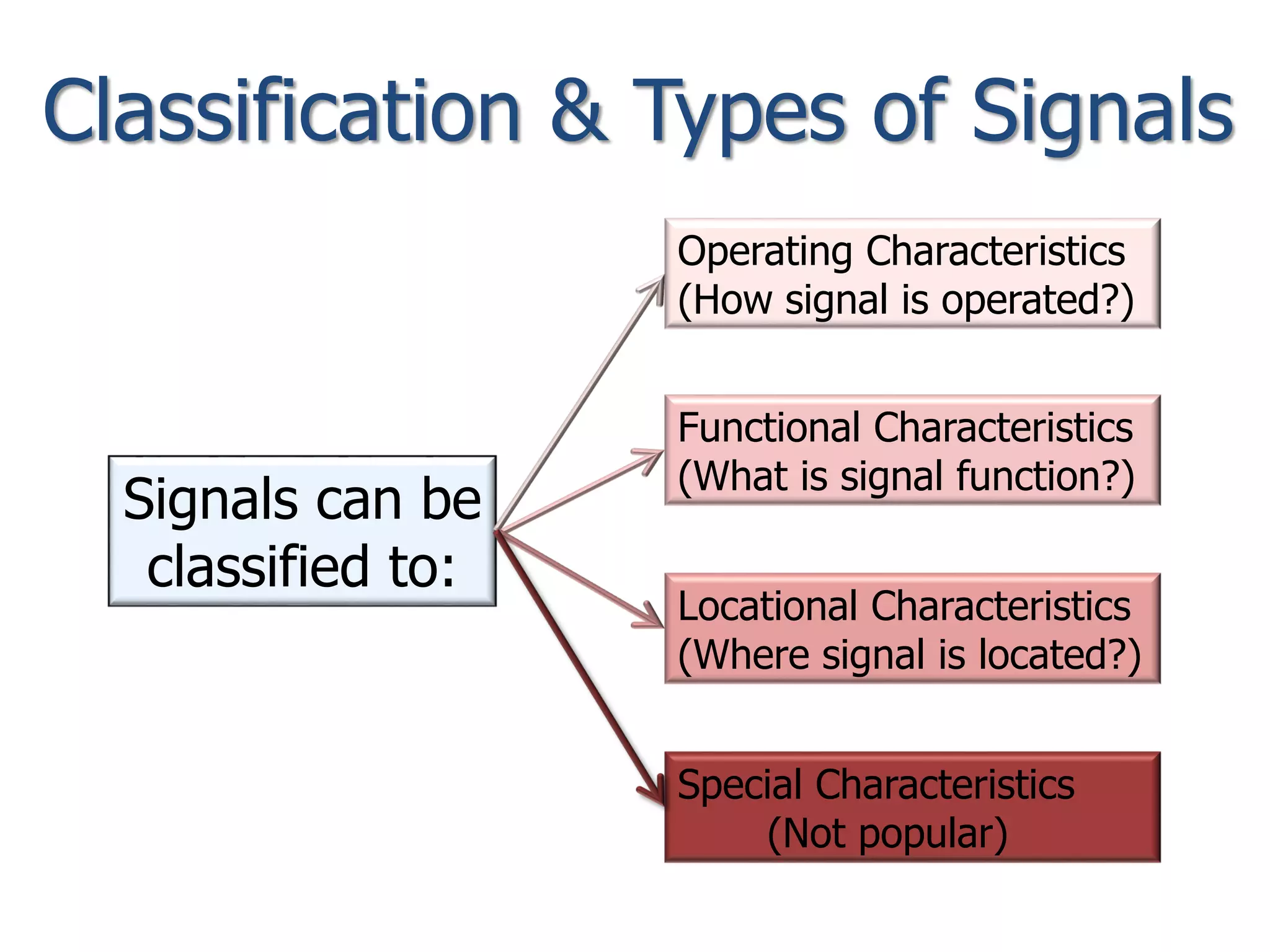
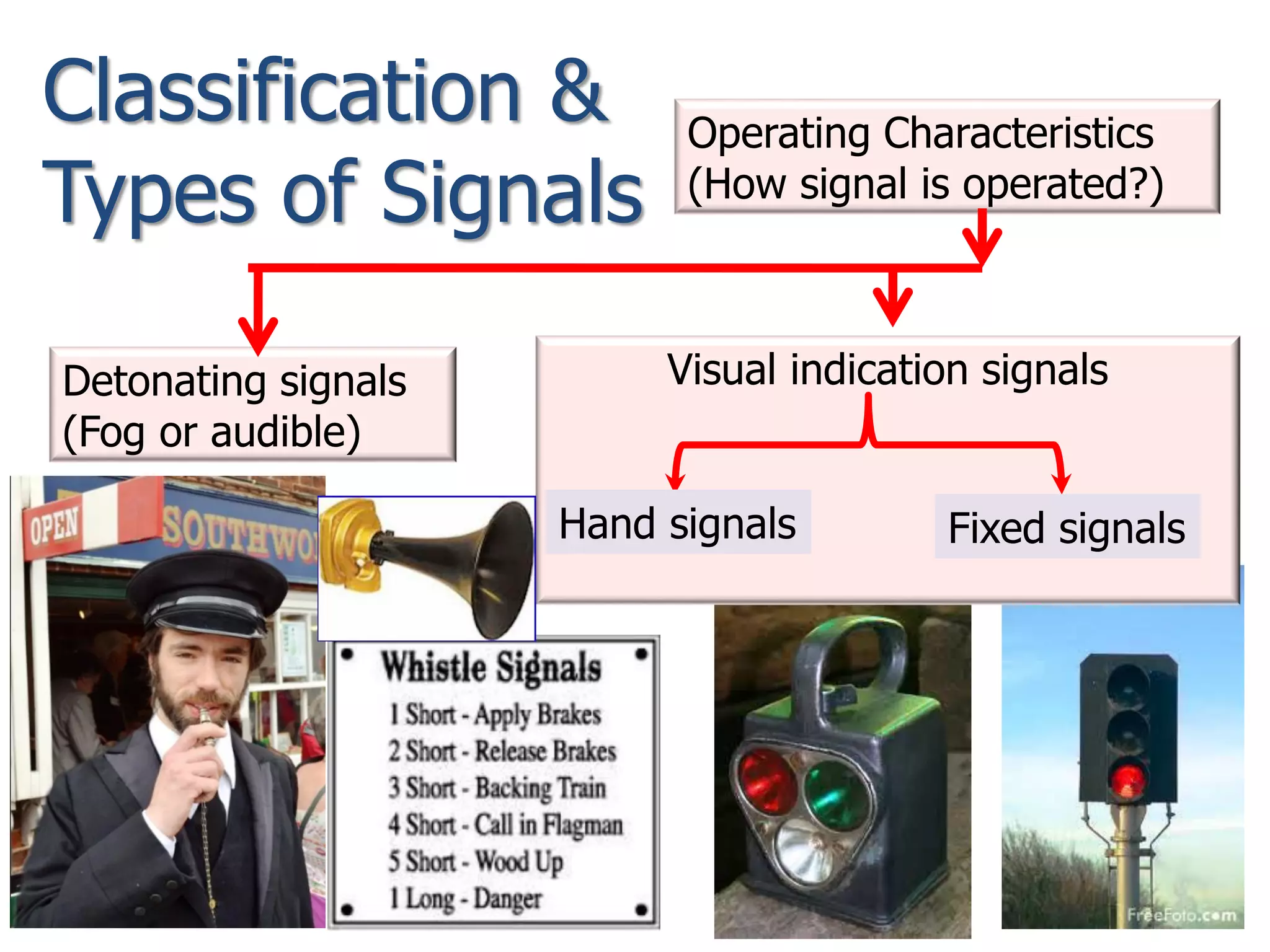
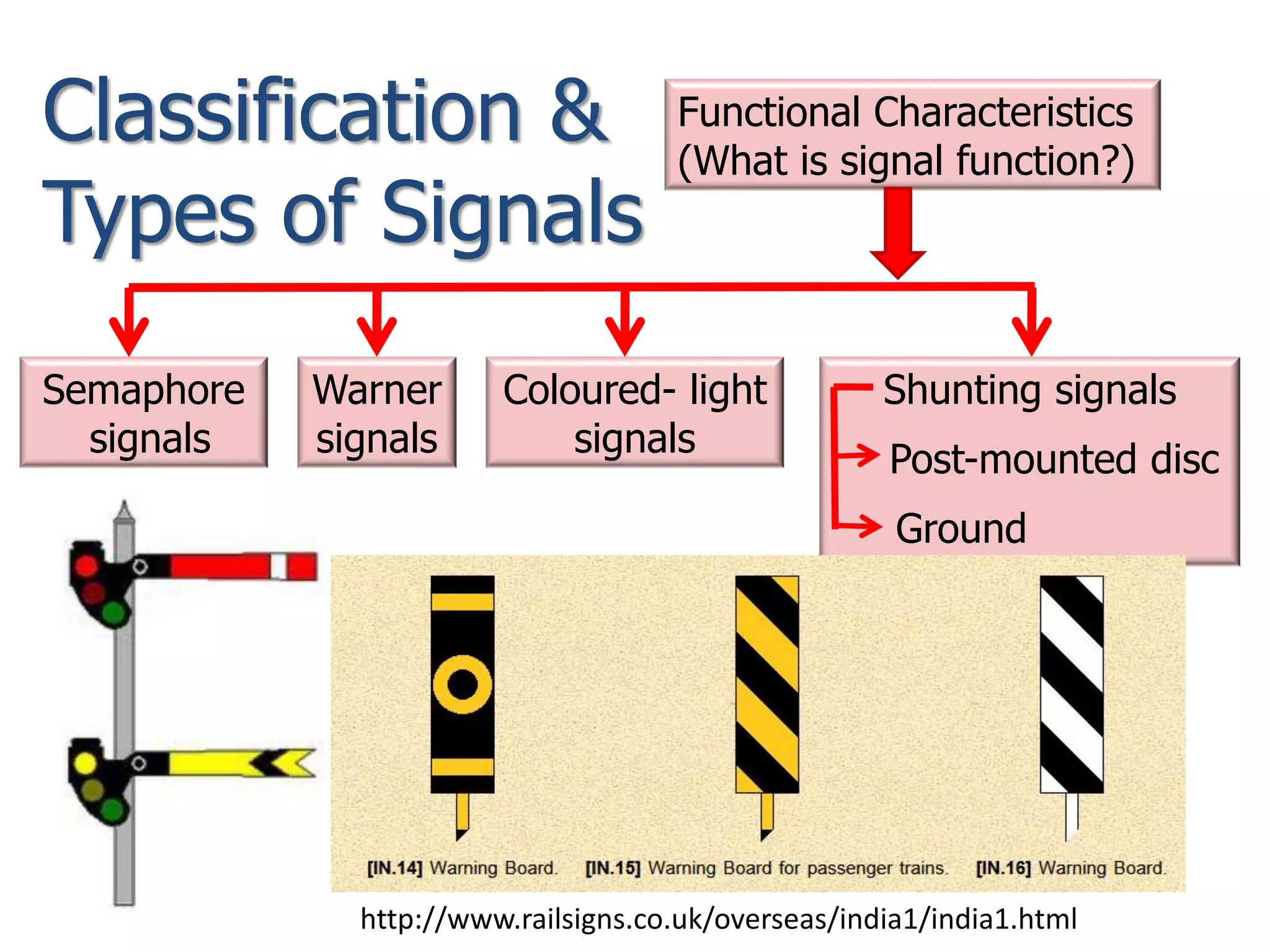
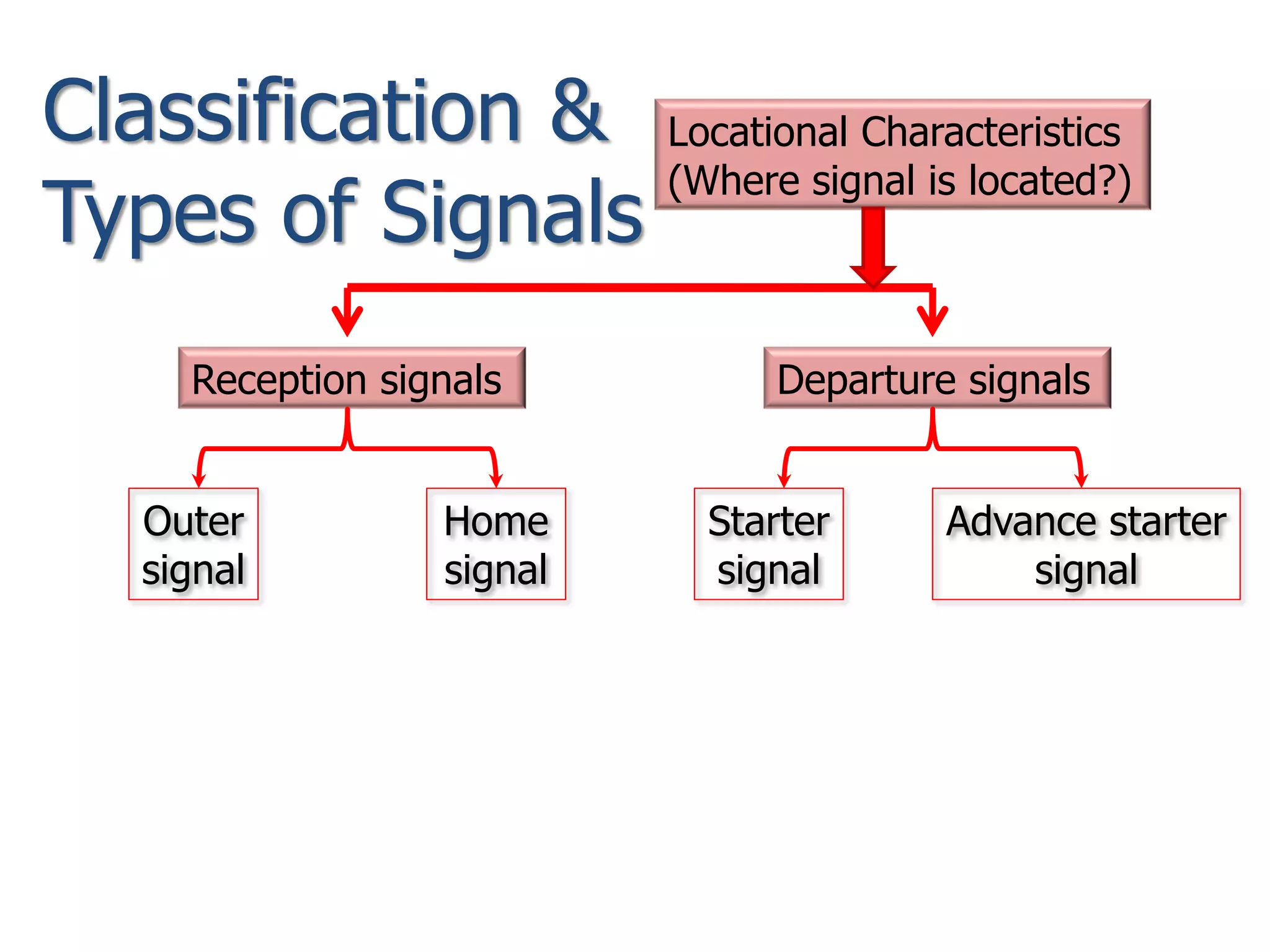
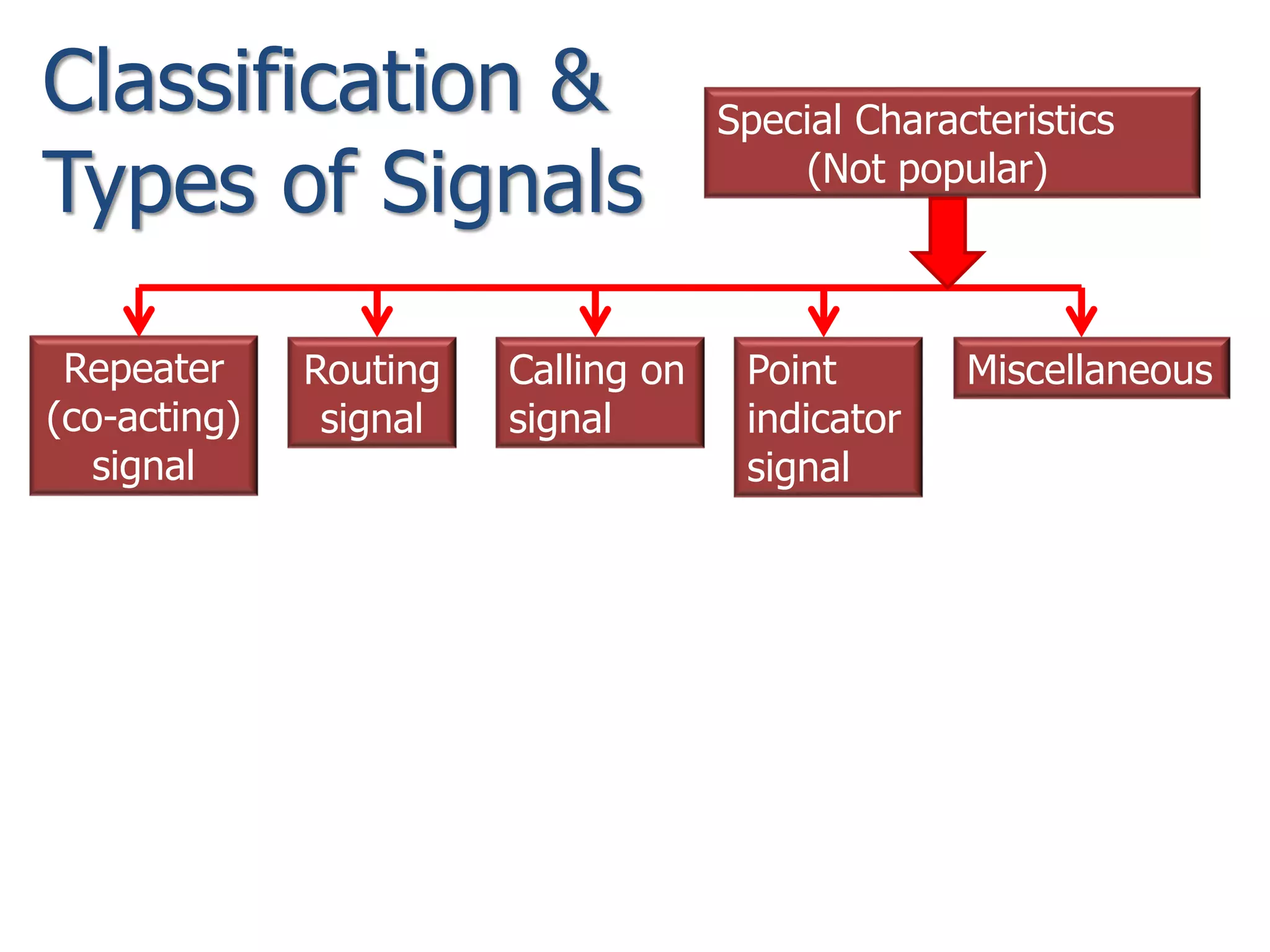
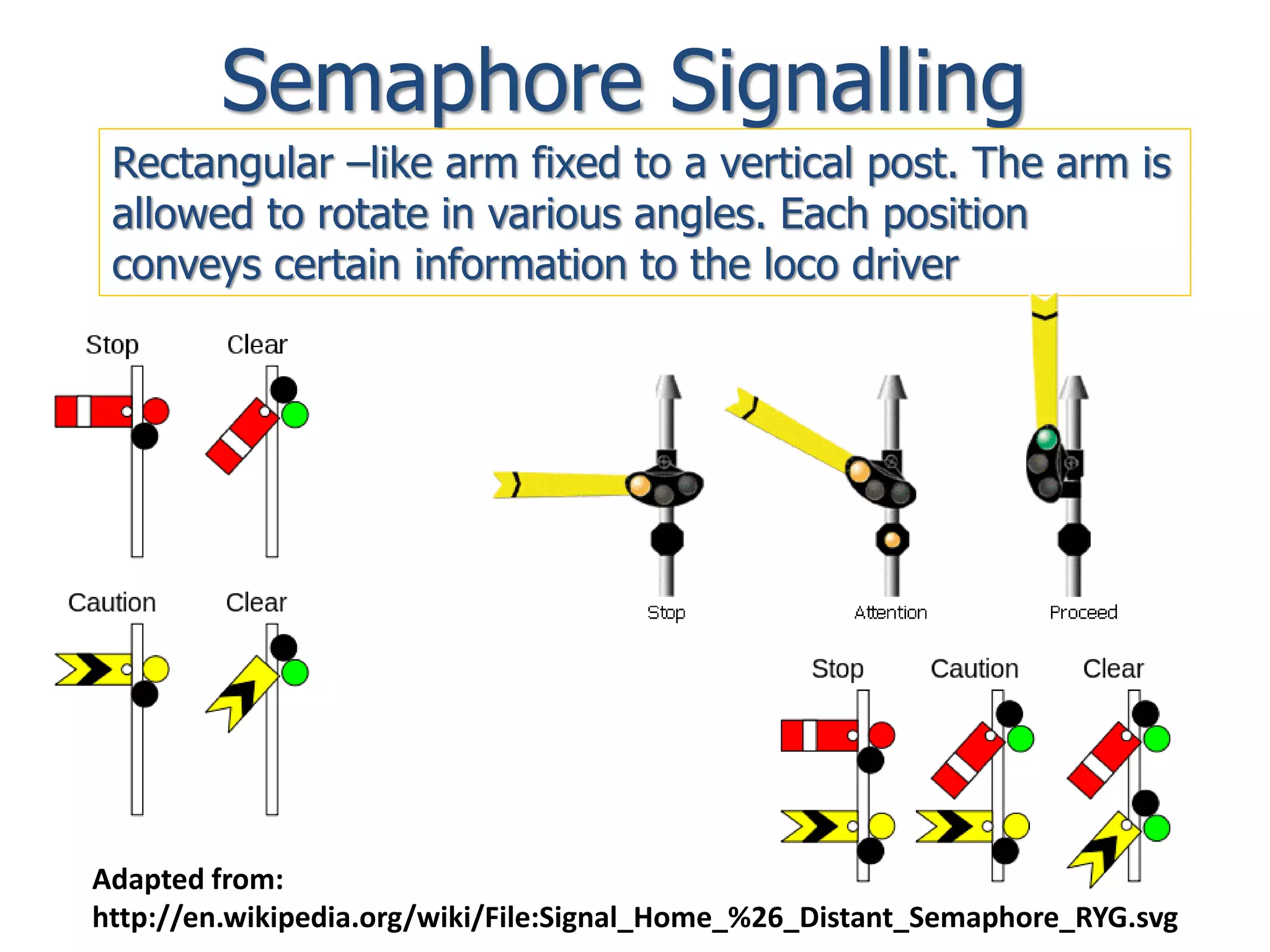
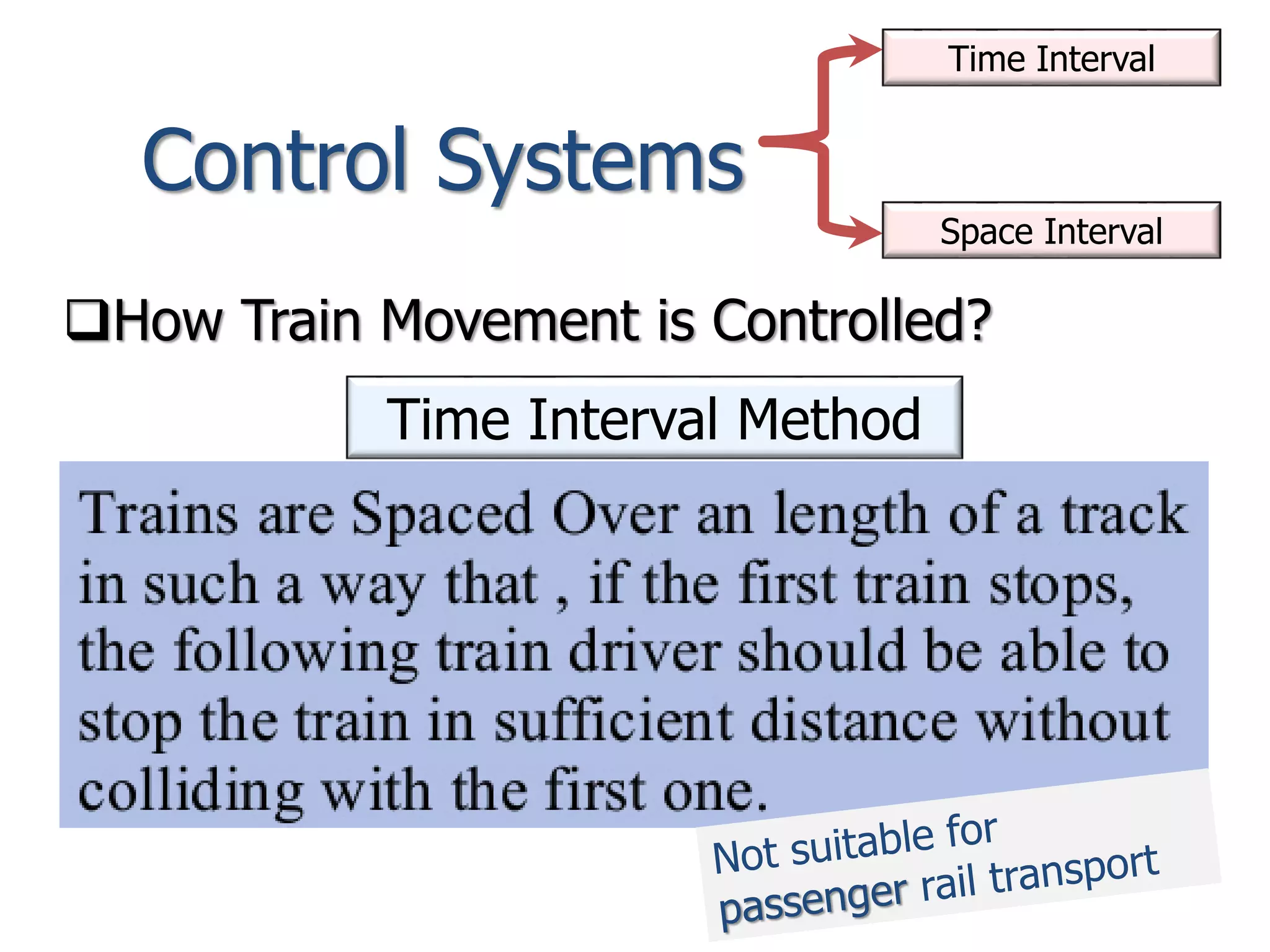
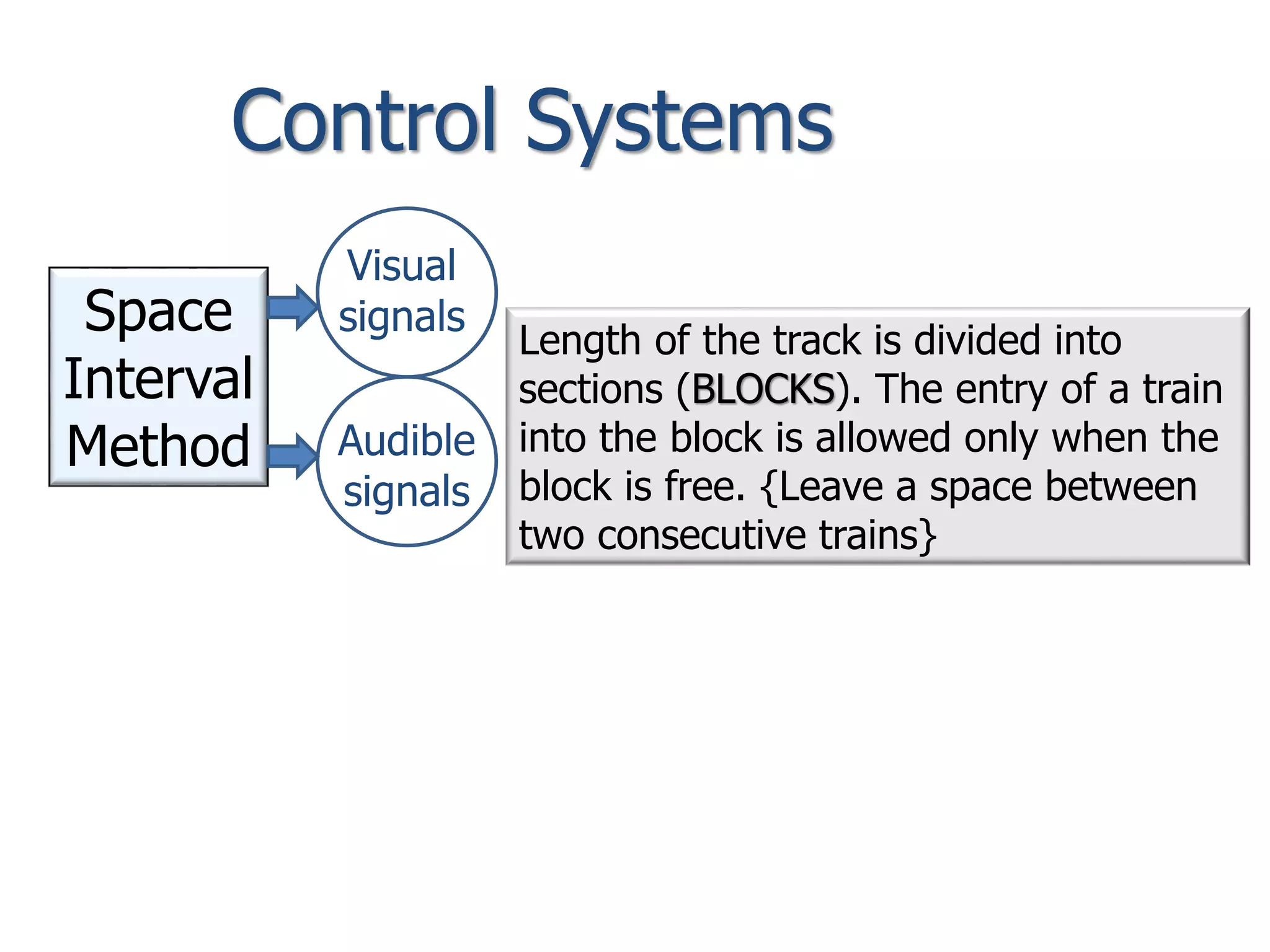
The document discusses railway signaling and control systems, emphasizing the importance of safe and efficient train operation. It classifies signals based on operating, functional, locational, and special characteristics, detailing various types such as semaphore and visual signals. Additionally, it explores control systems, including time interval and space interval methods for managing train movements.