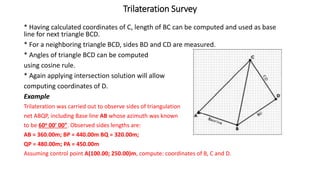
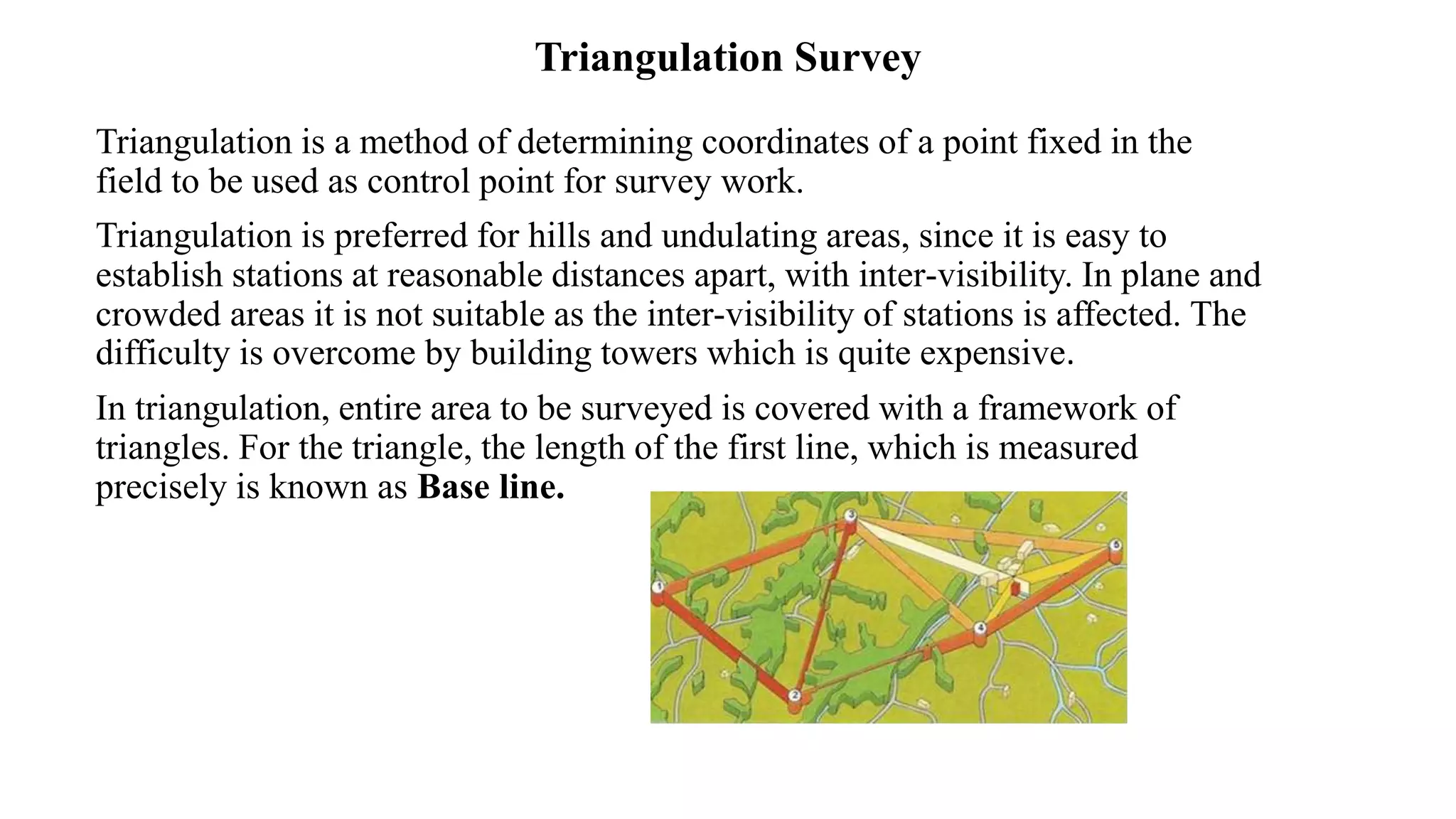
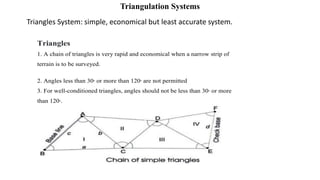
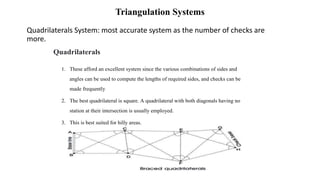
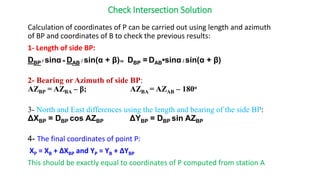
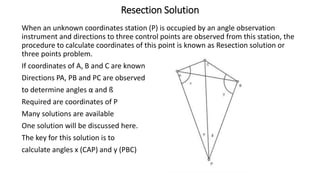
Triangulation is a surveying method that uses triangles to determine locations of points. It involves establishing a network of triangles connecting known points, then measuring angles and lengths within the triangles. Key steps include selecting station locations with good intervisibility, measuring baselines and angles, computing lengths and positions using trigonometry, and establishing additional points through intersection or resection. Modern trilateration uses distance measurements instead of angles to speed up the process and improve accuracy when using electronic distance measurement.








![Intersection Formula
The following formulae are called intersection formula, used to calculate
coordinates of P by directly substituting the given and observed data:
NP = {EA – EB + NA cot β + NB cot α} / [cot α + cot β]
EP = {NB - NA + EA cot β + EB cot α} / [cot α + cot β]
NOTE: Direct substitution should be done when observing A and B from P
should be seen clockwise direction. This means standing at P observing A,
you have to turn clockwise to observe B.
Example:
A and B are ground control points of coordinates: A(200.00, 400.00)m and
B(500.00, 600.00)m. Angles observed at A and B towards station P (almost
east of A) are 65o 00’ 00” and 67o 00’ 00” respectively, compute coordinates
of P.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/se312ch3-triangulationsurvey-230521135653-88736fff/85/se_312_ch_3_-triangulation_survey-pptx-13-320.jpg)


![Resection Solution
Solution of the two equations to give x and y:
1- compute constants k1 and k2
2- Substituting (1) in (2): sin x = k2 sin (k1 – x)
sin x = k2 [ sin k1 cos x - cos k1 sin x ]
Dividing both sides by cos x, tan x = k2 [sin k1 - cos k1 tan x],
hence:
tan x [1 + k2 cos k1] = k2 sin k1
tan x =k2 sin k1/[1 + k2 cos k1];
3- Substitute values of k1 and k2 to calculate x and y:
x = tan-1 {k2 sin k1/[1 + k2 cos k1]}
y = k1 –x
4- Check the solution:
In ∆ ACP, <ACP = C1; In ∆ BCP, <BCP = C2; C1 + C2 = C, already calculated in
∆ABC; also 180 – (α +C1) = x and 180 – (ß + C2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/se312ch3-triangulationsurvey-230521135653-88736fff/85/se_312_ch_3_-triangulation_survey-pptx-17-320.jpg)