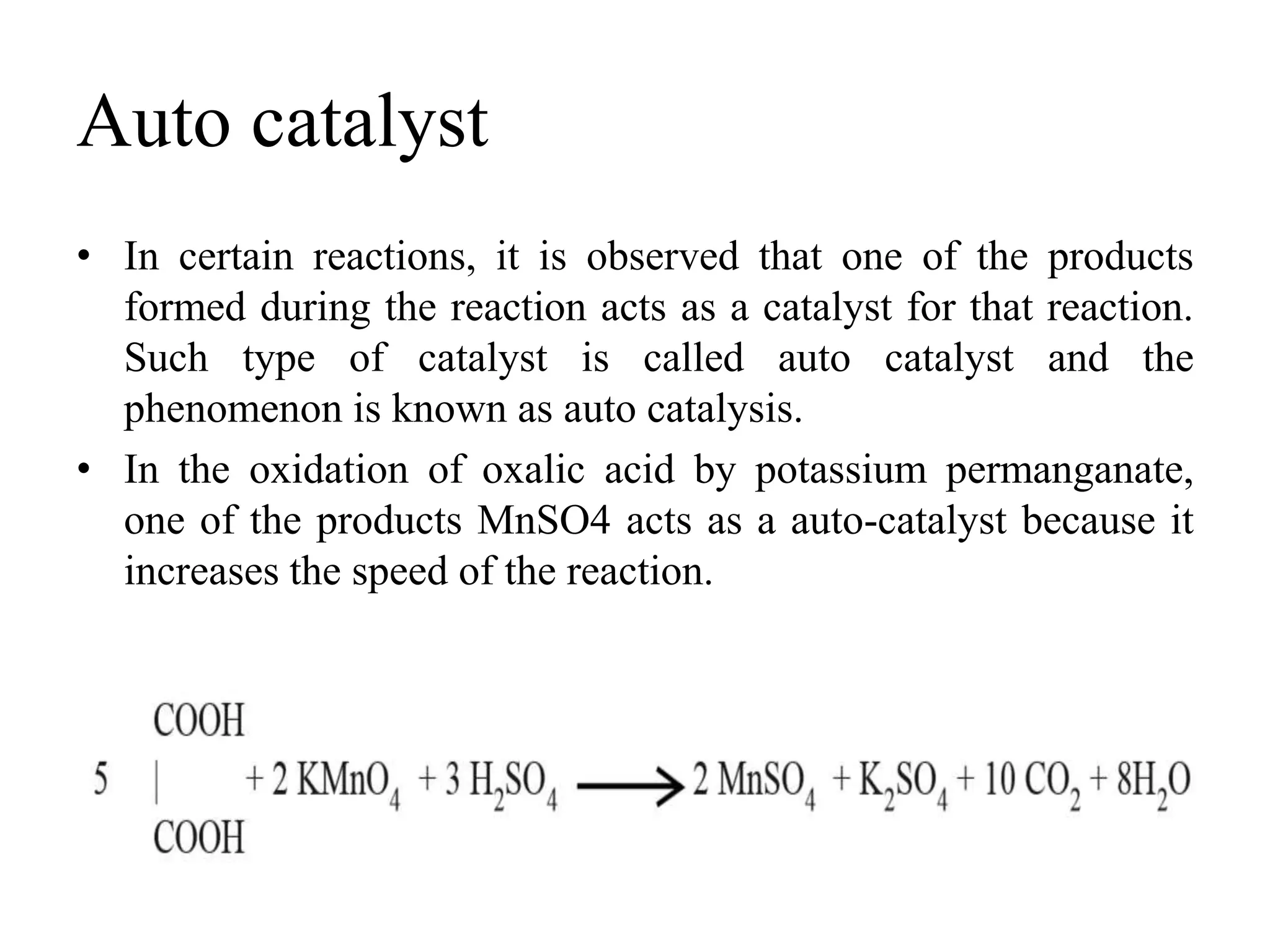
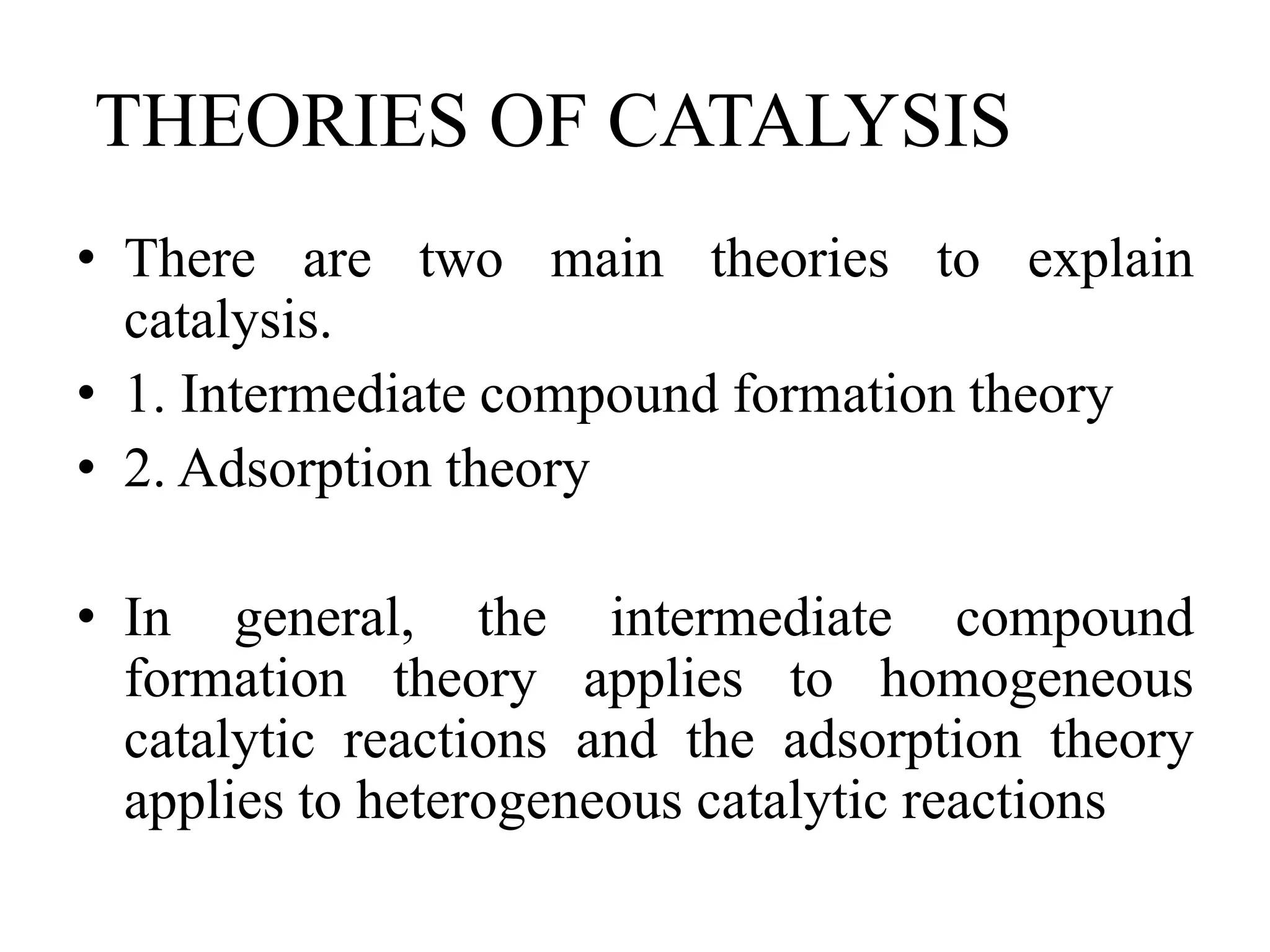
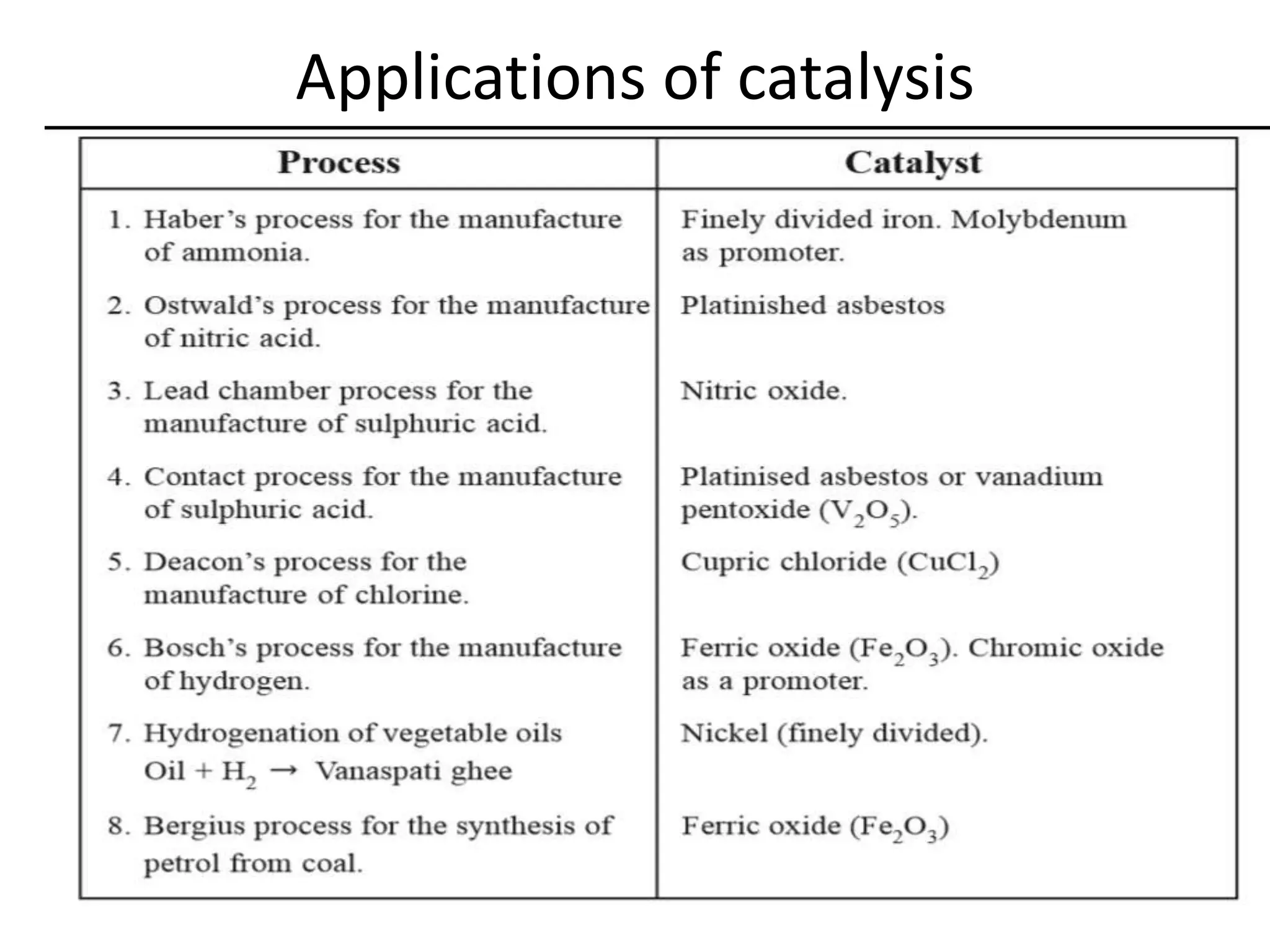
Catalysis is the process by which a catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any permanent chemical change. A catalyst works by providing an alternative reaction pathway or mechanism that has a lower activation energy. There are two main types of catalysis: homogeneous catalysis where the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants, and heterogeneous catalysis where the catalyst is in a different phase. Catalysts can be classified as positive or negative depending on whether they increase or decrease the reaction rate.