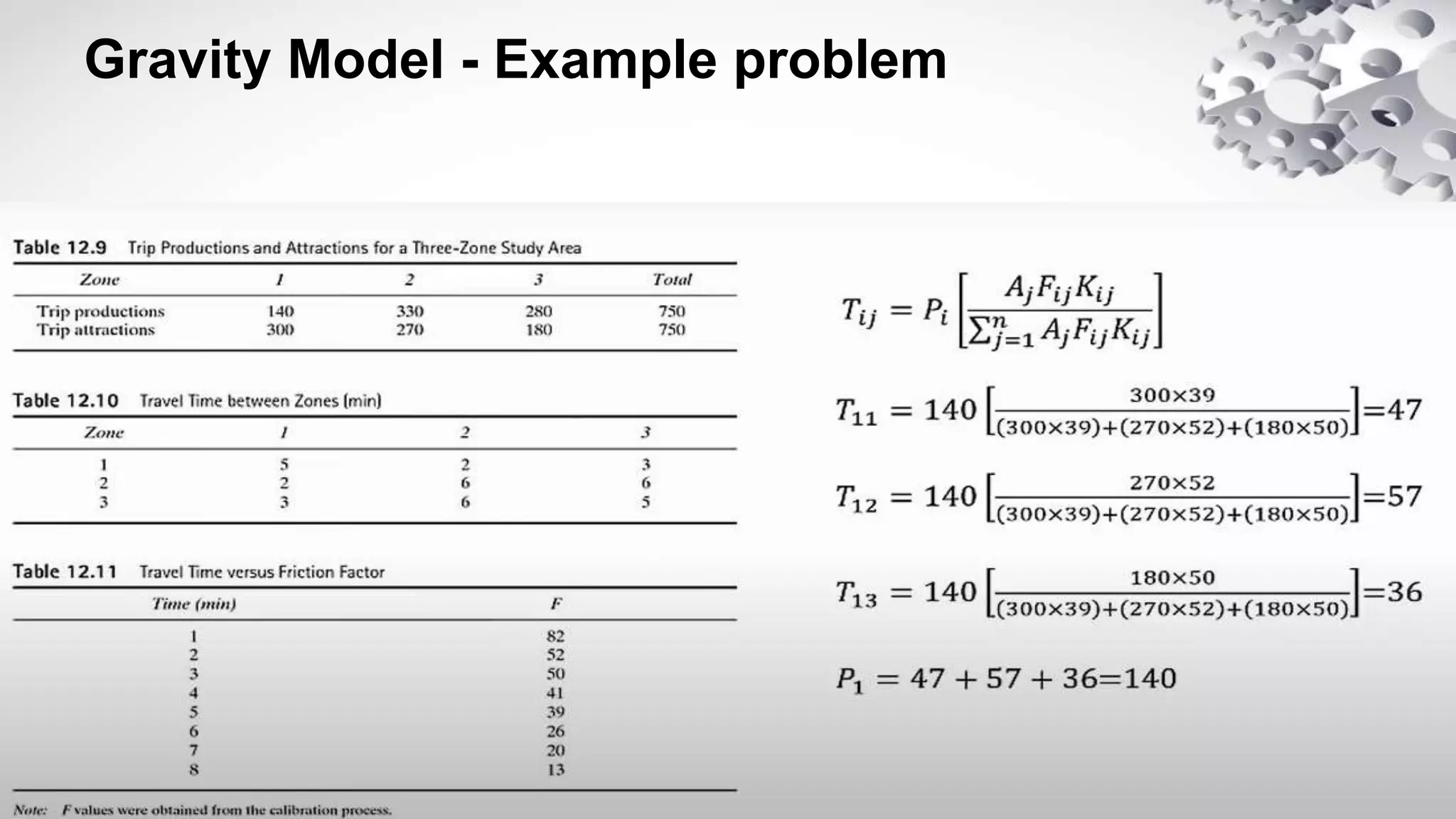
Trip distribution is a model that distributes trips between origin and destination zones based on trip production and attraction models. It balances productions and attractions within each zone by ensuring they are equal and proportionately adjusting attractions to match productions. The most widely used trip distribution method is the gravity model, which distributes trips throughout the transportation network based on travel time and other socioeconomic factors between zones.