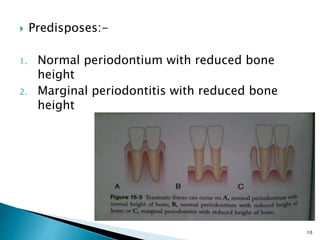
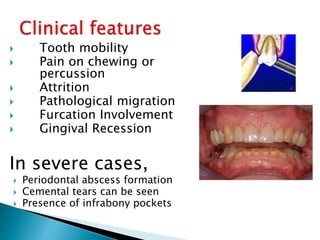
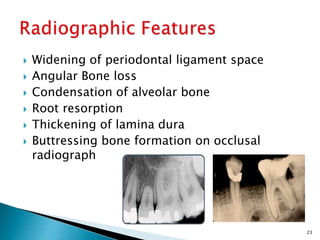
This document discusses trauma from occlusion (TFO). It begins by defining TFO as pathologic alterations or adaptive changes that develop in the periodontium as a result of undue force from chewing muscles. It describes primary TFO resulting from sudden impacts and secondary TFO from gradual changes that occur with reduced bone support. Clinical features include tooth pain and mobility. Radiographic features include widened ligament space and buttressing bone. Treatment focuses on reducing tooth mobility, eliminating prematurities, and using splints. While TFO alone may increase mobility, inflammation is required for attachment loss.