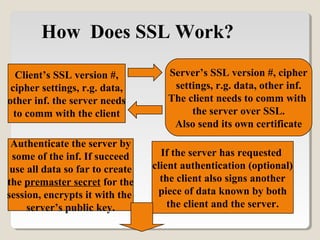
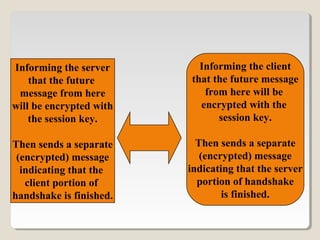
SSL is a protocol that allows clients and servers to securely communicate over the internet. It uses public-key encryption to authenticate servers, optionally authenticate clients, and establish an encrypted connection to securely transmit data. The SSL handshake allows the client and server to negotiate encryption parameters to generate shared secrets and session keys, which are then used to encrypt all further communication during the SSL session. Common implementations of SSL include OpenSSL and Apache-SSL.