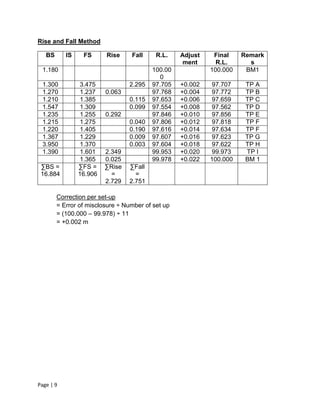
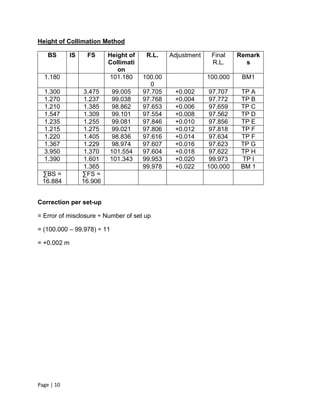
The document summarizes a fieldwork report on leveling. It includes an introduction to leveling, descriptions of leveling apparatus, objectives of the fieldwork, leveling data tables using rise and fall and height of collimation methods, and a conclusion. The leveling was conducted between a benchmark and turning points to determine reduced levels. The error of misclosure was within an acceptable range, so the leveling results were deemed accurate.