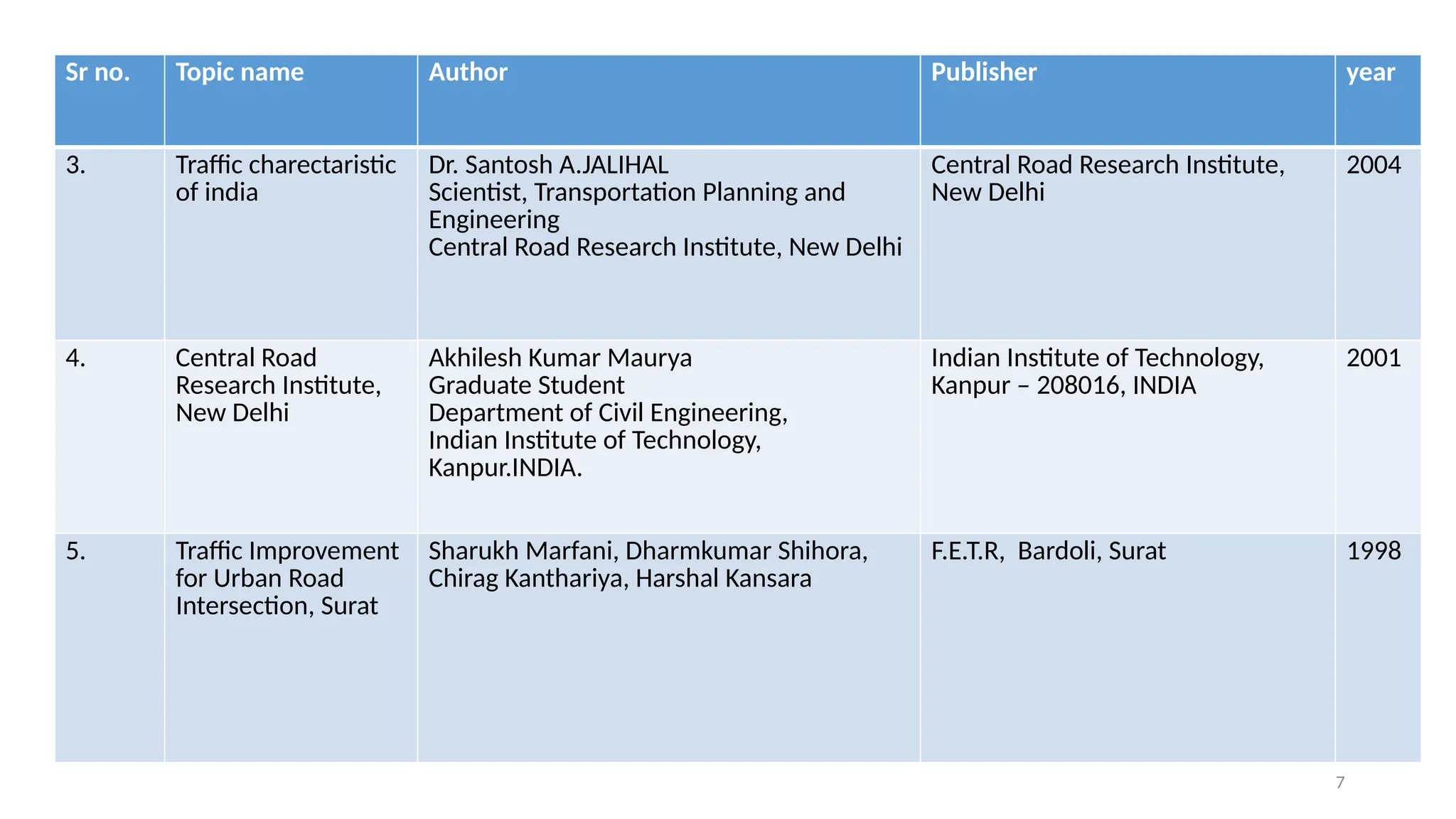
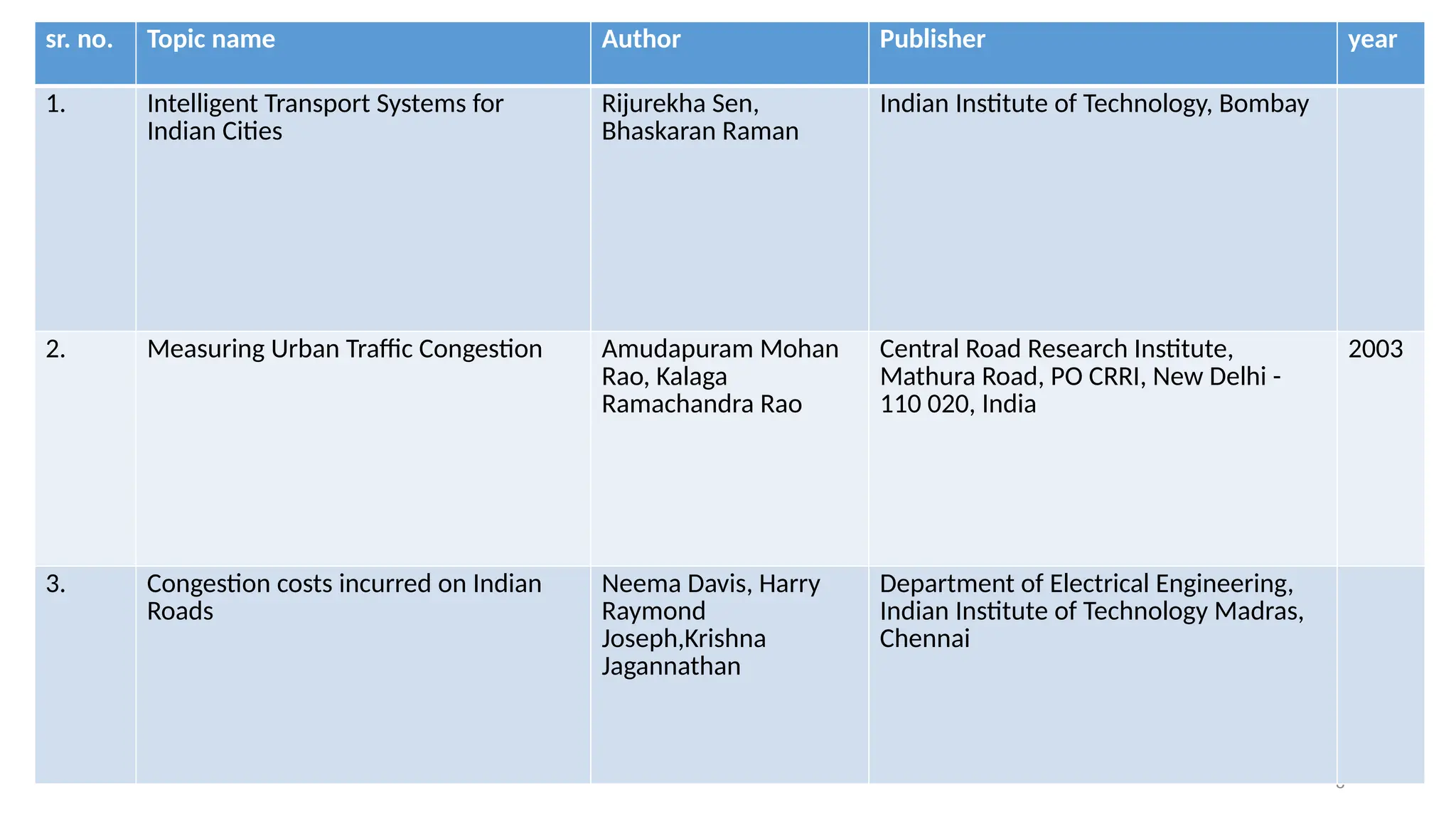
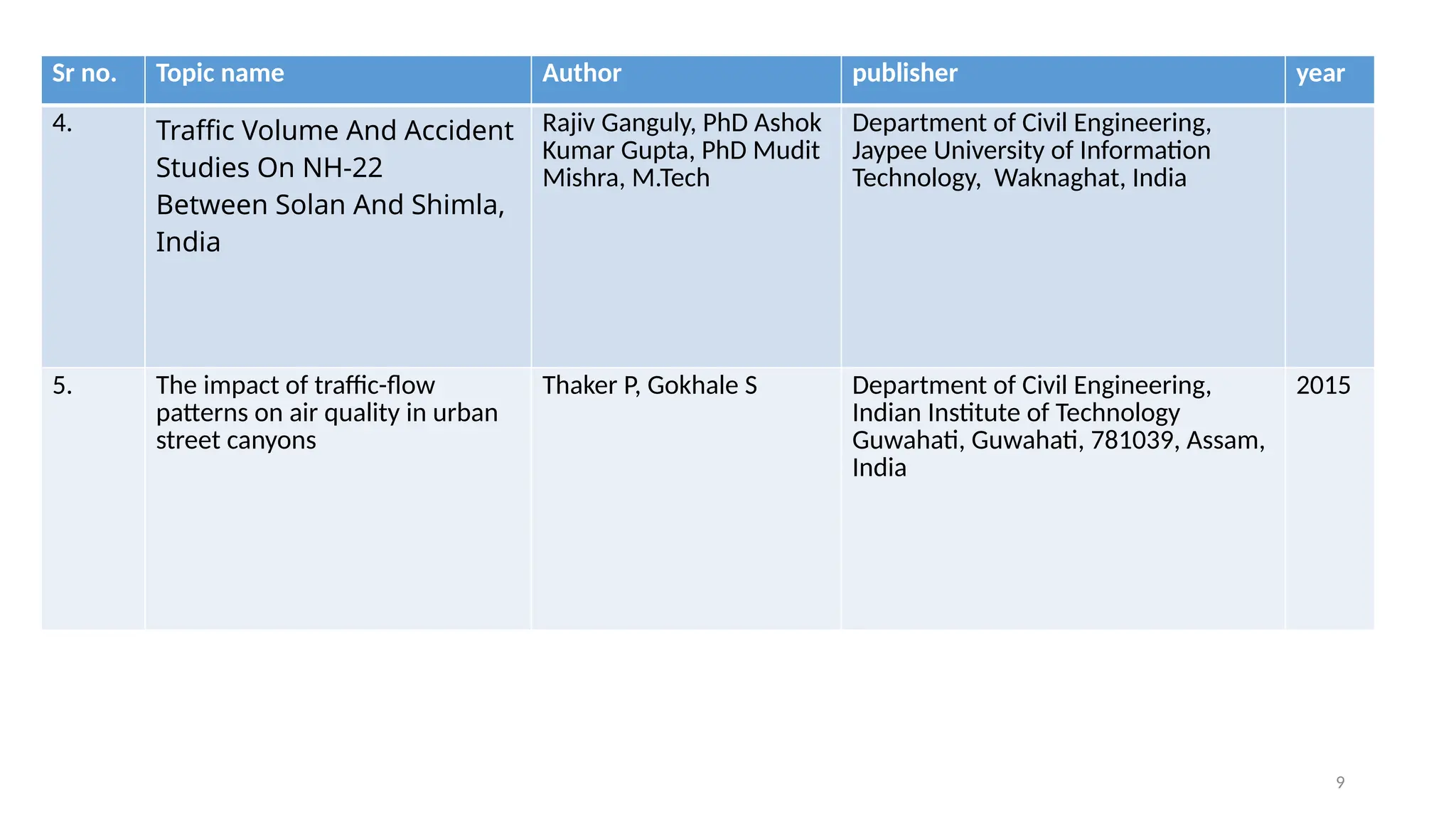
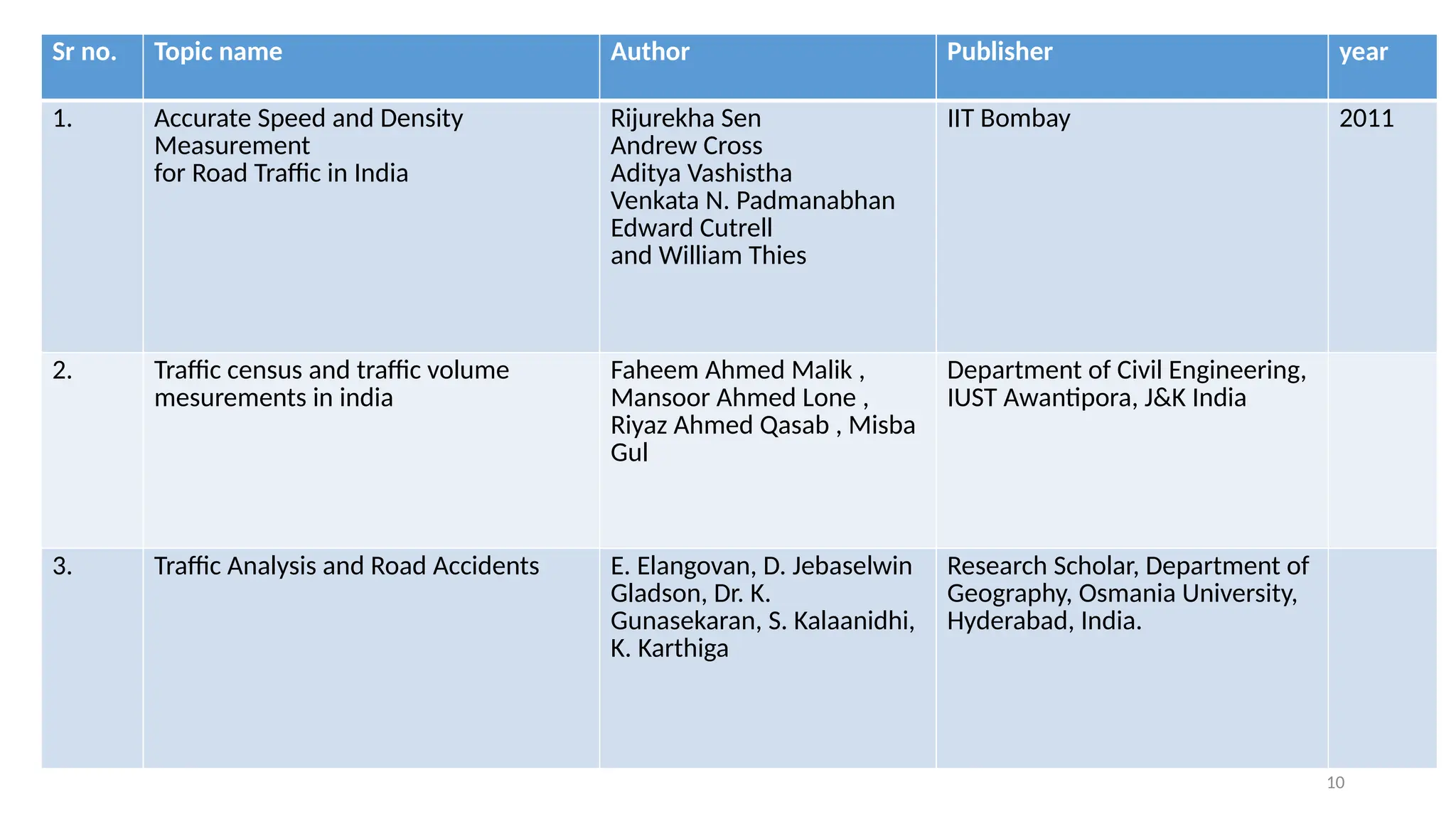
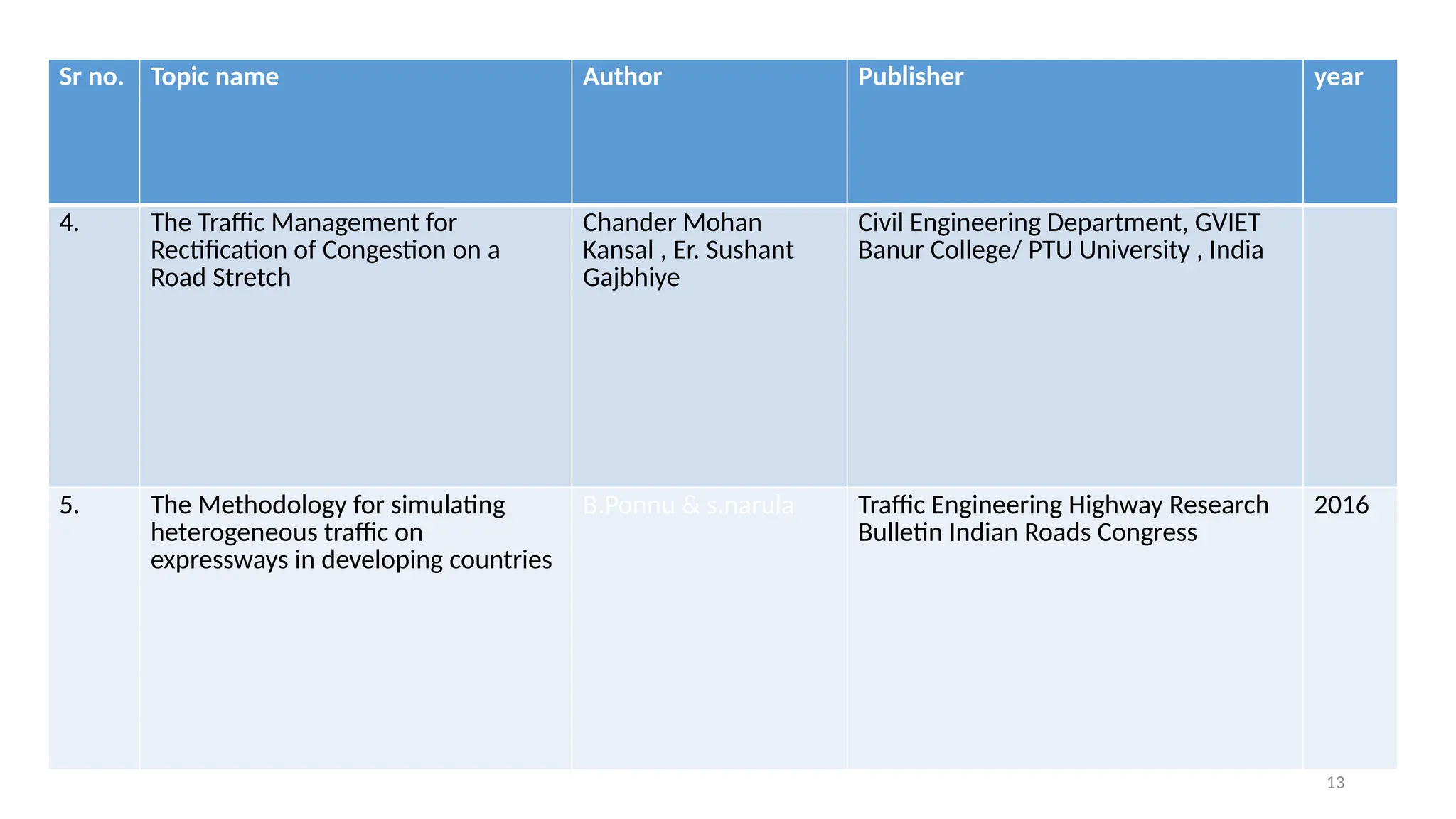
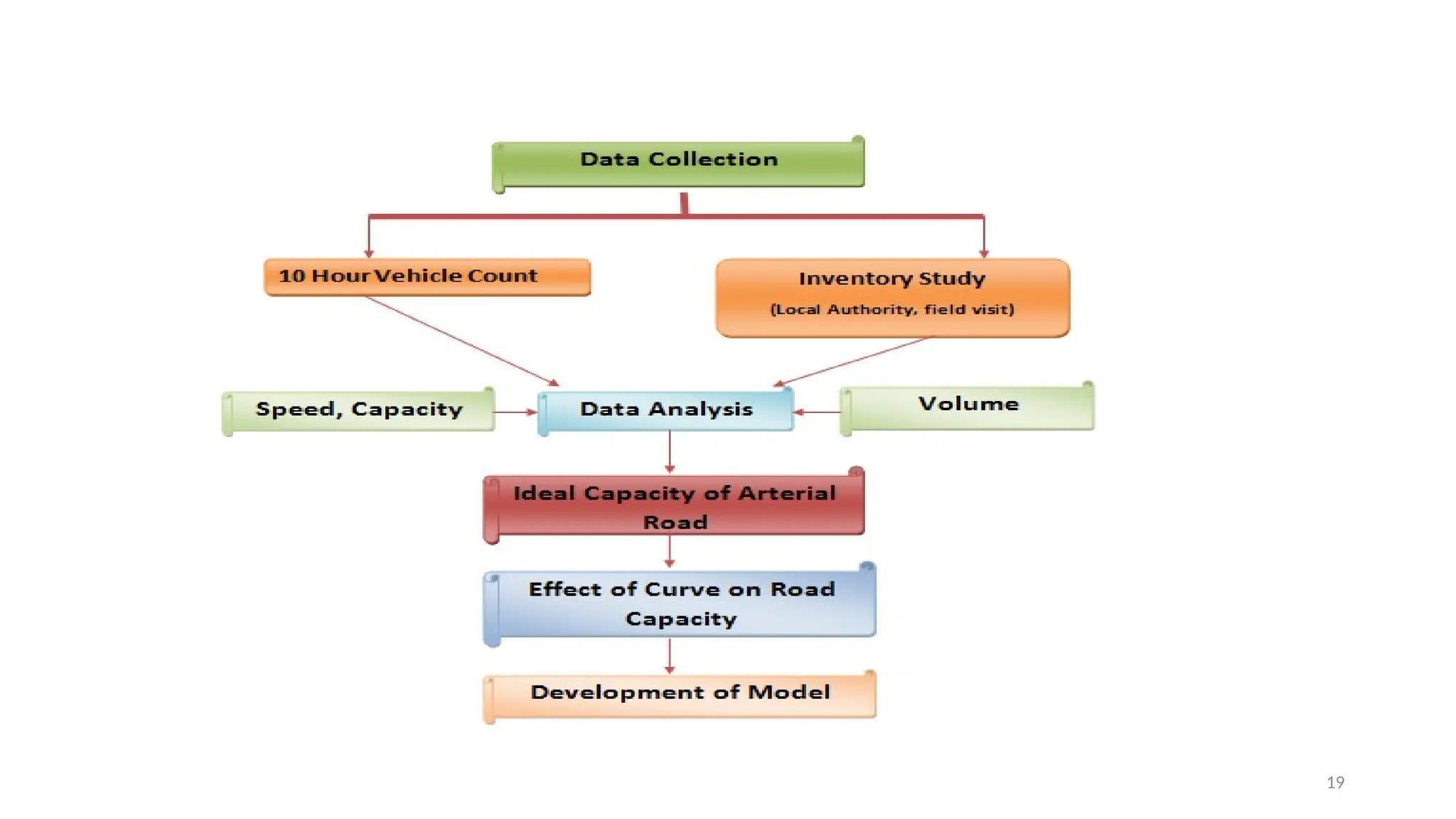
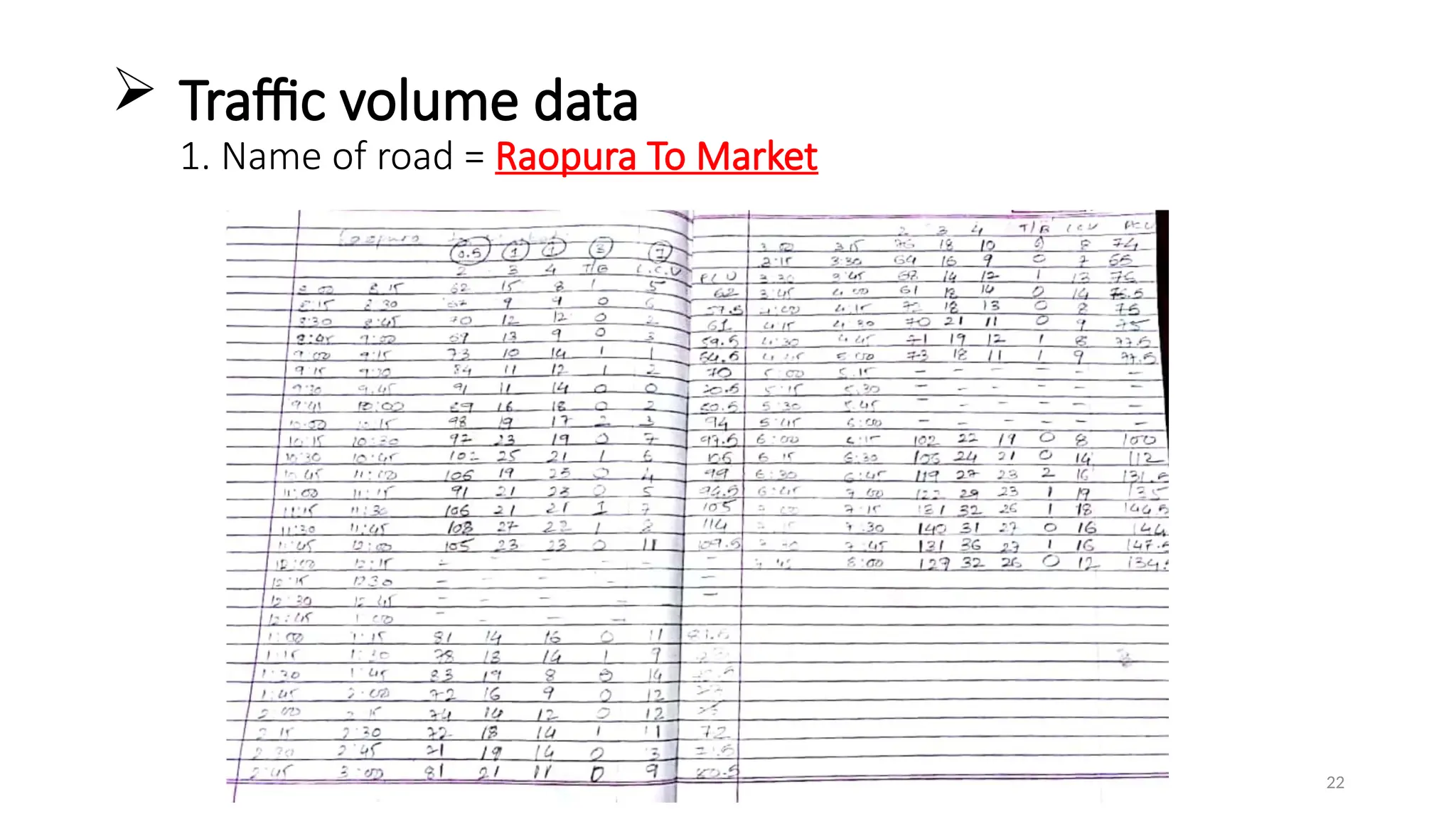
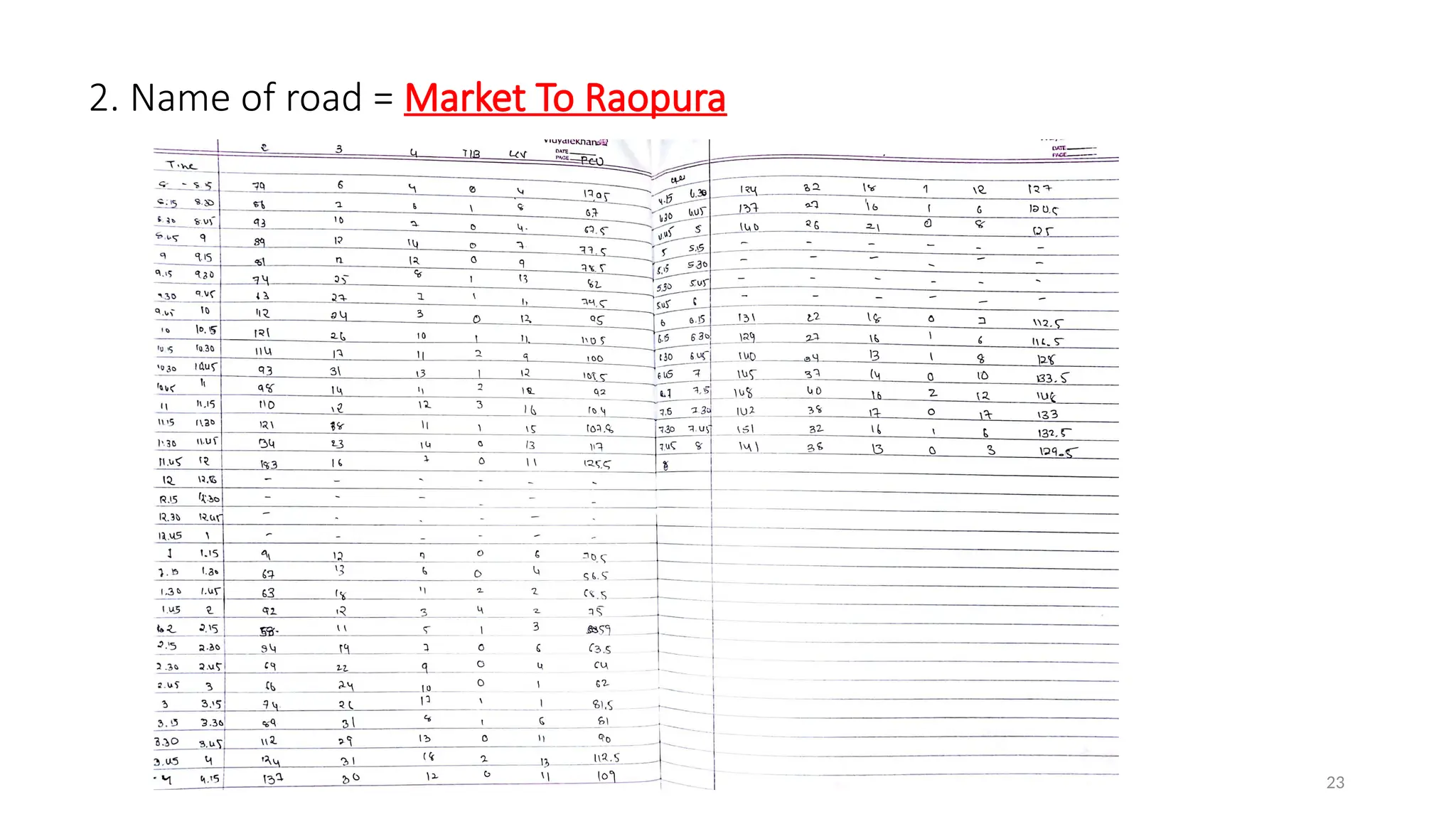
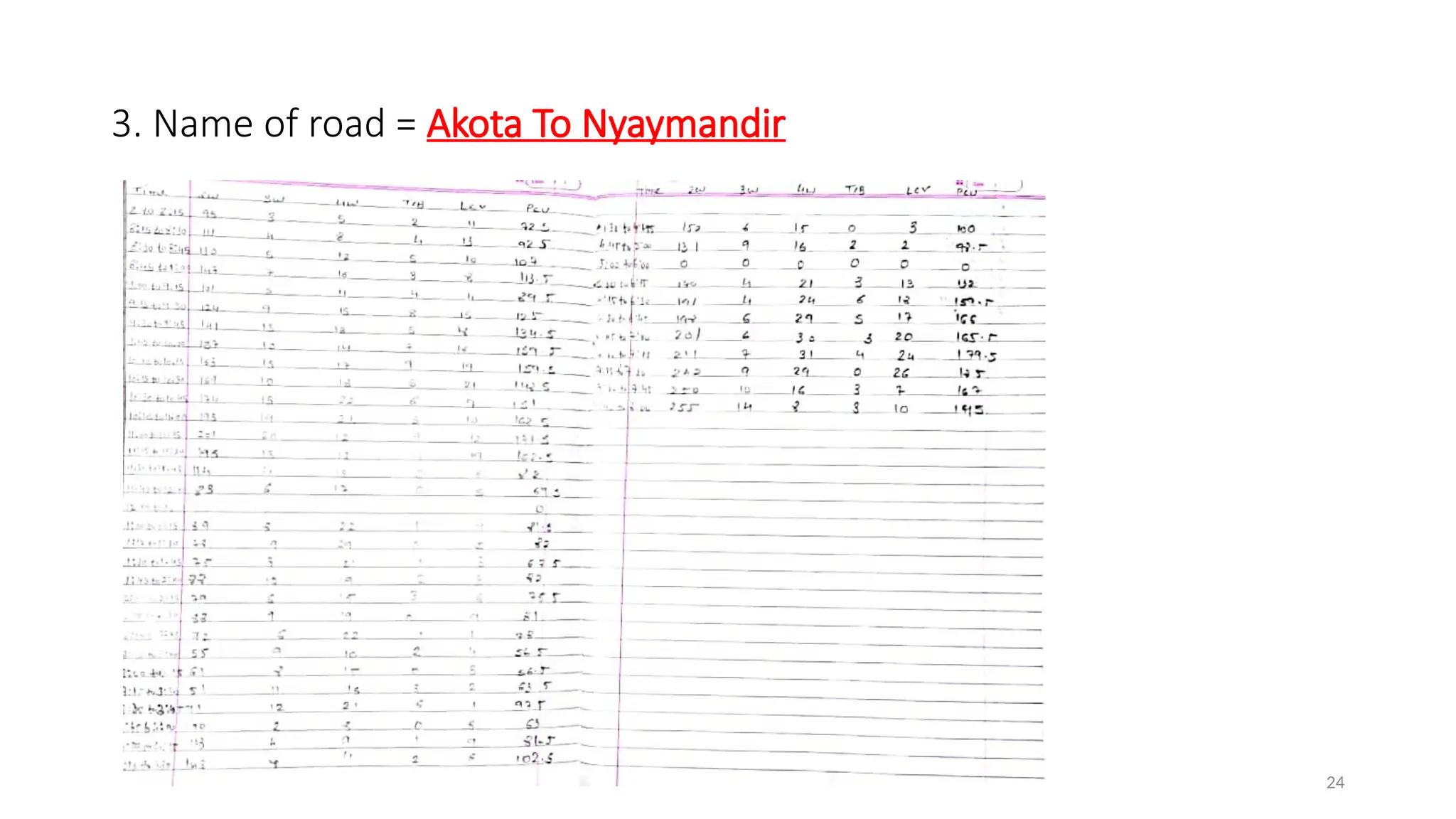
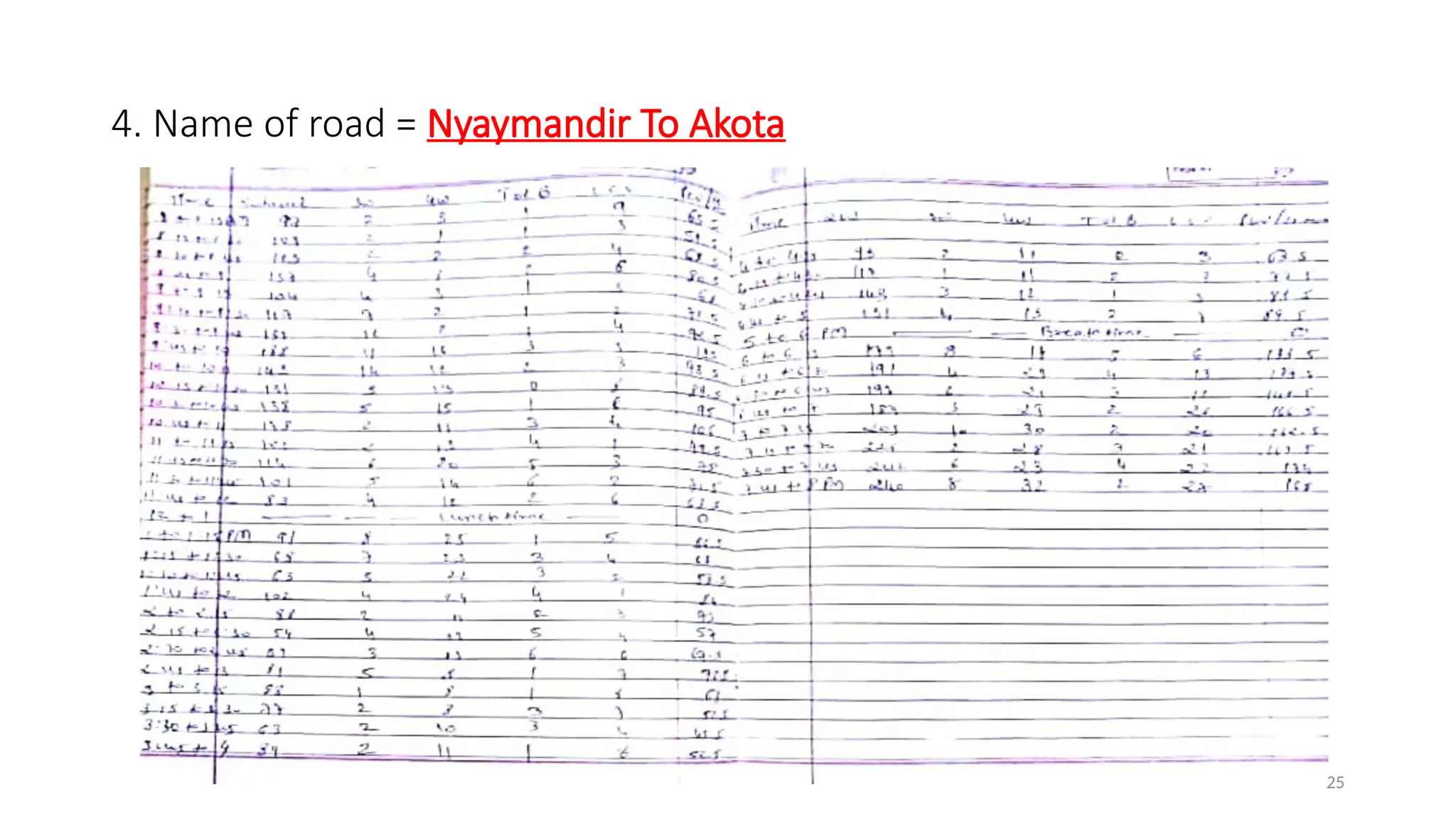
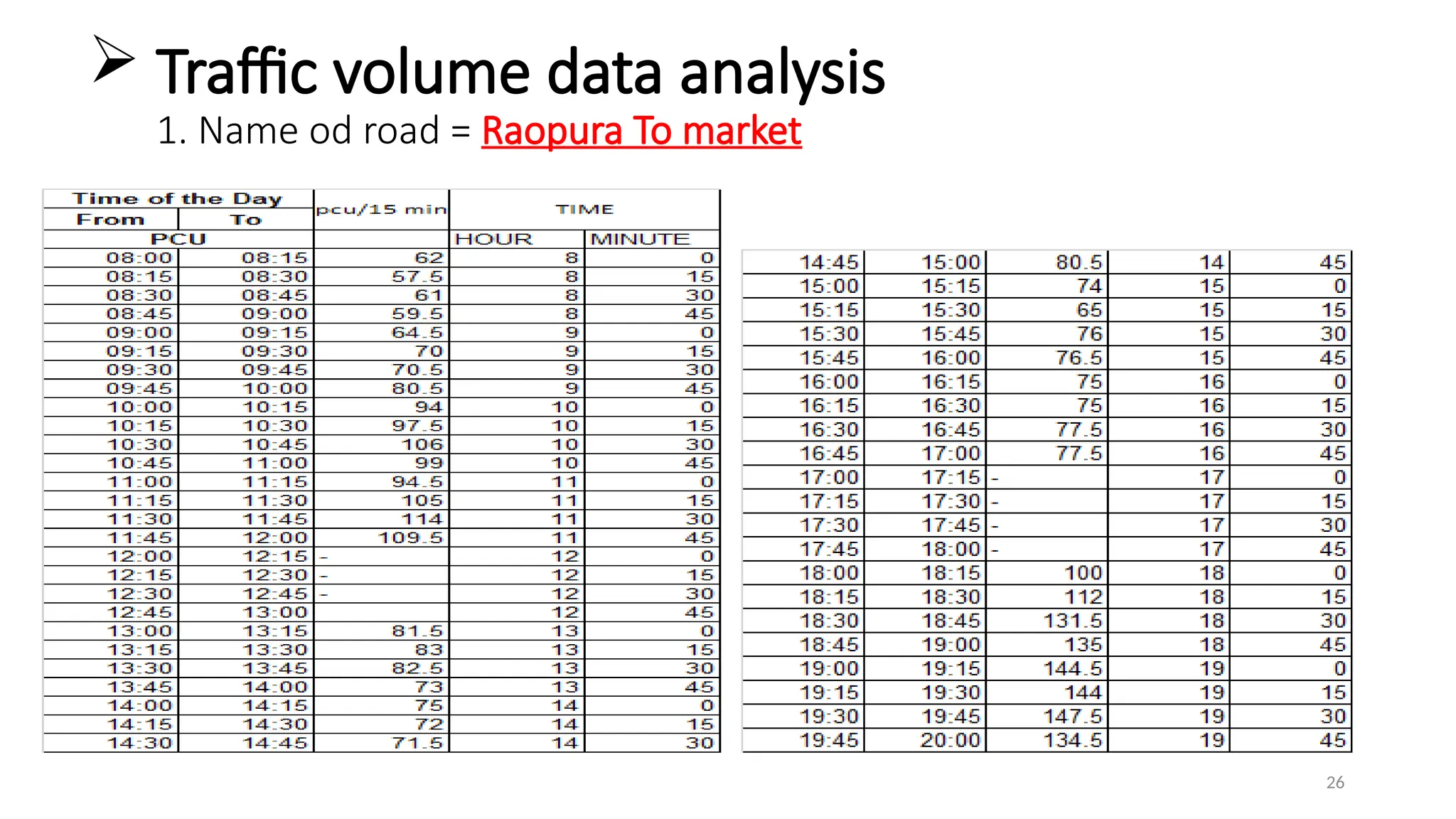
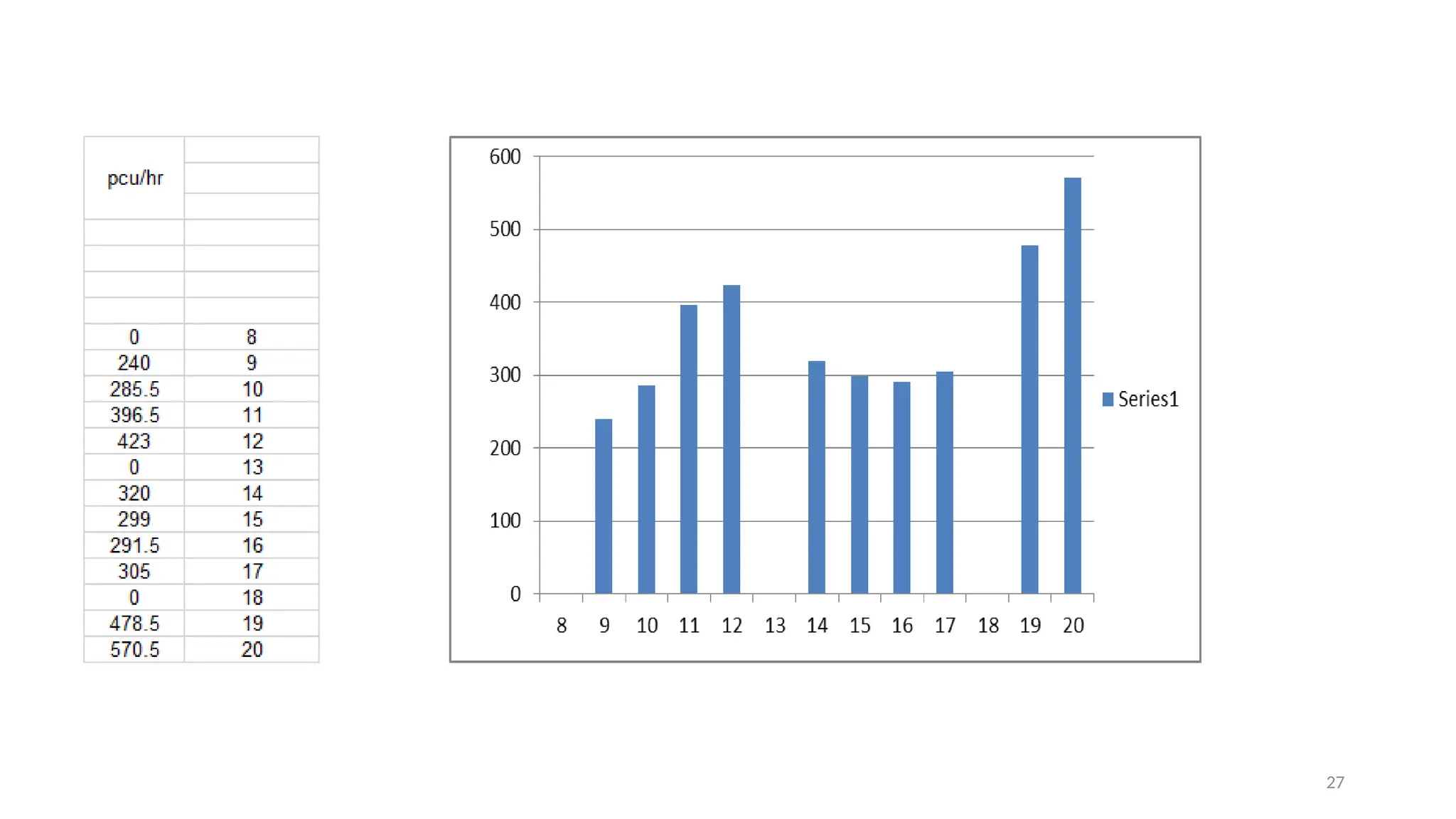
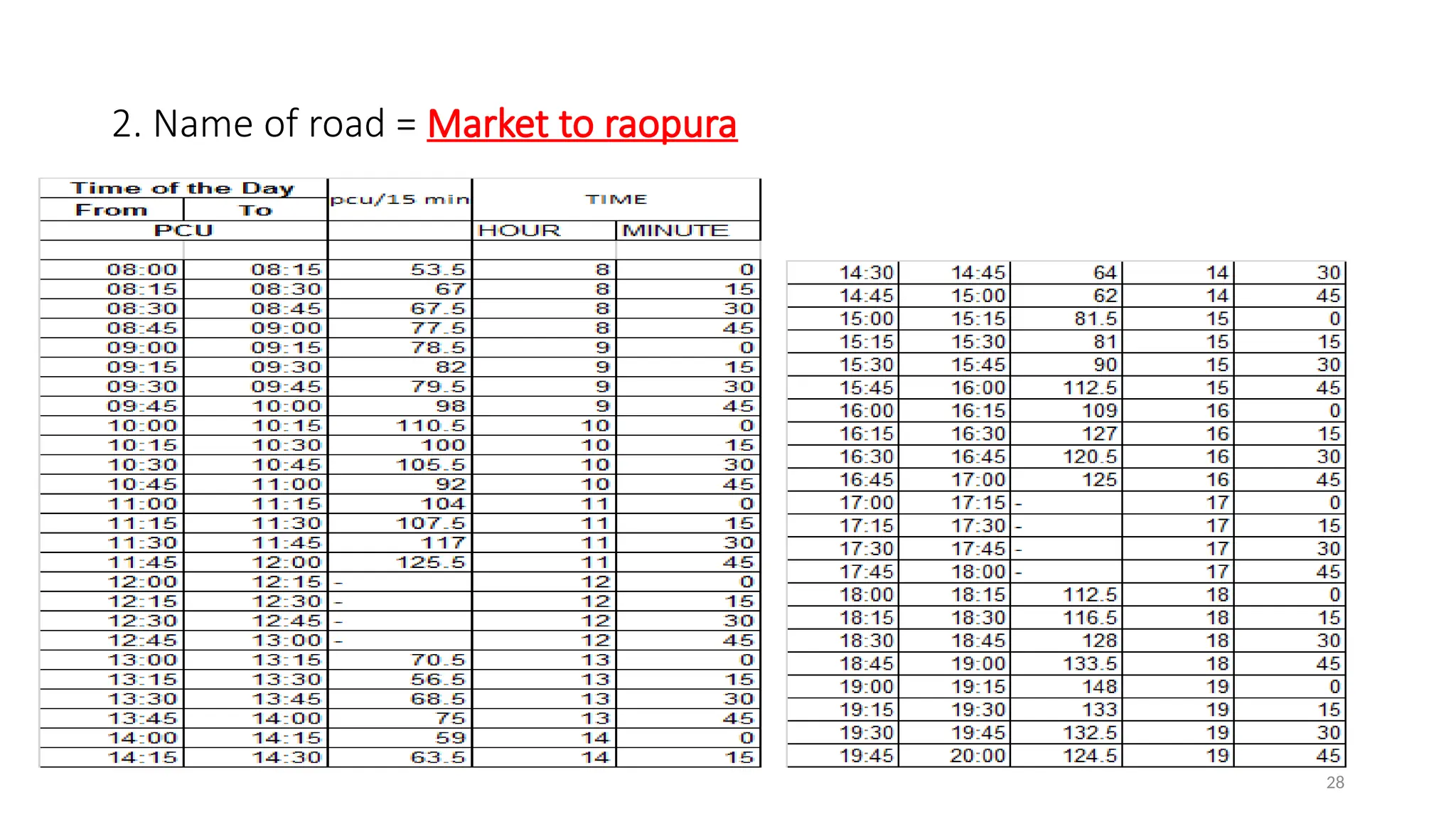
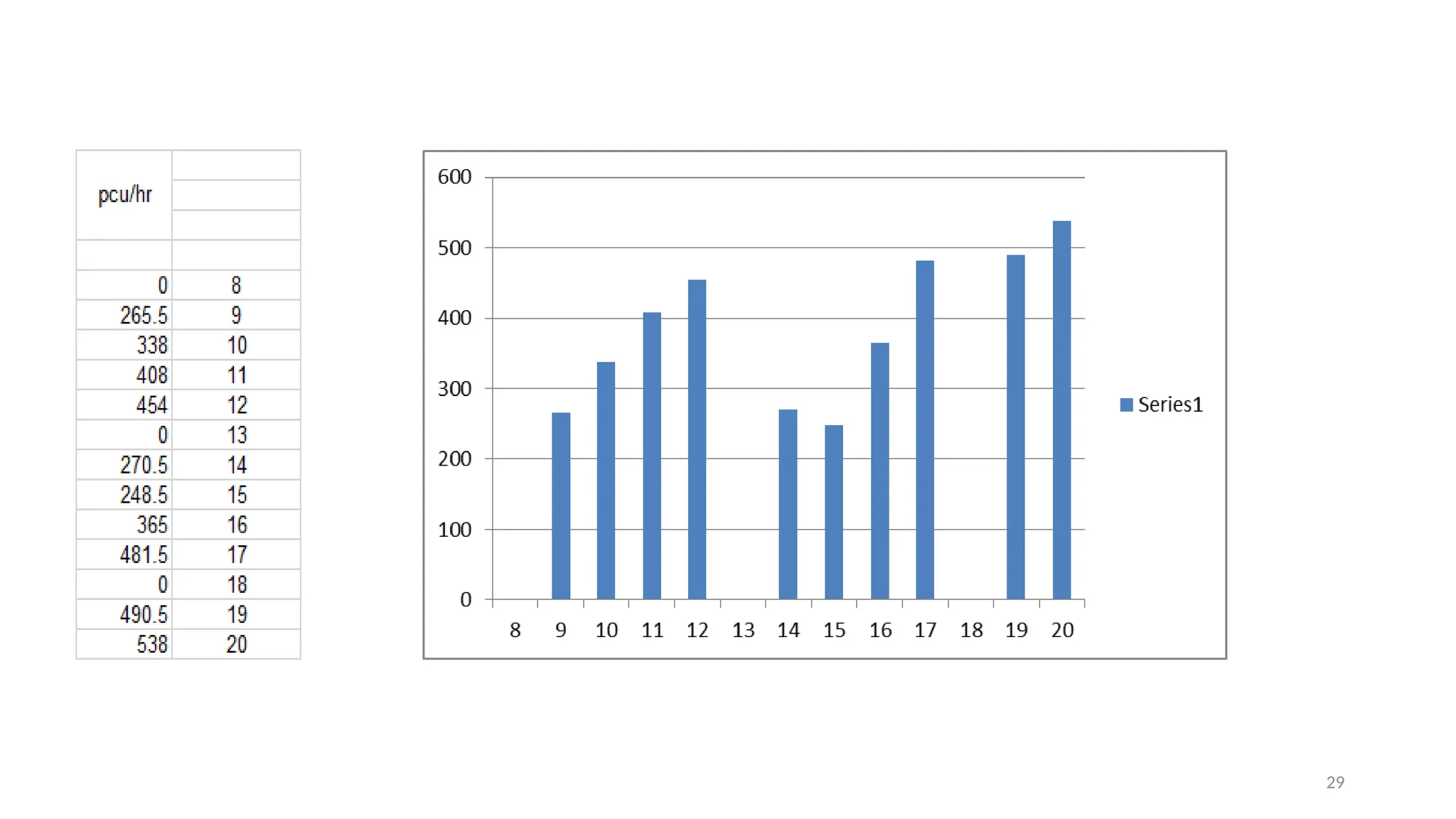
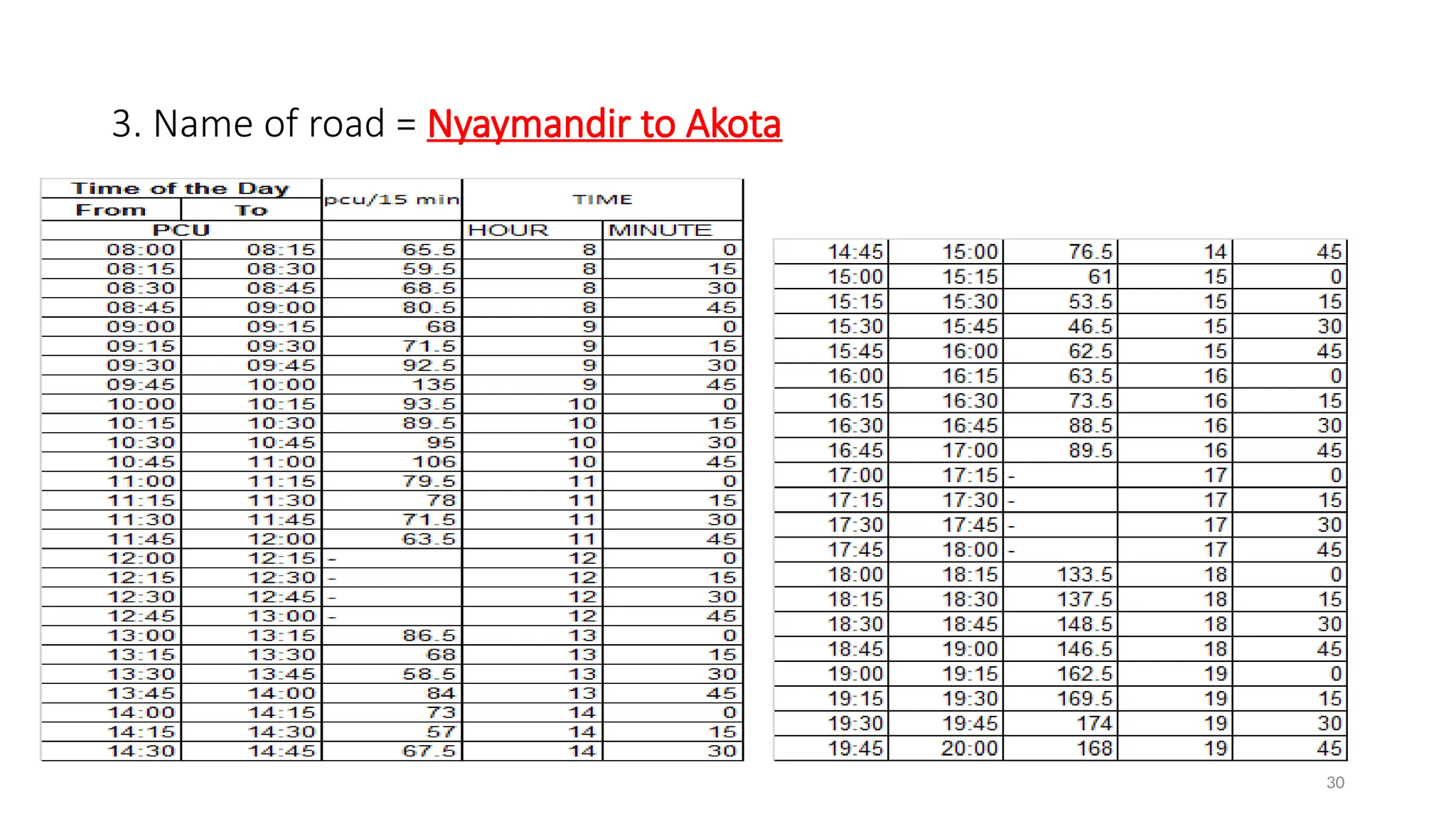
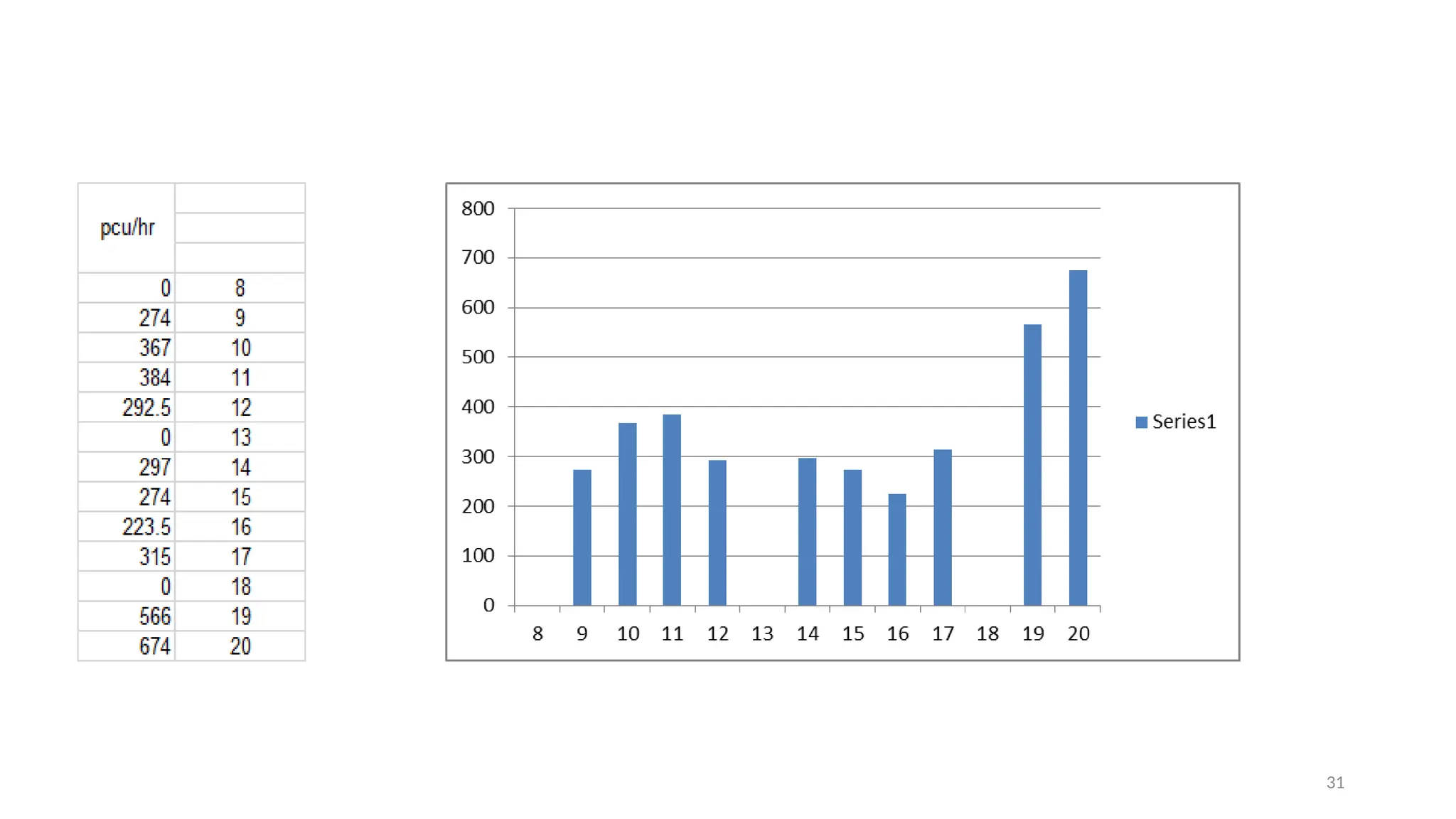
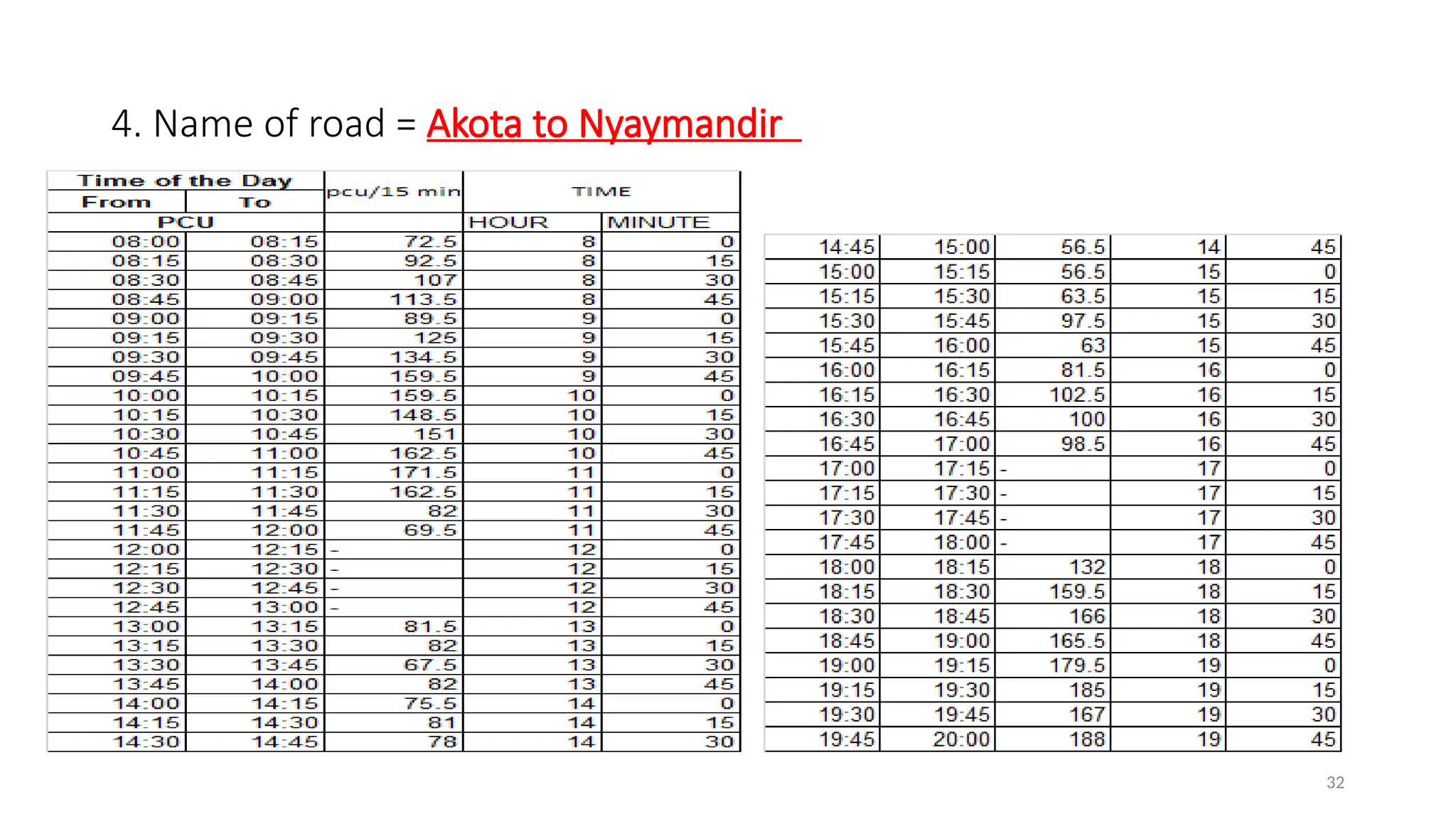
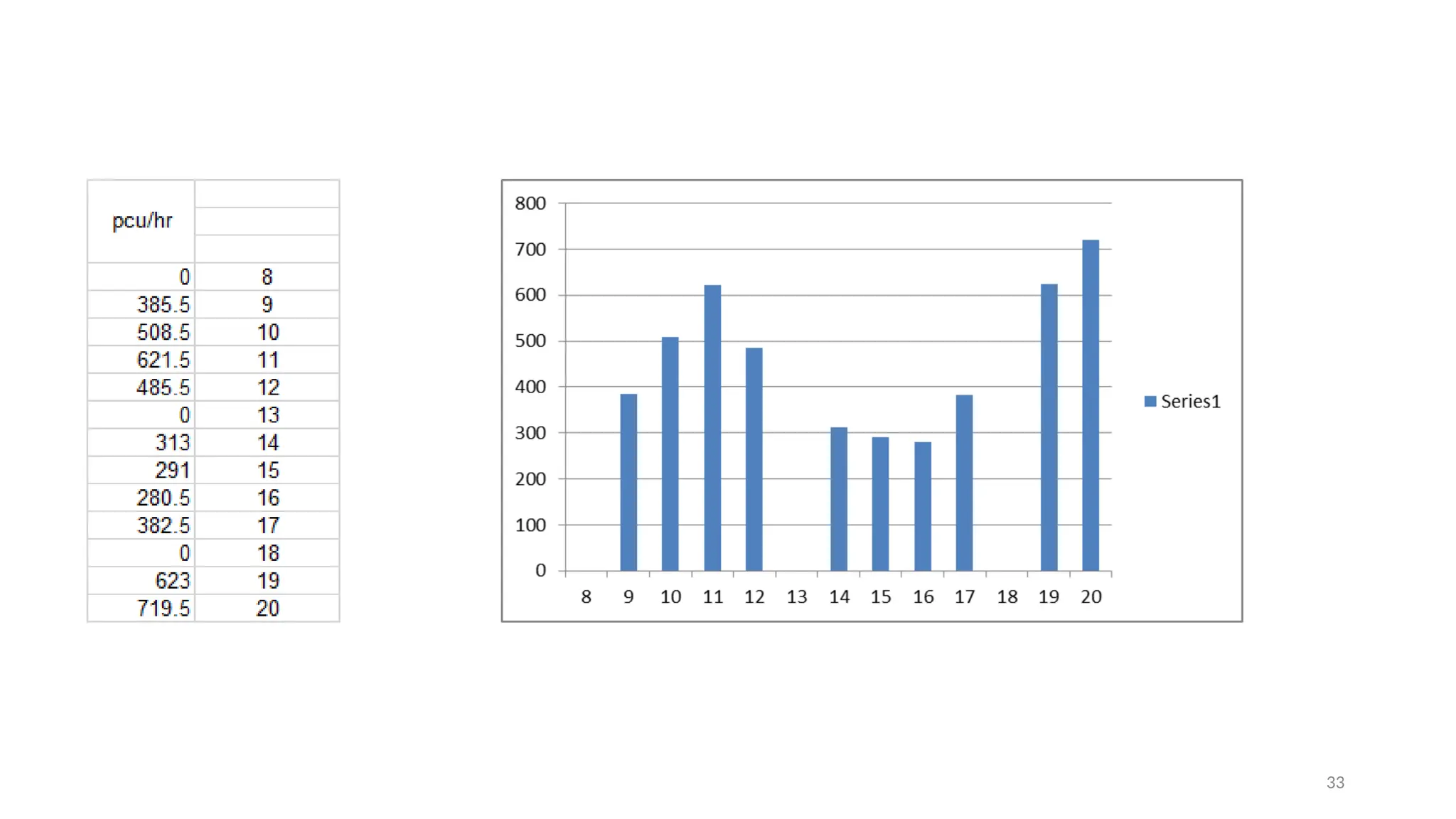
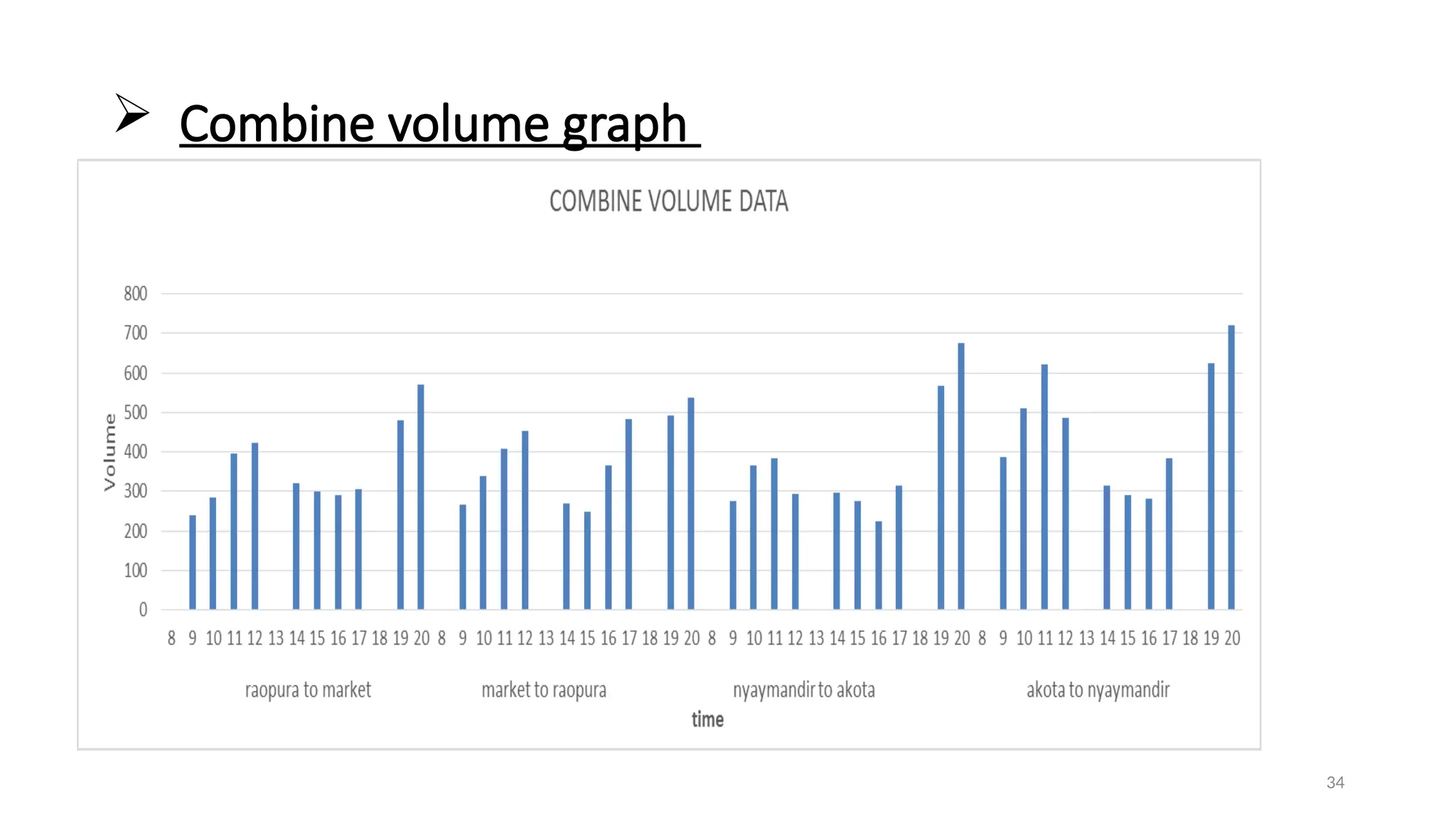
The document presents a case study on traffic flow patterns at Dandiya Bazar crossing in Vadodara, highlighting issues such as low public transport usage, congestion, and traffic signal mismanagement. It analyzes changing traffic characteristics and travel patterns, emphasizing the impact of increased vehicle ownership due to economic liberalization. A detailed methodology for data collection and analysis is provided, with reference to published studies on related traffic issues.