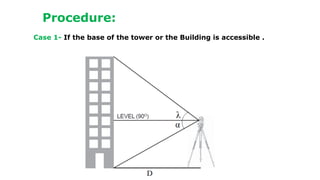
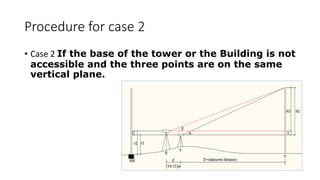
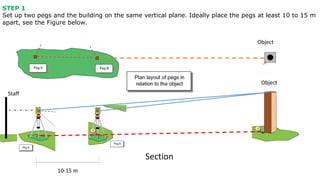
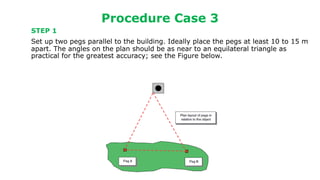
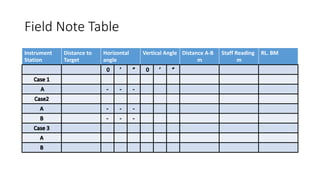
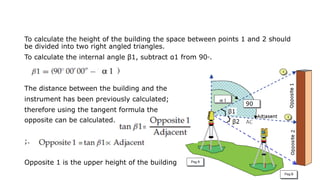
The document describes procedures for measuring the height of an inaccessible building using a theodolite. It outlines 3 cases: 1) the building base is accessible, 2) the base is inaccessible but 3 points lie on the same vertical plane, and 3) the base is inaccessible and points do not lie on the same plane. For each case, it provides step-by-step instructions, formulas used, and an example field note table. Calculations involve using trigonometric functions like tangent and sine based on measured angles and distances to calculate heights.