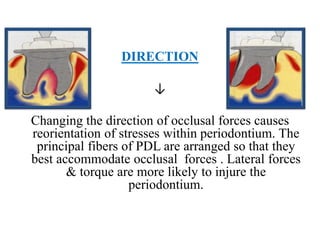
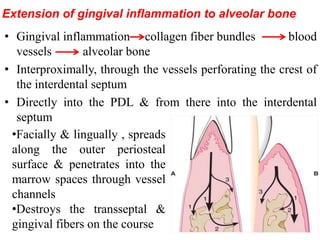
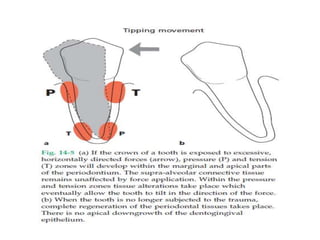
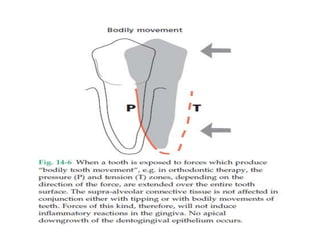
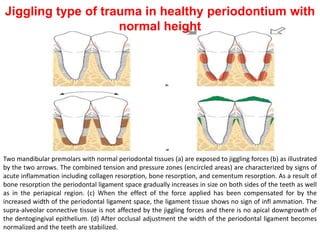
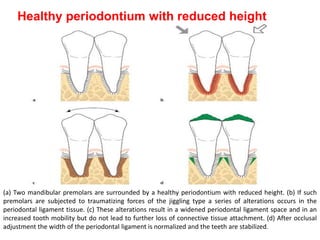
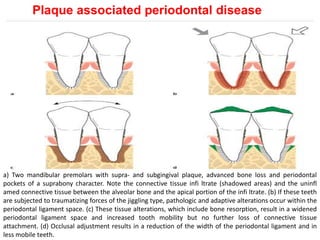
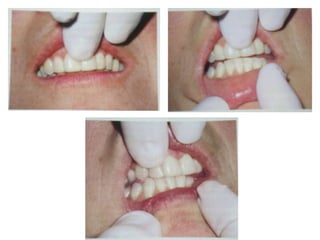
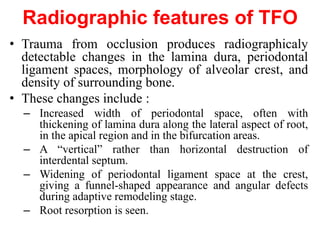
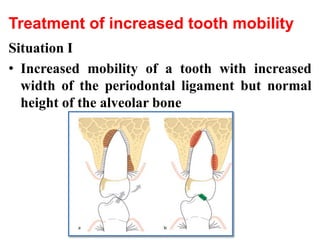
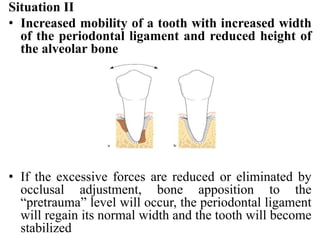
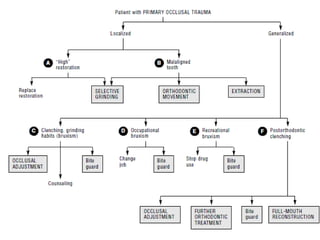
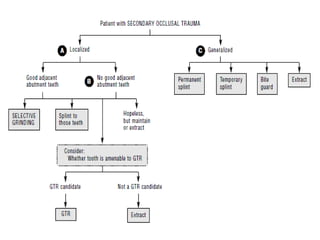
- Trauma from occlusion occurs when occlusal forces exceed the adaptive capacity of the periodontium, causing injury. It can be acute or chronic.
- The magnitude, direction, duration, and frequency of forces impact the periodontium's ability to adapt. Excessive pressure or tension can damage tissues.
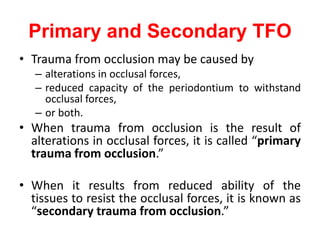
- Primary trauma from occlusion is caused by changes in occlusal forces, while secondary trauma occurs when reduced bone support impairs the tissues' resistance to normal forces.
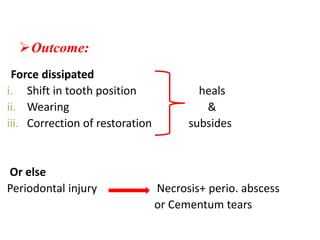
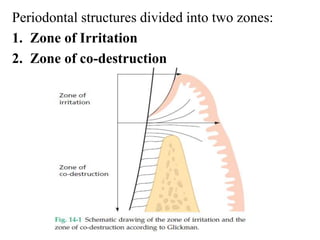
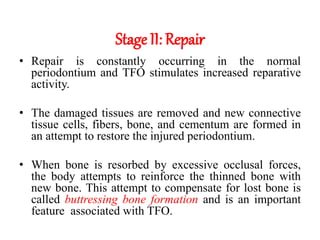
- The periodontium responds to trauma in three stages - injury, repair through new tissue formation, and adaptive remodeling to better withstand forces. Trauma can cause reversible damage if forces are reduced, or lead to irreversible injury if